Hadoop 的三架马车:HDFS、MR、YARN,实现分布式存储、计算、调度。大数据发展至今组件日益成熟,但 HDFS 在存储领域还是一枝独秀。本文从 HDFS 启动流程的角度分析其运行机制。
NameNode
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.NameNode
/**
* NameNode 控制两个关键的 Table
* filename -> blocksequence (namespace/文件到 block 映射)
* block -> machinelist ("inodes"/ block 到 DataNode 映射)
* 第一张表存储在磁盘中,非常重要;第二张表会在每次启动时重新构建 (DN 向 NN 汇报自身 block 信息)
**/
public class NameNode implements NameNodeStatusMXBean {
protected FSNamesystem namesystem; // 文件系统管理: 元数据管理
protected NameNodeHttpServer httpServer; // http server
// NameNode RPCServer,实现很多协议
private NameNodeRpcServer rpcServer;
ClientProtocol // 客户端访问操作
DatanodeProtocol // DataNode 通信协议
HAServiceProtocol // 实现 HA 协议
...
protected void initialize(Configuration conf) throws IOException {
...
// 启动 HttpServer,默认 50070 端口;
if (NamenodeRole.NAMENODE == role) {
startHttpServer(conf);
}
...
// FSNamesystem 元数据 => FSNamesystem.loadFromDisk(conf)
loadNamesystem(conf);
// NameNodeRpcServer => new NameNodeRpcServer(conf, this)
rpcServer = createRpcServer(conf);
if (clientNamenodeAddress == null) {
// This is expected for MiniDFSCluster. Set it now using
// the RPC server's bind address.
clientNamenodeAddress =
NetUtils.getHostPortString(rpcServer.getRpcAddress());
LOG.info("Clients are to use " + clientNamenodeAddress + " to access"
+ " this namenode/service.");
}
if (NamenodeRole.NAMENODE == role) {
httpServer.setNameNodeAddress(getNameNodeAddress());
httpServer.setFSImage(getFSImage());
}
...
//
startCommonServices(conf);
}
}
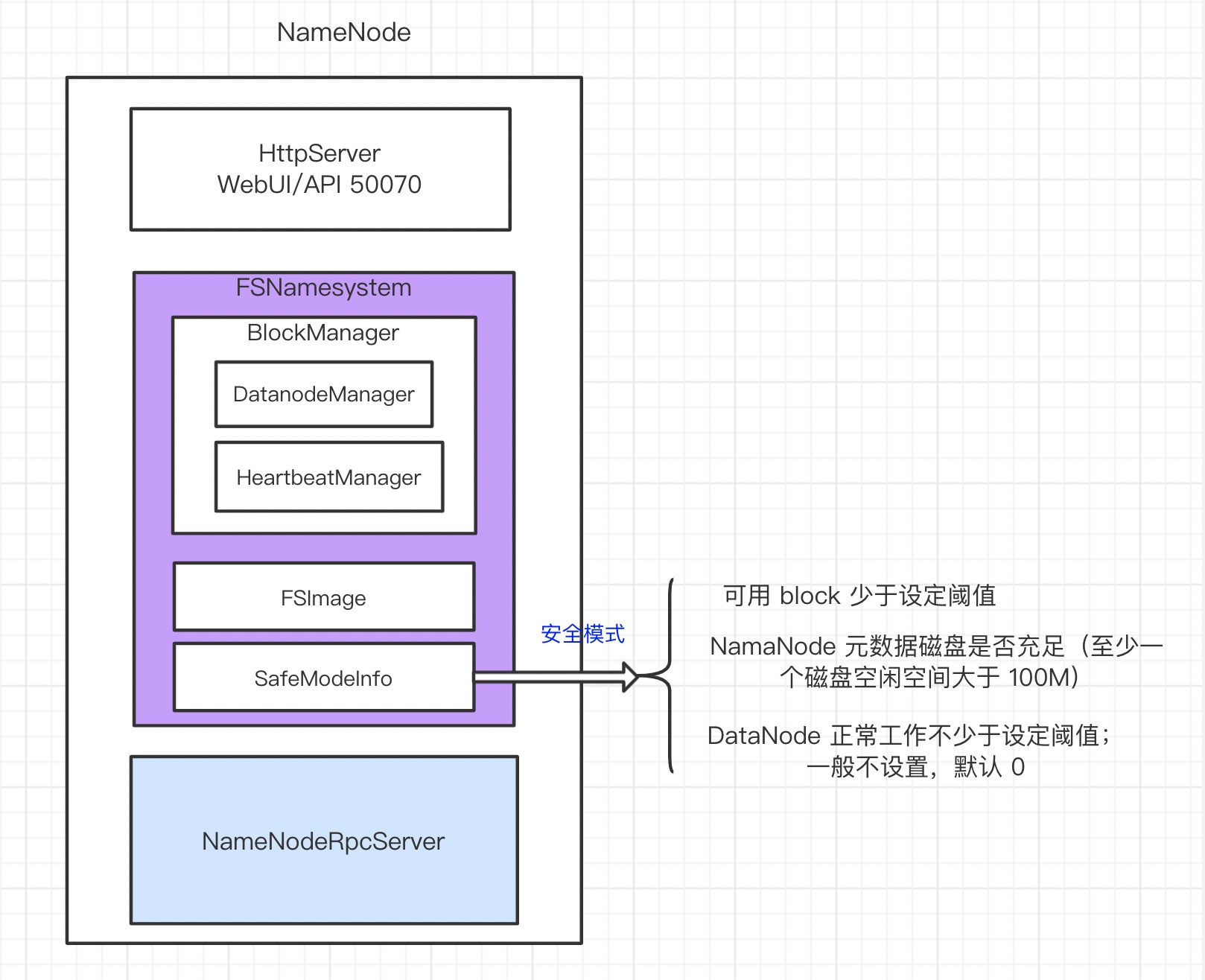
- HttpServer:HDFS WebUI 所示,默认端口 50070,实现很多 API 供查询 HDFS 使用
- FSNamesystem:元数据:
fsImage,blockManager - NameNodeRpcServer:处理 NameNode 所有 RPC 请求
- 安全模式:
- 可用 block 少于设定阈值
- DataNode 正常工作不少于设定阈值;一般不设置,默认 0
- NamaNode 元数据磁盘是否充足(至少一个磁盘空闲空间大于 100M)
元数据
HDFS 是分布式文件系统,必然有文件的元数据信息。
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.FSNamesystem
/*
* FSNamesystem 记录 DataNode 操作:增删改 data
* 重要的表:
* 1)磁盘上记录 文件 -> block list 映射
* 2)可用的 block (block 到文件映射)
* 3)block -> datanode 映射 (内存中,datanode 报告后会更新)
* 4)datanode -> 映射
* 5)datanode 心跳 LRU
*/
public class FSNamesystem implements Namesystem, FSNamesystemMBean,
NameNodeMXBean {
// standby NameNode 从 journalNode 同步 editlog
private EditLogTailer editLogTailer = null;
// standby NameNode 持久化 fsimage
private StandbyCheckpointer standbyCheckpointer;
// 非常重要:Block 和 DataNode 管理
private final BlockManager blockManager;
// fsimage
private final FSImage fsImage;
static FSNamesystem loadFromDisk(Configuration conf) throws IOException {
...
// 合并磁盘 image + editlog = 内存 fsimage
// 创建新 editlog => 非常重要,操作日志
FSImage fsImage = new FSImage(conf,
// namenode 本地磁盘空间:dfs.namenode.name.dir
FSNamesystem.getNamespaceDirs(conf),
// editlog 目录:editlog 要写两个地方
// dfs.namenode.edits.dir:NameNode 本地目录
// dfs.namenode.shared.edits.dir:JournalNode 上 NameNode editlog 目录
FSNamesystem.getNamespaceEditsDirs(conf));
// 创建 BlockManager,其包含 DatanodeManager 管理 datanode
// 创建 FSDirectory = HDFS 文件系统目录树(内存中)
FSNamesystem namesystem = new FSNamesystem(conf, fsImage, false);
StartupOption startOpt = NameNode.getStartupOption(conf);
if (startOpt == StartupOption.RECOVER) {
namesystem.setSafeMode(SafeModeAction.SAFEMODE_ENTER);
}
try {
namesystem.loadFSImage(startOpt);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
LOG.warn("Encountered exception loading fsimage", ioe);
fsImage.close();
throw ioe;
}
...
return namesystem;
}
}
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.FSImage
protected FSImage(Configuration conf,
Collection<URI> imageDirs,
List<URI> editsDirs)
throws IOException {
this.conf = conf;
storage = new NNStorage(conf, imageDirs, editsDirs);
if(conf.getBoolean(DFSConfigKeys.DFS_NAMENODE_NAME_DIR_RESTORE_KEY,
DFSConfigKeys.DFS_NAMENODE_NAME_DIR_RESTORE_DEFAULT)) {
storage.setRestoreFailedStorage(true);
}
// 创建 editlog :
/// namenode editlog (FileJournalManager)
// journalnode editlog(QuorumJournalManager)
this.editLog = new FSEditLog(conf, storage, editsDirs);
archivalManager = new NNStorageRetentionManager(conf, storage, editLog);
}
NameNodeRpcServer
NameNodeRpcServer 处理 NameNode 所有 RPC 调用。
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.NameNodeRpcServer
/** 处理 DataNode RPC 请求 */
private final RPC.Server serviceRpcServer;
/** 处理 客户端 RPC 请求 */
protected final RPC.Server clientRpcServer;
// 标准 hadoop RPC 创建方式
// 当前只是创建,后续会添加很多协议
this.serviceRpcServer = new RPC.Builder(conf)
.setProtocol(
org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.protocolPB.ClientNamenodeProtocolPB.class)
.setInstance(clientNNPbService)
.setBindAddress(bindHost)
.setPort(serviceRpcAddr.getPort()).setNumHandlers(serviceHandlerCount)
.setVerbose(false)
.setSecretManager(namesystem.getDelegationTokenSecretManager())
.build();
this.clientRpcServer = new RPC.Builder(conf)
.setProtocol(
org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.protocolPB.ClientNamenodeProtocolPB.class)
.setInstance(clientNNPbService)
.setBindAddress(bindHost)
.setPort(rpcAddr.getPort()).setNumHandlers(handlerCount)
.setVerbose(false)
.setSecretManager(namesystem.getDelegationTokenSecretManager())
.build();
安全模式
HDFS 启动时先进入安全模式,满足条件才切换到正常模式
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.FSNamesystem
void startCommonServices(Configuration conf, HAContext haContext) throws IOException {
...
try {
// 检查 namanode 元数据磁盘是否充足(editlog)
nnResourceChecker = new NameNodeResourceChecker(conf);
// 至少有一个磁盘的的元数据空闲空间 > 100M
checkAvailableResources();
...
// hdfs 安全模式,非常重要
setBlockTotal();
// 启动重要服务:datanodeManage heartbeatManager(心跳检测线程)
blockManager.activate(conf);
} finally {
writeUnlock();
}
...
}
public void setBlockTotal() {
// safeMode is volatile, and may be set to null at any time
SafeModeInfo safeMode = this.safeMode;
if (safeMode == null)
return;
// getCompleteBlocksTotal 获取正常可用的 block 数
safeMode.setBlockTotal((int)getCompleteBlocksTotal());
}
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.FSNamesystem.SafeModeInfo
private synchronized void setBlockTotal(int total) {
this.blockTotal = total;
// threshold 默认 0.999 ;block 正常可用少于阈值,则进入安全模式
this.blockThreshold = (int) (blockTotal * threshold);
this.blockReplQueueThreshold =
(int) (blockTotal * replQueueThreshold);
if (haEnabled) {
// After we initialize the block count, any further namespace
// modifications done while in safe mode need to keep track
// of the number of total blocks in the system.
this.shouldIncrementallyTrackBlocks = true;
}
if(blockSafe < 0)
this.blockSafe = 0;
// 是否进去安全模式判断
checkMode();
}
// 满足任意条件,进入安全模式
private boolean needEnter() {
// 一:可用 block 少于设定阈值
// 二:DataNode 正常工作不少于设定阈值;一般不设置,默认 0
// 三:NamaNode 元数据磁盘是否充足
return (threshold != 0 && blockSafe < blockThreshold) ||
(datanodeThreshold != 0 && getNumLiveDataNodes() < datanodeThreshold) ||
(!nameNodeHasResourcesAvailable());
}
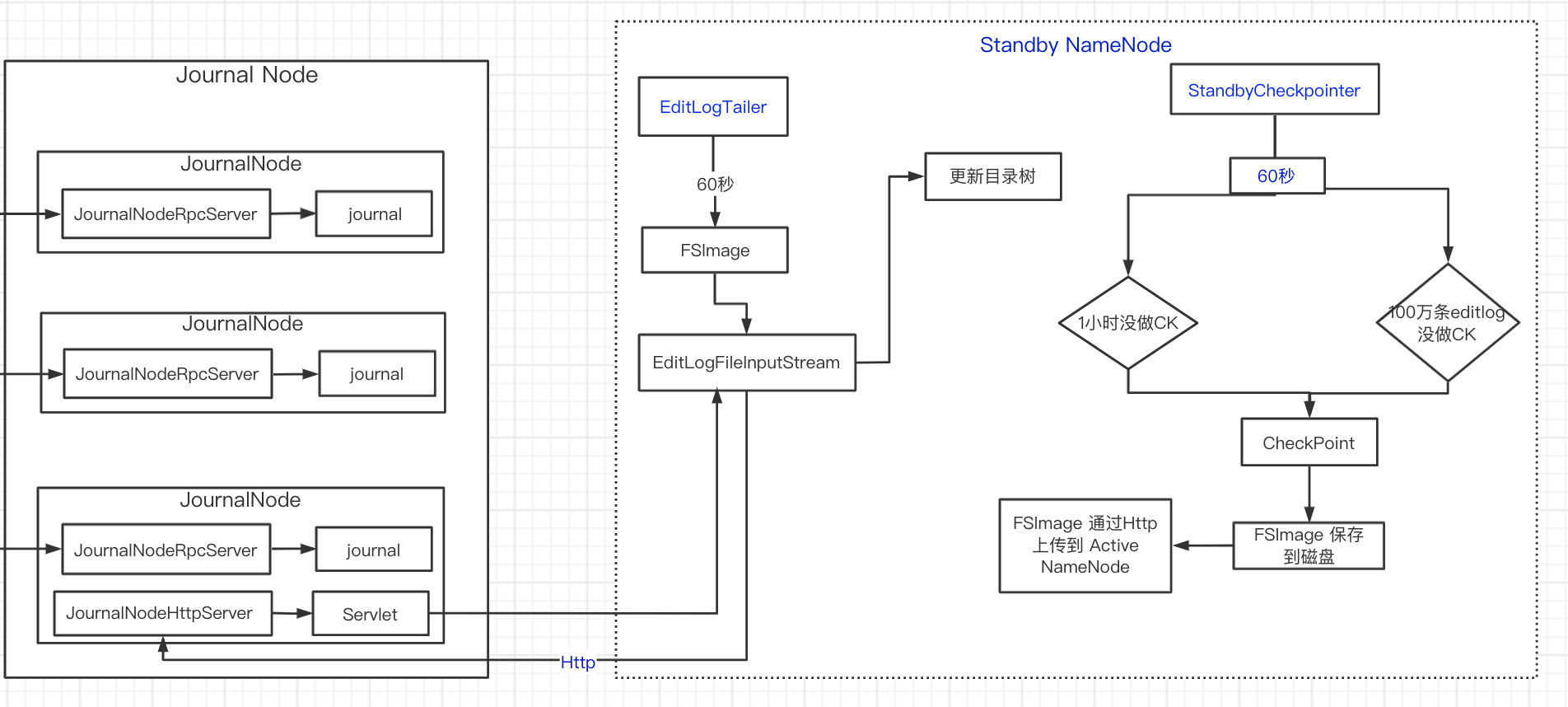
EditLogTailer
Standby NameNode 要和 Active NameNode 元数据相同,需要从 Journal Node 同步 editlog ,更新内存中的目录树并持久化到磁盘。
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.FSNamesystem
// Starting services required for standby state
void startStandbyServices(final Configuration conf) throws IOException {
if (!getFSImage().editLog.isOpenForRead()) {
// During startup, we're already open for read.
getFSImage().editLog.initSharedJournalsForRead();
}
blockManager.setPostponeBlocksFromFuture(true);
// Disable quota checks while in standby.
dir.disableQuotaChecks();
// 同步 editlog
editLogTailer = new EditLogTailer(this, conf);
editLogTailer.start();
if (standbyShouldCheckpoint) {
// 生产新的 fsimage CheckpointerThread
standbyCheckpointer = new StandbyCheckpointer(conf, this);
standbyCheckpointer.start();
}
}
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.ha.EditLogTailer
/*
* EditLogTailer 是一个线程,定期通过 Http 从 journal node 同步 editlog 并支持事务性更新 FSNamesystem
*/
public class EditLogTailer {
private final EditLogTailerThread tailerThread;
private void doWork() {
while (shouldRun) {
try {
...
try {
// editlog
doTailEdits();
}
...
// 60s
try {
Thread.sleep(sleepTimeMs);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
LOG.warn("Edit log tailer interrupted", e);
}
}
}
void doTailEdits() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
...
try {
FSImage image = namesystem.getFSImage();
// 获取当前 editlog offset
long lastTxnId = image.getLastAppliedTxId();
...
Collection<EditLogInputStream> streams;
try {
// 获取 editlog
// 实质是获取 EditLogFileInputStream (http 传输的 editlog outputStream)
streams = editLog.selectInputStreams(lastTxnId + 1, 0, null, false);
}
...
long editsLoaded = 0;
try {
// editlog 去更新 目录树
editsLoaded = image.loadEdits(streams, namesystem);
}
// 保存已更新 editlog offset
lastLoadedTxnId = image.getLastAppliedTxId();
}
...
}
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.EditLogFileInputStream
public static EditLogInputStream fromUrl(
URLConnectionFactory connectionFactory, URL url, long startTxId,
long endTxId, boolean inProgress) {
return new EditLogFileInputStream(new URLLog(connectionFactory, url),
startTxId, endTxId, inProgress);
}
// log.getInputStream 获取 inputStream
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
return SecurityUtil.doAsCurrentUser(
new PrivilegedExceptionAction<InputStream>() {
@Override
public InputStream run() throws IOException {
HttpURLConnection connection;
try {
// http 请求
// JournalNodeHttpServer/getJournal
connection = (HttpURLConnection)
connectionFactory.openConnection(url, isSpnegoEnabled);
} catch (AuthenticationException e) {
throw new IOException(e);
}
...
return connection.getInputStream();
}
});
}
}
StandbyCheckpointer
EditLogTailer 将 editlog 同步到内存中,StandbyCheckpointer 将 editlog 与 fsimage 合并在磁盘上产生新的 fsimage。
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.ha.StandbyCheckpointer
private void doWork() {
final long checkPeriod = 1000 * checkpointConf.getCheckPeriod();
lastCheckpointTime = monotonicNow();
while (shouldRun) {
// 60s 检查一次
boolean needRollbackCheckpoint = namesystem.isNeedRollbackFsImage();
if (!needRollbackCheckpoint) {
try {
// 60s 周期
Thread.sleep(checkPeriod);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
}
if (!shouldRun) {
break;
}
}
try {
...
if (needCheckpoint) {
LOG.info("Triggering a rollback fsimage for rolling upgrade.");
} else if (uncheckpointed >= checkpointConf.getTxnCount()) {
// 100万条 editlog 没有 checkpoint
needCheckpoint = true;
} else if (secsSinceLast >= checkpointConf.getPeriod()) {
// 1小时没有 checkpoint
needCheckpoint = true;
}
synchronized (cancelLock) {
if (now < preventCheckpointsUntil) {
LOG.info("But skipping this checkpoint since we are about to failover!");
canceledCount++;
continue;
}
assert canceler == null;
canceler = new Canceler();
}
if (needCheckpoint) {
// 做 checkpoint
doCheckpoint();
if (needRollbackCheckpoint
&& namesystem.getFSImage().hasRollbackFSImage()) {
// 重置
namesystem.setCreatedRollbackImages(true);
namesystem.setNeedRollbackFsImage(false);
}
// 更新 lastCheckpointTime
lastCheckpointTime = now;
}
}
...
}
}
DataNode
NameNode 启动很多服务,基于主从架构 DataNode 必然会与之打交道。
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.datanode.DataNode
/**
* 一个集群可以有多个 DataNode,DataNode 存储数据
* DataNode 启动后周期性跟 每个NameNode 汇报(心跳,汇报 block)
* NameNode 不会直接操作 DataNode,而是以心跳指令返回的方式操作 DataNode
* DataNode 也会启动 RPC 服务,供其他组件调用
*/
// 接受 http 请求
private HttpServer2 infoServer = null;
private DatanodeHttpServer httpServer = null;
// NameNode 交互
private BlockPoolManager blockPoolManager;
// 接受和发送 block data 服务,每次接受都会新建 DataXceiver 线程
DataXceiverServer xserver = null;
void startDataNode(Configuration conf,
List<StorageLocation> dataDirs,
SecureResources resources
) throws IOException {
...
// DataXceiverServer: 操作 block data
initDataXceiver(conf);
// httpserver
startInfoServer(conf);
...
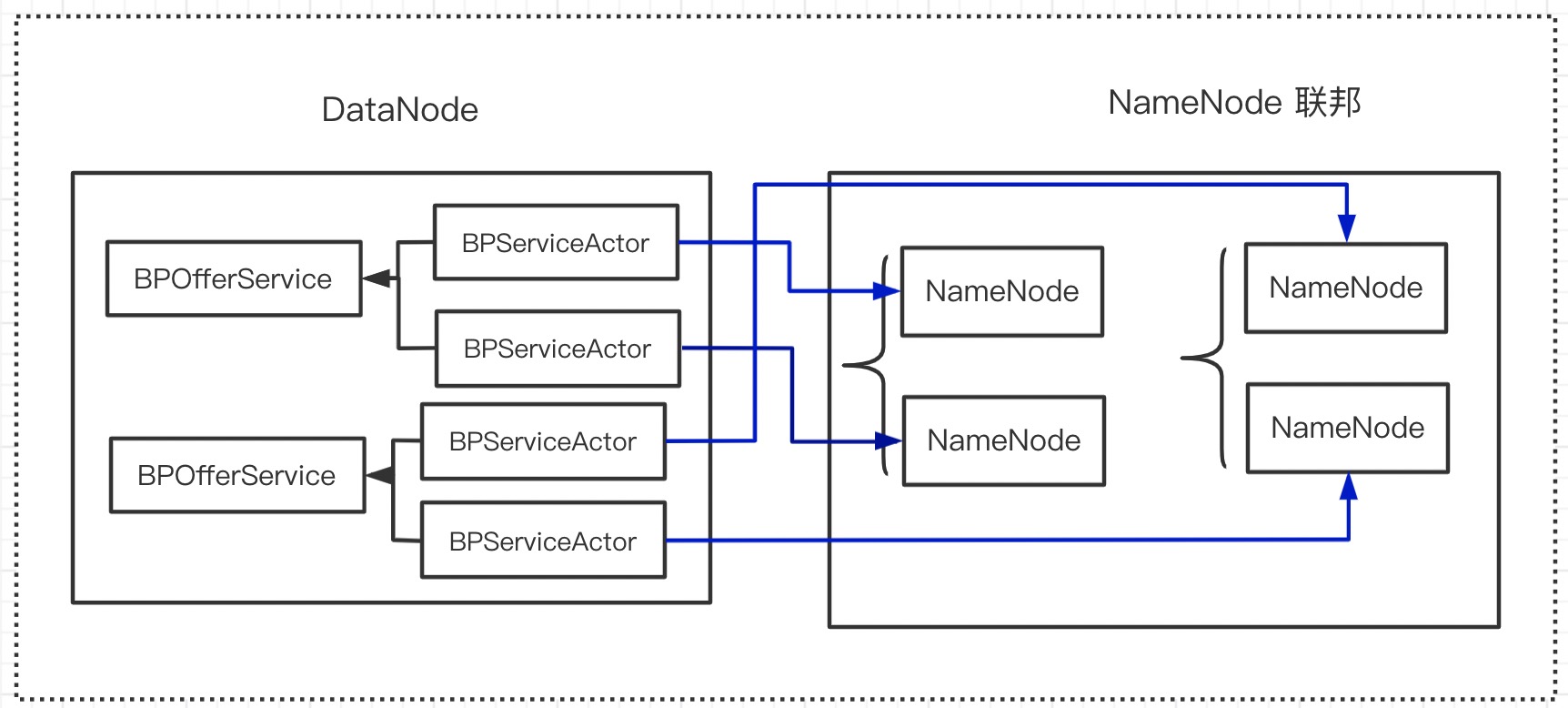
// 一个联邦对应 BPOfferService
// 每个 NameNode 对应 一个 BPServiceActor
// 即一个 BPOfferService 对应两个 BPServiceActor(如下图所示)
// 向 NameNode 注册并发送心跳 =>
// 向 NameNode 操作都由 BPServiceActor 执行
blockPoolManager = new BlockPoolManager(this);
blockPoolManager.refreshNamenodes(conf);
...
}
由于单个 NameNode 的内存受限导致存储 HDFS 个数有限 。在超大集群中,一般会有多个 NameNode 来管理。基于HA每个 Active NameNode 都有对应的 standby NameNode,这种形式称为联邦。
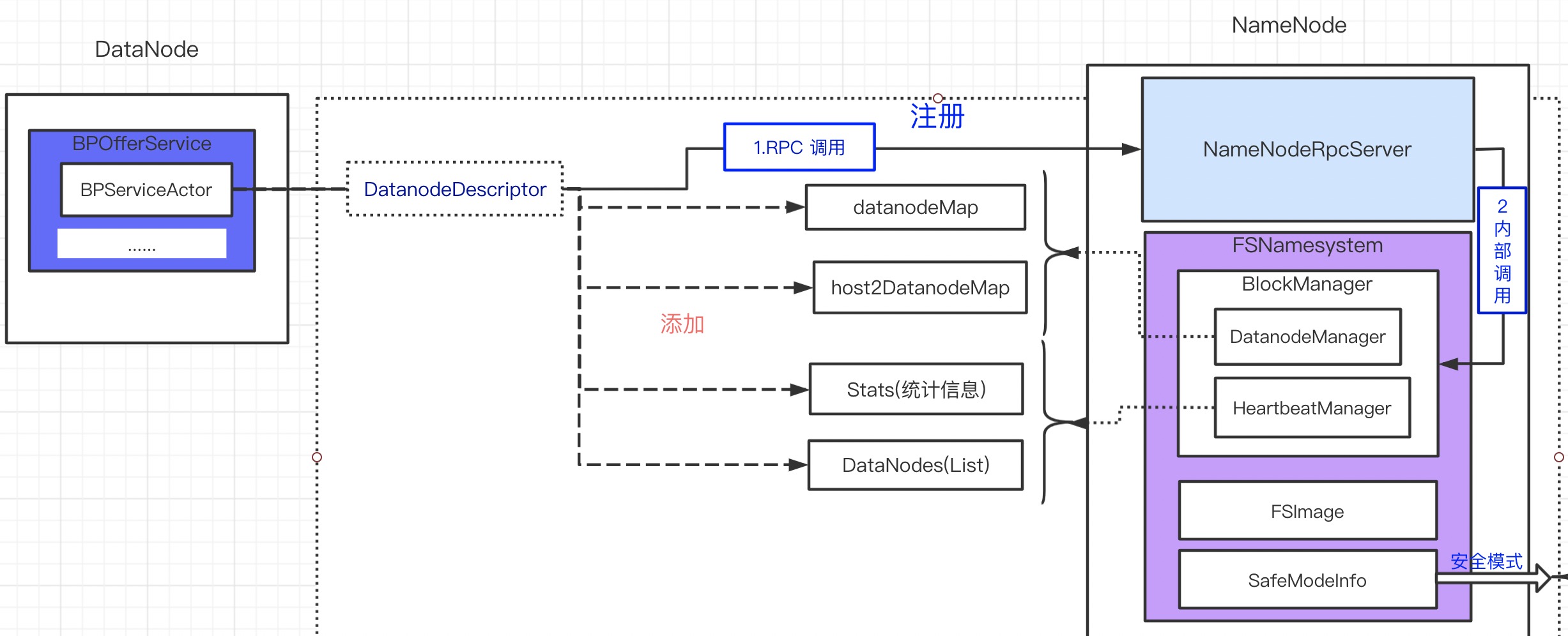
注册
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.datanode.BPOfferService
void start() {
for (BPServiceActor actor : bpServices) {
actor.start();
}
}
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.datanode.BPServiceActor
// Namenode 代理
DatanodeProtocolClientSideTranslatorPB bpNamenode;
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
// 死循环,保证注册成功
try {
// 注册
connectToNNAndHandshake();
break;
}
...
}
...
while (shouldRun()) {
try {
// 心跳
offerService();
}
...
}
runningState = RunningState.EXITED;
...
}
// 注册
private void connectToNNAndHandshake() throws IOException {
// 获取 Namenode 代理
bpNamenode = dn.connectToNN(nnAddr);
// NameNode 握手第一阶段:获取 NameSpace
NamespaceInfo nsInfo = retrieveNamespaceInfo();
...
// NameNode 握手第一阶段:注册
register(nsInfo);
}
void register(NamespaceInfo nsInfo) throws IOException {
// 创建注册信息
bpRegistration = bpos.createRegistration();
LOG.info(this + " beginning handshake with NN");
while (shouldRun()) {
//
try {
// RPC 调用 NameNodeRPCServer 注册方法
bpRegistration = bpNamenode.registerDatanode(bpRegistration);
bpRegistration.setNamespaceInfo(nsInfo);
break;
}
...
}
// 注册成功
LOG.info("Block pool " + this + " successfully registered with NN");
bpos.registrationSucceeded(this, bpRegistration);
// random short delay - helps scatter the BR from all DNs
scheduleBlockReport(dnConf.initialBlockReportDelay);
}
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.NameNodeRpcServer
@Override // DatanodeProtocol
public DatanodeRegistration registerDatanode(DatanodeRegistration nodeReg)
throws IOException {
checkNNStartup();
verifySoftwareVersion(nodeReg);
namesystem.registerDatanode(nodeReg);
return nodeReg;
}
注册实质就是将 DataNode 信息添加到 NameNode 的结构体。注册时将 DataNode 信息封装成 DatanodeDescriptor,添加到如下结构体(主要):
- DatanodeManager
- datanodeMap:key = DataNodeUUID ,value = DatanodeDescriptor
- host2DatanodeMap:key = ip,value = DatanodeDescriptor
- HeartbeatManager
- stats:DataNode 统计信息
- datanodes:DatanodeDescriptor 数组
心跳
DataNode 周期性的向每个 NameNode 发送心跳汇报自身情况,并在返回时携带 NameNode 指令。
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.datanode.BPServiceActor
while (shouldRun()) {
try {
final long startTime = monotonicNow();
// 默认 3s 一个心跳
if (startTime - lastHeartbeat >= dnConf.heartBeatInterval) {
// 心跳携带的信息
// datanode 名称,端口,总容量,剩余空间
// block 信息下面单独汇报(blockReport)
lastHeartbeat = startTime;
if (!dn.areHeartbeatsDisabledForTests()) {
// 发送心跳:NameNodeRPCServer.sendHeartbeat
// 最终转到 HeartbeatManager.updateHeartbeat
HeartbeatResponse resp = sendHeartBeat();
assert resp != null;
dn.getMetrics().addHeartbeat(monotonicNow() - startTime);
bpos.updateActorStatesFromHeartbeat(
this, resp.getNameNodeHaState());
state = resp.getNameNodeHaState().getState();
if (state == HAServiceState.ACTIVE) {
handleRollingUpgradeStatus(resp);
}
long startProcessCommands = monotonicNow();
// 处理心跳返回的 NameNode 指令
if (!processCommand(resp.getCommands()))
continue;
long endProcessCommands = monotonicNow();
if (endProcessCommands - startProcessCommands > 2000) {
LOG.info("Took " + (endProcessCommands - startProcessCommands)
+ "ms to process " + resp.getCommands().length
+ " commands from NN");
}
}
}
if (sendImmediateIBR ||
(startTime - lastDeletedReport > dnConf.deleteReportInterval)) {
reportReceivedDeletedBlocks();
lastDeletedReport = startTime;
}
// 汇报 block 信息,并处理 NameNode 指令
List<DatanodeCommand> cmds = blockReport();
processCommand(cmds == null ? null : cmds.toArray(new DatanodeCommand[cmds.size()]));
DatanodeCommand cmd = cacheReport();
processCommand(new DatanodeCommand[]{ cmd });
// 休眠直到下一个心跳时间
long waitTime = dnConf.heartBeatInterval -
(monotonicNow() - lastHeartbeat);
synchronized(pendingIncrementalBRperStorage) {
if (waitTime > 0 && !sendImmediateIBR) {
try {
pendingIncrementalBRperStorage.wait(waitTime);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
LOG.warn("BPOfferService for " + this + " interrupted");
}
}
} // synchronized
}
...
processQueueMessages();
} // while (shouldRun())
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.blockmanagement.HeartbeatManager
synchronized void updateHeartbeat(final DatanodeDescriptor node,
StorageReport[] reports, long cacheCapacity, long cacheUsed,
int xceiverCount, int failedVolumes,
VolumeFailureSummary volumeFailureSummary) {
stats.subtract(node);
// 更新 DataNode 信息和最后心跳时间 = lastUpdateMonotonic
node.updateHeartbeat(reports, cacheCapacity, cacheUsed,
xceiverCount, failedVolumes, volumeFailureSummary);
// Stats 更新统计信息
stats.add(node);
}
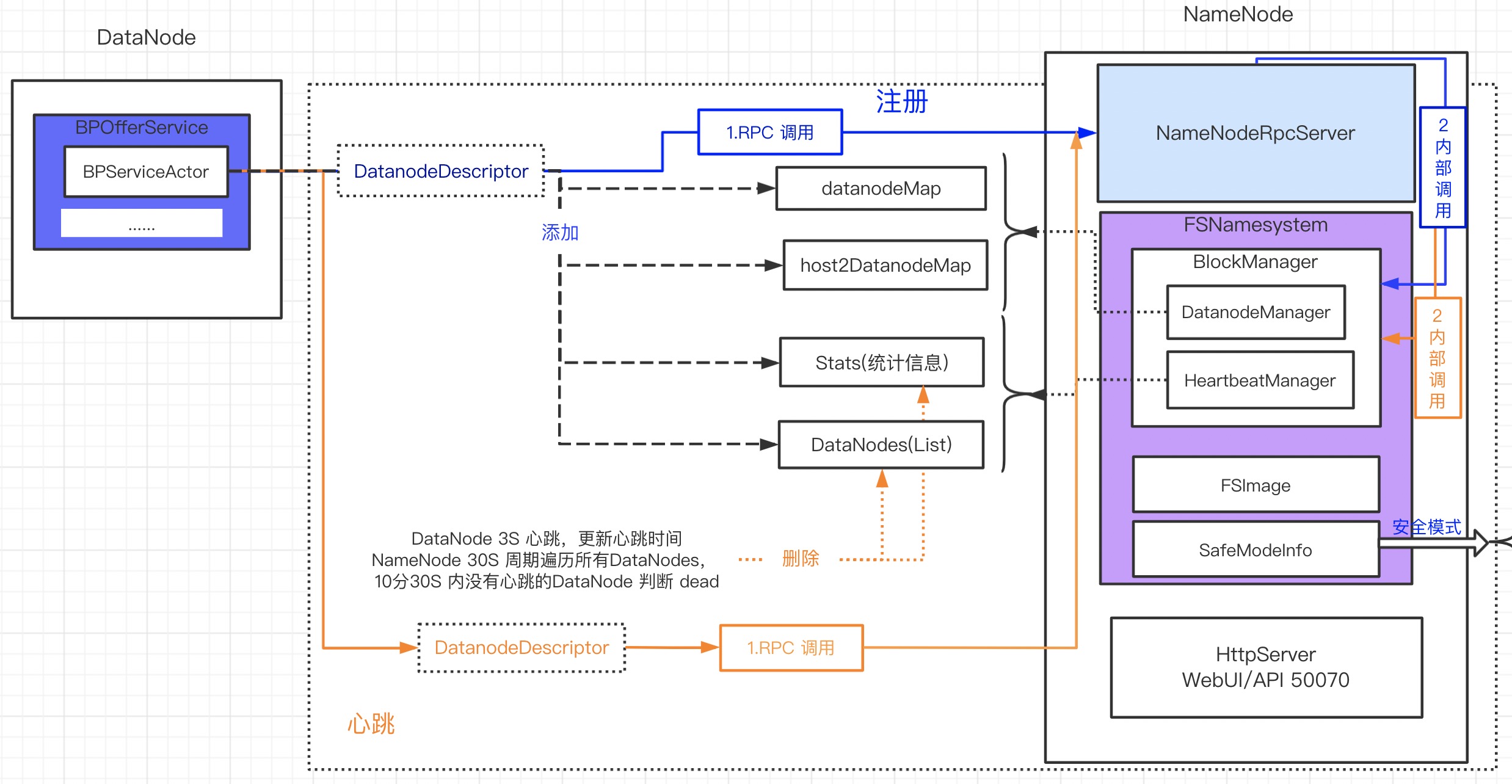
DataNode 定期上报心跳,NameNode 可根据心跳判断当前 DataNode 是否存活。
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.blockmanagement.HeartbeatManager
// HeartbeatManager 有心跳检测线程,在 NameNode 启动时运行
public void run() {
while(namesystem.isRunning()) {
try {
final long now = Time.monotonicNow();
// 默认 30s 检查一次
if (lastHeartbeatCheck + heartbeatRecheckInterval < now) {
// 心跳检查
// 默认 10分30s 没心跳,则表示 DataNode dead
heartbeatCheck();
lastHeartbeatCheck = now;
}
...
}
}
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.blockmanagement.DatanodeManager
private void removeDatanode(DatanodeDescriptor nodeInfo) {
assert namesystem.hasWriteLock();
// 删除 stats.subtract(node);
// 删除 datanodes.remove(node);
heartbeatManager.removeDatanode(nodeInfo);
blockManager.removeBlocksAssociatedTo(nodeInfo);
// 删除
networktopology.remove(nodeInfo);
decrementVersionCount(nodeInfo.getSoftwareVersion());
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("remove datanode " + nodeInfo);
}
// 判断是否进入安全模式
namesystem.checkSafeMode();
}
- DataNode 默认 3s 一个心跳上传到 NameNode 更新当前 DataNode 的最后心跳时间
- NameNode 默认 30s 遍历所有 DataNode 的最后心跳时间,发现 10分30s 间隔内都没有发送心跳
- HeartbeatManager.Stats:减去 dead DataNode 的信息
- HeartbeatManager.datanodes:移除 dead DataNode 的信息
主从架构分布式系统:注册 (从节点信息添加到主节点的结构体中) 和心跳 (从节点更新心跳时间,主节点根据心跳时间判断从节点是否存活)
文件夹操作
HDFS 是一个文件系统,我们在此基础上可以进行文件操作。
FileSystem.mkdirs(path)
-> DFSClient.mkdirs
-> NameNodeRPCServer.mkdirs
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.FSNamesystem
boolean mkdirs(String src, PermissionStatus permissions,
boolean createParent) throws IOException {
...
try {
// 文件创建
auditStat = FSDirMkdirOp.mkdirs(this, src, permissions, createParent);
}
...
// 写 editlog 和 JournalNode 日志,磁盘写
// 写磁盘是很耗时的操作,HDFS 如何保证高并发呢?
getEditLog().logSync();
return true;
}
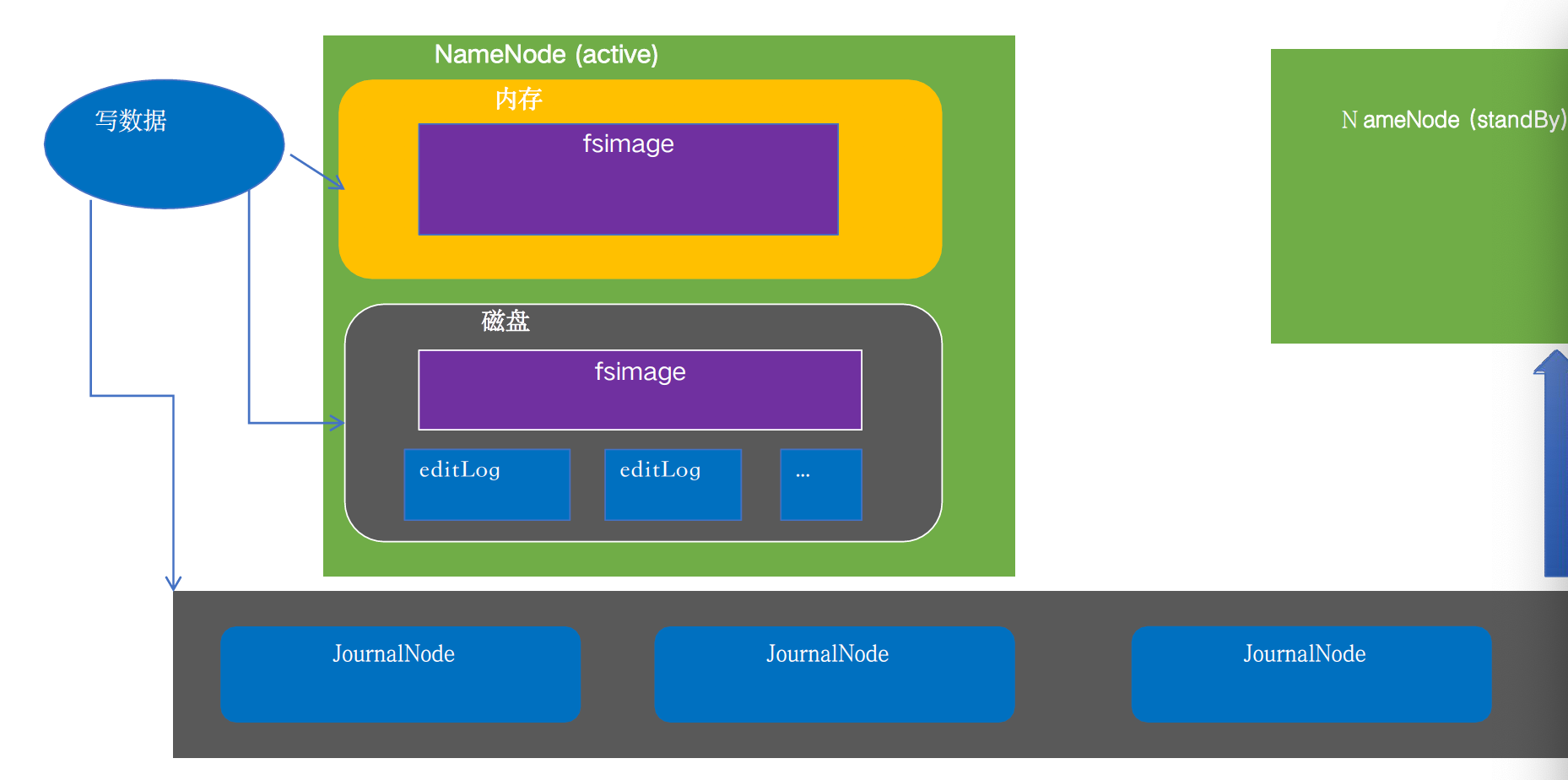
客户端创建文件夹时会更新 HDFS 元数据,需经过如下操作:
- 直接写 NameNode 内存里的 fsimage
- 写 NameNode 磁盘的 editLog 文件,供后续 磁盘 editlog + 磁盘 fsimage => 新的 fsimage
- 写 JournalNode editlog 文件,Standby NameNode 同步元数据使用
FSDirectory
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.FSDirMkdirOp
static HdfsFileStatus mkdirs(FSNamesystem fsn, String src,
PermissionStatus permissions, boolean createParent) throws IOException {
// FSDirectory = HDFS 文件系统目录树
// new FSNamesystem 时创建
FSDirectory fsd = fsn.getFSDirectory();
...
try {
src = fsd.resolvePath(pc, src, pathComponents);
INodesInPath iip = fsd.getINodesInPath4Write(src);
if (fsd.isPermissionEnabled()) {
fsd.checkTraverse(pc, iip);
}
// 改文件父目录的文件夹
// /data/1/2/3/4,假设 2/3 文件夹是新建的
// 那么 lastINode = /data/1/2/3
final INode lastINode = iip.getLastINode();
if (lastINode != null && lastINode.isFile()) {
throw new FileAlreadyExistsException("Path is not a directory: " + src);
}
// 本案例中,lastINode = /data/1/2/3 显然是不存在的
// existing = /data/1/2
INodesInPath existing = lastINode != null ? iip : iip.getExistingINodes();
if (lastINode == null) {
...
// nonExisting = [3,4]
List<String> nonExisting = iip.getPath(existing.length(),
iip.length() - existing.length());
// 创建
int length = nonExisting.size();
if (length > 1) {
// 先创建 3 这个目录:先创建父目录
List<String> ancestors = nonExisting.subList(0, length - 1);
// 创建文件夹
existing = createChildrenDirectories(fsd, existing, ancestors,
addImplicitUwx(permissions, permissions));
if (existing == null) {
throw new IOException("Failed to create directory: " + src);
}
}
// 再创建最后一个文件夹
if ((existing = createChildrenDirectories(fsd, existing,
nonExisting.subList(length - 1, length), permissions)) == null) {
throw new IOException("Failed to create directory: " + src);
}
}
return fsd.getAuditFileInfo(existing);
}
}
private static INodesInPath createChildrenDirectories(FSDirectory fsd,
INodesInPath existing, List<String> children, PermissionStatus perm)
throws IOException {
...
for (String component : children) {
existing = createSingleDirectory(fsd, existing, component, perm);
if (existing == null) {
return null;
}
}
return existing;
}
private static INodesInPath createSingleDirectory(FSDirectory fsd,
INodesInPath existing, String localName, PermissionStatus perm)
throws IOException {
// 更新 FSDirctory 目录树
// 新建文件夹并添加到 existing 目录
// 无论是 文件 INodeFile 还是文件夹 INodeDirectory,在 HDFS 中都表示 INode
// INodeDirectory 有属性 List<INode> children,保存目录下所有的文件夹和文件
// FSDirctory 目录树 大致形状如下
// INodeDirectory
// INodeDirectory
// INodeFile
// INodeFile
// INodeDirectory
// INodeDirectory
existing = unprotectedMkdir(fsd, fsd.allocateNewInodeId(), existing,
localName.getBytes(Charsets.UTF_8), perm, null, now());
if (existing == null) {
return null;
}
final INode newNode = existing.getLastINode();
...
String cur = existing.getPath();
// 创建文件夹操作记录写 editlog
fsd.getEditLog().logMkDir(cur, newNode);
if (NameNode.stateChangeLog.isDebugEnabled()) {
NameNode.stateChangeLog.debug("mkdirs: created directory " + cur);
}
return existing;
}
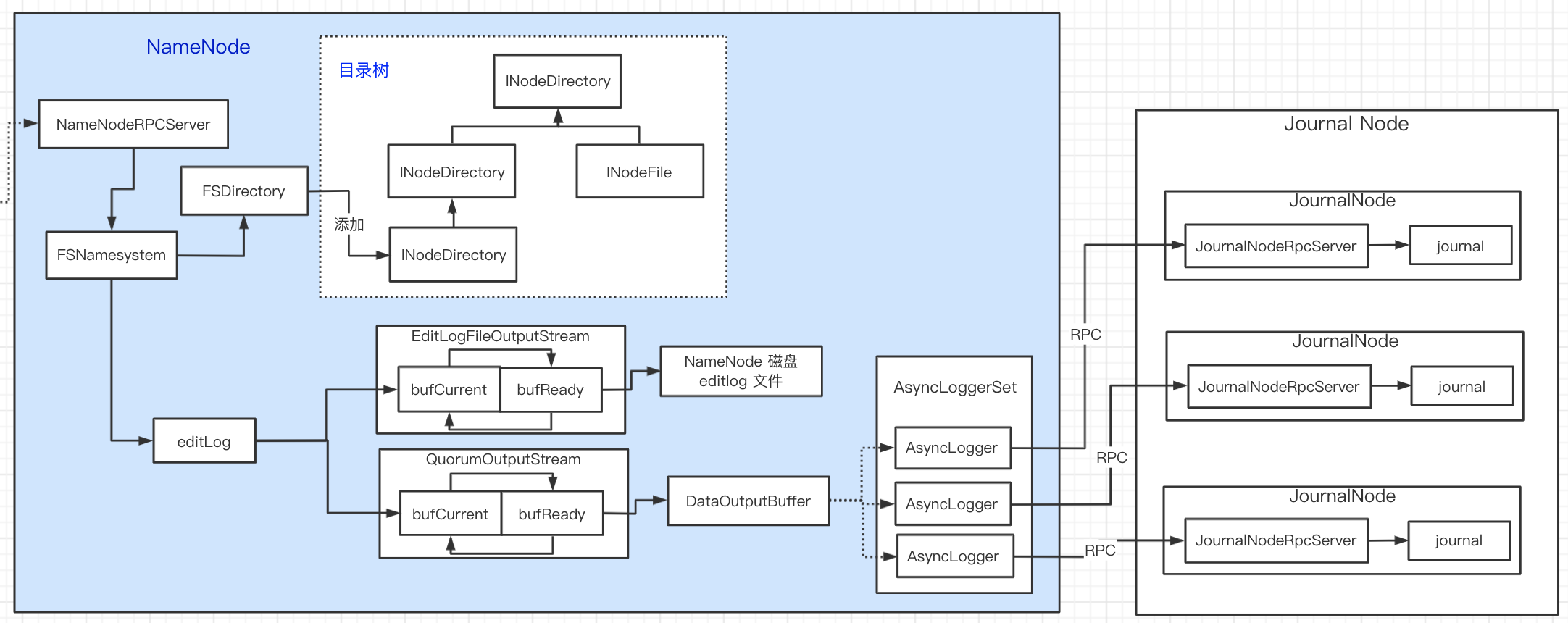
editlog
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.FSEditLog
void logEdit(final FSEditLogOp op) {
// 写数据,加锁
synchronized (this) {
...
long start = beginTransaction();
op.setTransactionId(txid);
try {
// editLogStream = JournalSetOutputStream,写两次
// EditLogFileOutputStream NameNode 本地磁盘 editlog
// QuorumOutputStream journal Node editlog
// 上面两个 OutputStream 底层都是利用 EditsDoubleBuffer 实现双缓存
editLogStream.write(op);
}
...
endTransaction(start);
// 不满足刷磁盘的条件,直接返回
if (!shouldForceSync()) {
return;
}
isAutoSyncScheduled = true;
}
// 刷 editlog 到磁盘,双缓冲内存切换时也要加锁
logSync();
}
写操作有点绕,看下图配合理解:
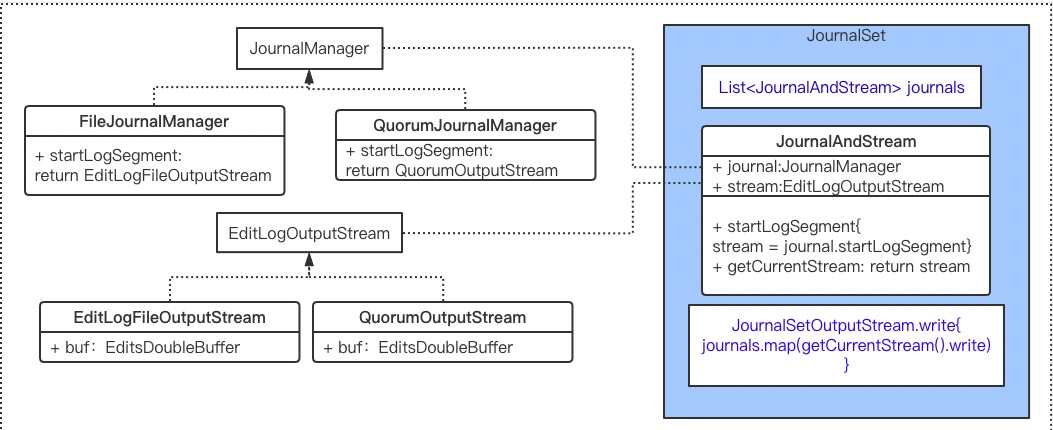
- editLogStream = JournalSetOutputStream,JournalSetOutputStream 可以访问 journals
- journals 包含 FileJournalManager 和 QuorumJournalManager
双缓冲
editlog 首先会写内存,内存满之后刷磁盘,这保证 editlog 能高效写入(元数据高并发)。
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.FSEditLog
public void logSync() {
long syncStart = 0;
// 全局唯一事务 ID,可以判断当前 事务ID 是否在刷
long mytxid = myTransactionId.get().txid;
boolean sync = false;
try {
EditLogOutputStream logStream = null;
// 加锁
synchronized (this) {
try {
// 判断是否已经在刷,如果是则死等
while (mytxid > synctxid && isSyncRunning) {
try {
// wait 释放锁
wait(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
}
//
// 已经在刷了,无需重复执行
//
if (mytxid <= synctxid) {
numTransactionsBatchedInSync++;
if (metrics != null) {
// Metrics is non-null only when used inside name node
metrics.incrTransactionsBatchedInSync();
}
return;
}
// 准备开始刷磁盘,isSyncRunning = true;
syncStart = txid;
isSyncRunning = true;
sync = true;
// swap buffers
try {
// 内存交换
// doubleBuf.setReadyToFlush();
editLogStream.setReadyToFlush();
}
}
logStream = editLogStream;
}// 双缓冲内存交换后,释放锁,开始 刷磁盘
// 刷磁盘是耗时操作,不加锁
long start = monotonicNow();
try {
if (logStream != null) {
// 刷磁盘
// EditLogFileOutputStream.flushAndSync
// QuorumOutputStream.flushAndSync
logStream.flush();
}
}
...
} finally {
// Prevent RuntimeException from blocking other log edit sync
synchronized (this) {
// editlog 写入磁盘后,重置标志位 isSyncRunning,并唤醒等待线程
if (sync) {
synctxid = syncStart;
isSyncRunning = false;
}
this.notifyAll();
}
}
}
高并发下如何保证写 editlog 线程安全:
- 加锁,写单条 editlog
- 加锁,双缓冲内存切换
- ready editlog 内存数据刷磁盘
NameNode editlog 本地磁盘 写
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.EditLogFileOutputStream
private EditsDoubleBuffer doubleBuf;
// 切换
public void setReadyToFlush() throws IOException {
doubleBuf.setReadyToFlush();
}
// 写数据到文件
public void flushAndSync(boolean durable) throws IOException {
...
doubleBuf.flushTo(fp);
...
}
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.EditsDoubleBuffer
/*
* editlog 双写
* 1. 数据写到内存1
* 2. 当内存1数据长度满足条件后,内存1和内存2地址交换:tmp = 内存1,内存1=内存2,内存2=tmp1 (目的是清空内存1)
* 3. 内存2 的数据刷到 磁盘
*/
// bufCurrent 写,写满之后,切换内存
public void writeOp(FSEditLogOp op) throws IOException {
bufCurrent.writeOp(op);
}
/**
* 内存区交换:ready 内存和 current 内存交换
*/
public void setReadyToFlush() {
assert isFlushed() : "previous data not flushed yet";
TxnBuffer tmp = bufReady;
bufReady = bufCurrent;
bufCurrent = tmp;
}
public void flushTo(OutputStream out) throws IOException {
// 文件流操作,内存清空
bufReady.writeTo(out); // write data to file
bufReady.reset(); // erase all data in the buffer
}
Journal Node editlog 写
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.qjournal.client.QuorumOutputStream
private EditsDoubleBuffer buf;
public void setReadyToFlush() throws IOException {
buf.setReadyToFlush();
}
/**
* editlog 刷到 journal 集群
*/
@Override
protected void flushAndSync(boolean durable) throws IOException {
int numReadyBytes = buf.countReadyBytes();
if (numReadyBytes > 0) {
int numReadyTxns = buf.countReadyTxns();
long firstTxToFlush = buf.getFirstReadyTxId();
...
// 1)ready 内存先刷到 DataOutputBuffer (journal 集群是多个节点,先备份数据)
// 2)DataOutputBuffer 刷到 journal 集群
DataOutputBuffer bufToSend = new DataOutputBuffer(numReadyBytes);
buf.flushTo(bufToSend);
assert bufToSend.getLength() == numReadyBytes;
byte[] data = bufToSend.getData();
assert data.length == bufToSend.getLength();
// journal 集群 editlog 写
// private final List<AsyncLogger> loggers;
QuorumCall<AsyncLogger, Void> qcall = loggers.sendEdits(
segmentTxId, firstTxToFlush,
numReadyTxns, data);
loggers.waitForWriteQuorum(qcall, writeTimeoutMs, "sendEdits");
...
}
}
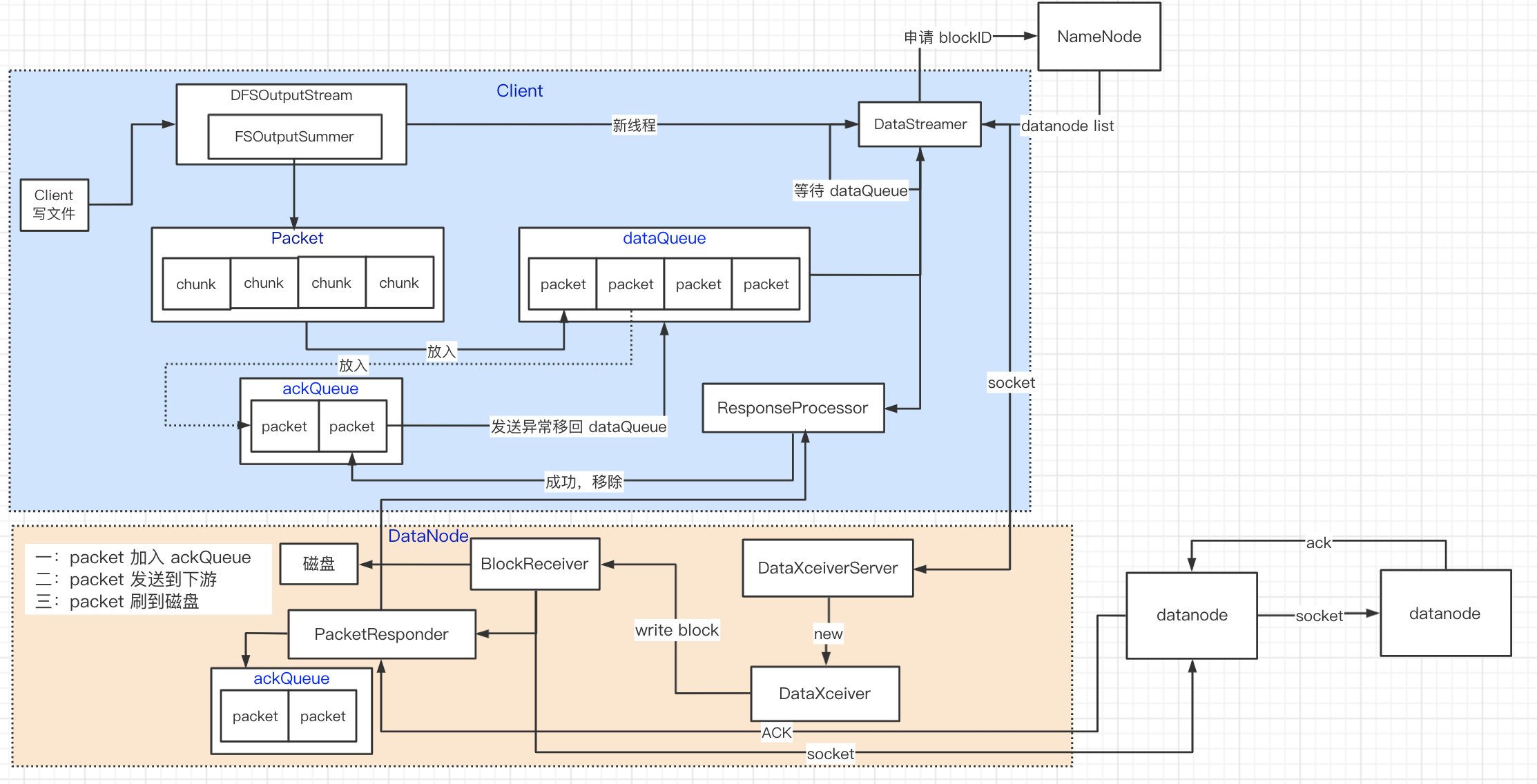
读写流程
DFSOutputStream
NameNodeRpcServer.create
-> FSNamesystem.startFile
-> DistributedFileSystem.create
-> DFSOutputStream.newStreamForCreate
-> NameNodeRPCServer.startFile
-> FSNamesystem.startFileInternal 添加 INodeFile 节点
// org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.DFSOutputStream
static DFSOutputStream newStreamForCreate(DFSClient dfsClient, String src,
FsPermission masked, EnumSet<CreateFlag> flag, boolean createParent,
short replication, long blockSize, Progressable progress, int buffersize,
DataChecksum checksum, String[] favoredNodes) throws IOException {
...
boolean shouldRetry = true;
int retryCount = CREATE_RETRY_COUNT;
while (shouldRetry) {
shouldRetry = false;
try {
// 上传文件:
// 创建文件
// 添加契约
stat = dfsClient.namenode.create(src, masked, dfsClient.clientName,
new EnumSetWritable<CreateFlag>(flag), createParent, replication,
blockSize, SUPPORTED_CRYPTO_VERSIONS);
break;
}
...
// DataStreamer 非常重要,写 datanode
final DFSOutputStream out = new DFSOutputStream(dfsClient, src, stat,
flag, progress, checksum, favoredNodes);
// 启动 DataStreamer,等待写入数据
out.start();
return out;
}
}
private DFSOutputStream(DFSClient dfsClient, String src, HdfsFileStatus stat,
EnumSet<CreateFlag> flag, Progressable progress,
DataChecksum checksum, String[] favoredNodes) throws IOException {
// 主要功能:创建 DataStreamer
streamer = new DataStreamer(stat, null);
if (favoredNodes != null && favoredNodes.length != 0) {
streamer.setFavoredNodes(favoredNodes);
}
}
// 通过管道往 datanode 发送 packets 数据包
// 从 NameNode 申请 block,并写数据到 datanode
// 每个 packet 有一个序列号,当所有 packet 都传输完毕,DataStreamer 关闭
class DataStreamer extends Daemon {
public void run() {
long lastPacket = Time.monotonicNow();
TraceScope scope = NullScope.INSTANCE;
while (!streamerClosed && dfsClient.clientRunning) {
...
try {
// process datanode IO errors if any
boolean doSleep = false;
if (hasError && (errorIndex >= 0 || restartingNodeIndex.get() >= 0)) {
// 发送 block 异常处理
doSleep = processDatanodeError();
}
synchronized (dataQueue) {
// wait for a packet to be sent.
long now = Time.monotonicNow();
// dataQueue 没数据就 wait
while ((!streamerClosed && !hasError && dfsClient.clientRunning
&& dataQueue.size() == 0 &&
(stage != BlockConstructionStage.DATA_STREAMING ||
stage == BlockConstructionStage.DATA_STREAMING &&
now - lastPacket < dfsClient.getConf().socketTimeout/2)) || doSleep ) {
long timeout = dfsClient.getConf().socketTimeout/2 - (now-lastPacket);
timeout = timeout <= 0 ? 1000 : timeout;
timeout = (stage == BlockConstructionStage.DATA_STREAMING)?
timeout : 1000;
try {
dataQueue.wait(timeout);
...
// get packet to be sent.
if (dataQueue.isEmpty()) {
one = createHeartbeatPacket();
assert one != null;
} else {
// 获取 packet
one = dataQueue.getFirst(); // regular data packet
...
if (stage == BlockConstructionStage.PIPELINE_SETUP_CREATE) {
if(DFSClient.LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
DFSClient.LOG.debug("Allocating new block");
}
// 向 NameNode 申请 block
// 创建数据管道
setPipeline(nextBlockOutputStream());
// 创建 ResponseProcessor,等待 block 发送 返回 ack
// 发送成功,移除 ackQueue 中 block
initDataStreaming();
}
...
// 发送 block
Span span = null;
synchronized (dataQueue) {
// move packet from dataQueue to ackQueue
if (!one.isHeartbeatPacket()) {
span = scope.detach();
one.setTraceSpan(span);
// dataQueue 移除当前要发送的 block
// 并添加到 ackQueue,若block 发送异常,则 ackQueue 中 block 再次移到 dataQueue
dataQueue.removeFirst();
ackQueue.addLast(one);
dataQueue.notifyAll();
}
}
// write out data to remote datanode
TraceScope writeScope = Trace.startSpan("writeTo", span);
try {
// 发送 block 数据
one.writeTo(blockStream);
blockStream.flush();
}
...
}
}
// org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSOutputSummer
// DFSOutputStream 父类
// 写数据
public synchronized void write(int b) throws IOException {
buf[count++] = (byte)b;
// 攒数据,buffer 写
if(count == buf.length) {
flushBuffer();
}
}
protected synchronized int flushBuffer(boolean keep,
boolean flushPartial) throws IOException {
int bufLen = count;
int partialLen = bufLen % sum.getBytesPerChecksum();
int lenToFlush = flushPartial ? bufLen : bufLen - partialLen;
if (lenToFlush != 0) {
// 非常重要
// 目录 -> 文件 -> block(128M) -> packet(64k)-> chunk(512 字节数据 + 4 字节校验)
// 数据组装成 chunk,多个 chunk 组装成 packet,
// packet 放入 ,唤醒 DataStreamer 发送 packet
writeChecksumChunks(buf, 0, lenToFlush);
if (!flushPartial || keep) {
count = partialLen;
System.arraycopy(buf, bufLen - count, buf, 0, count);
} else {
count = 0;
}
}
// total bytes left minus unflushed bytes left
return count - (bufLen - lenToFlush);
}