Kafka 是一个支持高并发,高性能,高可用的分布式消息系统。下面从三个角度来分析,为何 Kafka 性能如此优越。
- 生产时:
- batch 发送:提高吞吐量
- batch 存储的 buffer 重复利用:减少 JVM GC,防止 Full GC
- 同个主机上的不同分区 msg 一起发送:减少网络创建开销
- 服务器:
- 顺序读写:顺序读写磁盘比随机读写性能高三个数量级
- 零拷贝:减少上下文切换和重复的数据拷贝
- NIO + 消息队列:提升网络请求性能
- 消费时:
- 跳表设计:log 文件名称就是当前文件存储最早 msg 的 offset,可根据读取的 offset 直接选中目标文件读取
- 稀疏索引:每个 log 文件有对应的 index 文件,记录 offset msg 对应的磁盘地址
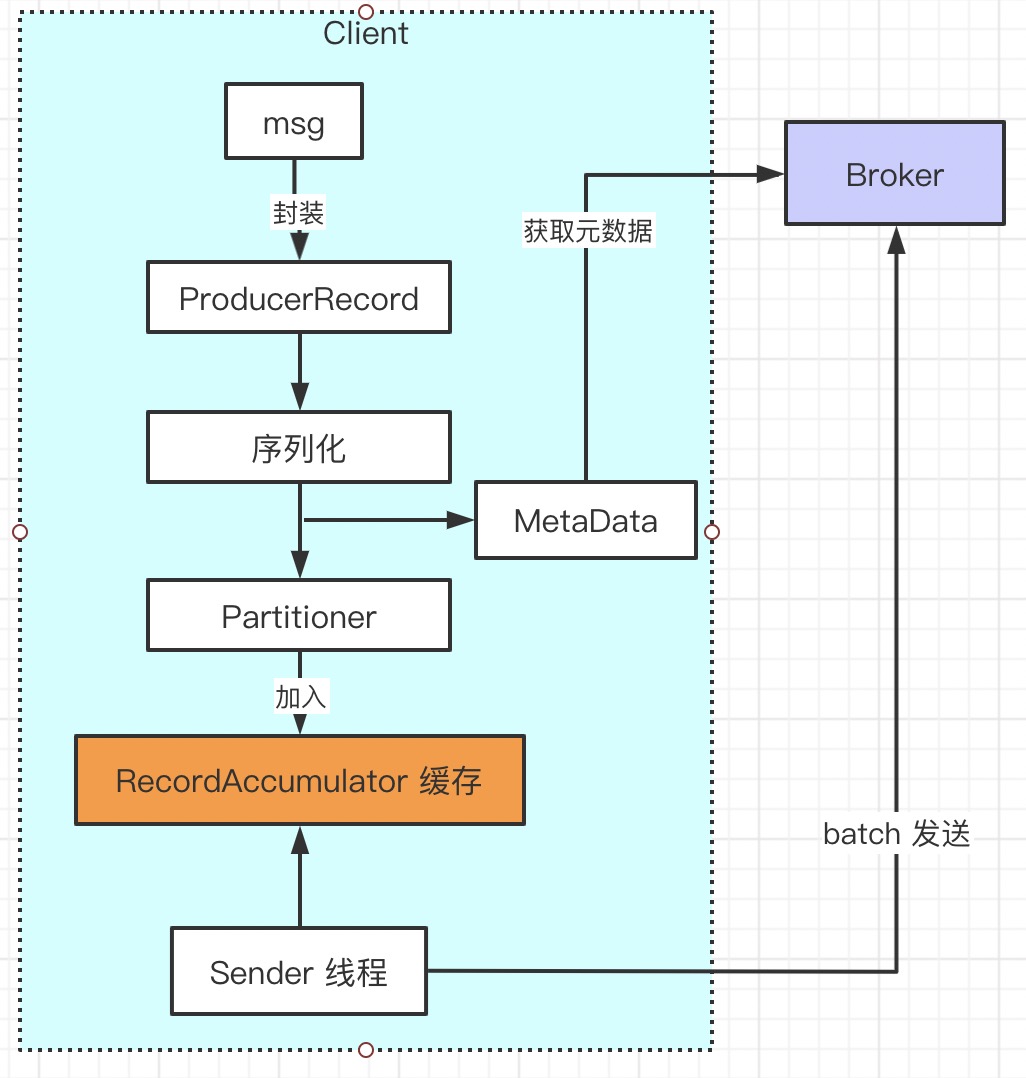
Producer
Kafka 生产端发送数据流程:
- msg 封装成 ProducerRecord
- Record 序列化
- 第一次发送时先获取 kafka 集群元数据
- Record 根据元数据得到要发送到 topic 的分区
- Record 添加到
RecordAccumulator缓冲区(每个分区都有独立的缓冲队列) - Sender 线程从
RecordAccumulator获取 batch record 发送到 Broker
// org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.KafkaProducer
public class KafkaProducer<K, V> implements Producer<K, V> {
// 分区器,可以自定义
private final Partitioner partitioner;
// kafka 集群元数据
private final Metadata metadata;
// 缓冲区
private final RecordAccumulator accumulator;
// 发送线程
private final Sender sender;
// 步骤一:封装成 ProducerRecord
public Future<RecordMetadata> send(ProducerRecord<K, V> record, Callback callback) {
// intercept the record, which can be potentially modified; this method does not throw exceptions
ProducerRecord<K, V> interceptedRecord = this.interceptors == null ? record : this.interceptors.onSend(record);
return doSend(interceptedRecord, callback);
}
private Future<RecordMetadata> doSend(ProducerRecord<K, V> record, Callback callback) {
TopicPartition tp = null;
try {
// 第一次发送数据时,先确保已经有 kafka metadata
ClusterAndWaitTime clusterAndWaitTime = waitOnMetadata(record.topic(), record.partition(), maxBlockTimeMs);
// maxBlockTimeMs 默认 60s
long remainingWaitMs = Math.max(0, maxBlockTimeMs - clusterAndWaitTime.waitedOnMetadataMs);
Cluster cluster = clusterAndWaitTime.cluster;
byte[] serializedKey;
// 步骤二:序列化
try {
serializedKey = keySerializer.serialize(record.topic(), record.key());
}
byte[] serializedValue;
try {
serializedValue = valueSerializer.serialize(record.topic(), record.value());
}
// 步骤三:获取分区
int partition = partition(record, serializedKey, serializedValue, cluster);
int serializedSize = Records.LOG_OVERHEAD + Record.recordSize(serializedKey, serializedValue);
ensureValidRecordSize(serializedSize);
tp = new TopicPartition(record.topic(), partition);
...
// 步骤四:record 添加到 accumulator 缓存
RecordAccumulator.RecordAppendResult result = accumulator.append(tp, timestamp, serializedKey, serializedValue, interceptCallback, remainingWaitMs);
if (result.batchIsFull || result.newBatchCreated) {
log.trace("Waking up the sender since topic {} partition {} is either full or getting a new batch", record.topic(), partition);
// 满足 batch 发送条件,唤醒 sender 发送数据
this.sender.wakeup();
}
return result.future;
...
}
}
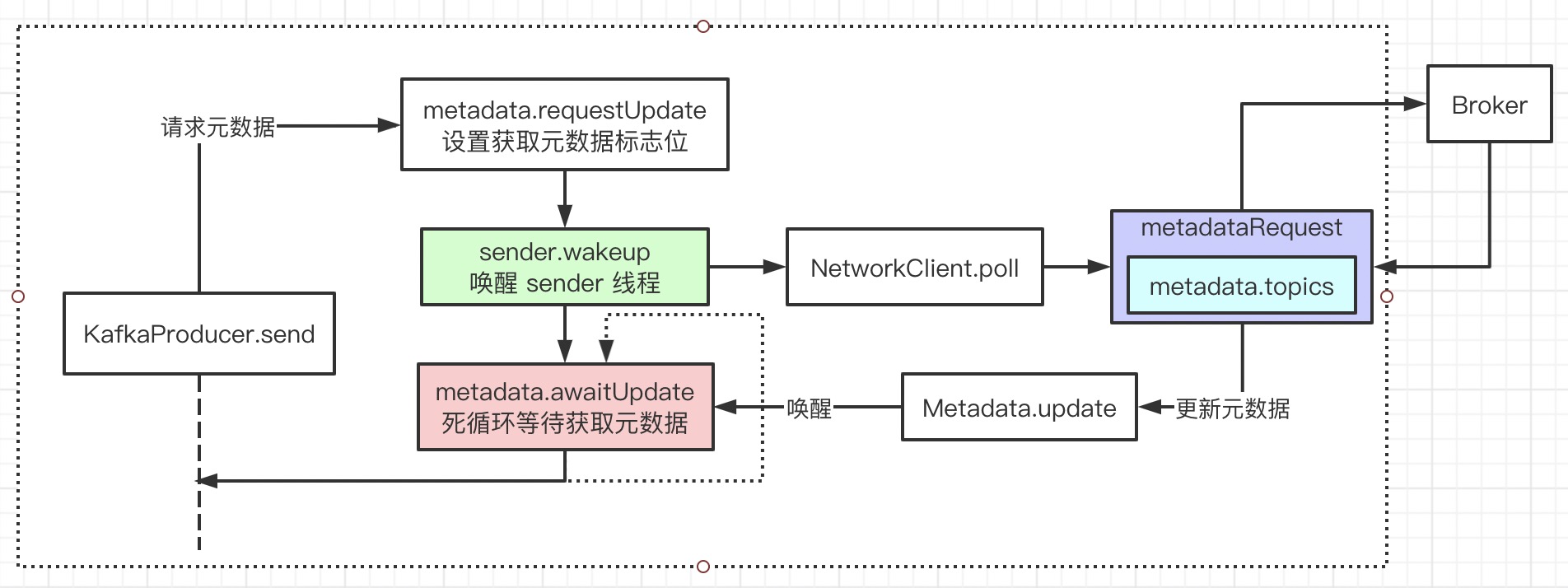
元数据
Client 需要从 Broker 节点获取 Topic 的元数据,才知道将当前 Record 发送哪个分区。
// org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.KafkaProducer
private ClusterAndWaitTime waitOnMetadata(String topic, Integer partition, long maxWaitMs) throws InterruptedException {
// 添加要获取元数据的 topic,Map 结构
metadata.add(topic);
Cluster cluster = metadata.fetch();
Integer partitionsCount = cluster.partitionCountForTopic(topic);
// 如果已经有元数据,直接返回
if (partitionsCount != null && (partition == null || partition < partitionsCount))
return new ClusterAndWaitTime(cluster, 0);
// 死循环一直到获取元数据/超时
do {
int version = metadata.requestUpdate();
// 唤醒 sender 线程去获取
sender.wakeup();
try {
// wait 直到sender 获取到元数据后唤醒
// 或者超时
metadata.awaitUpdate(version, remainingWaitMs);
}
...
} while (partitionsCount == null);
...
return new ClusterAndWaitTime(cluster, elapsed);
}
/*
* Sender.run(this.client.poll(pollTimeout, now);)
* NetworkClient.poll -> NetworkClient.handleCompletedReceives
* metadataUpdater.maybeUpdate -> NetworkClient.maybeHandleCompletedReceive
* metadataRequest = new MetadataRequest(new ArrayList<>(metadata.topics())); // 只获取 metadata 中 topic
* NetworkClient.handleResponse -> MetaData.update
*/
// org.apache.kafka.clients.Metadata
// kafka 元数据结构
private Cluster cluster;
public synchronized void update(Cluster cluster, long now) {
...
if (topicExpiryEnabled) {
// Handle expiry of topics from the metadata refresh set.
// 移除 TOPIC_EXPIRY_MS(5分钟) 时间段内没有发送数据的 topic
// 下次获取元数据时就不获取此 topic 元数据
// 获取元数据的条件:cluster 元数据中没有需要 topic 的信息
for (Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Long>> it = topics.entrySet().iterator(); it.hasNext(); ) {
Map.Entry<String, Long> entry = it.next();
long expireMs = entry.getValue();
if (expireMs == TOPIC_EXPIRY_NEEDS_UPDATE)
entry.setValue(now + TOPIC_EXPIRY_MS);
else if (expireMs <= now) {
// 当前 topic 过期,移除
it.remove();
log.debug("Removing unused topic {} from the metadata list, expiryMs {} now {}", entry.getKey(), expireMs, now);
}
}
}
// 更新元数据
this.cluster = cluster;
// 唤醒 metadata
notifyAll();
}
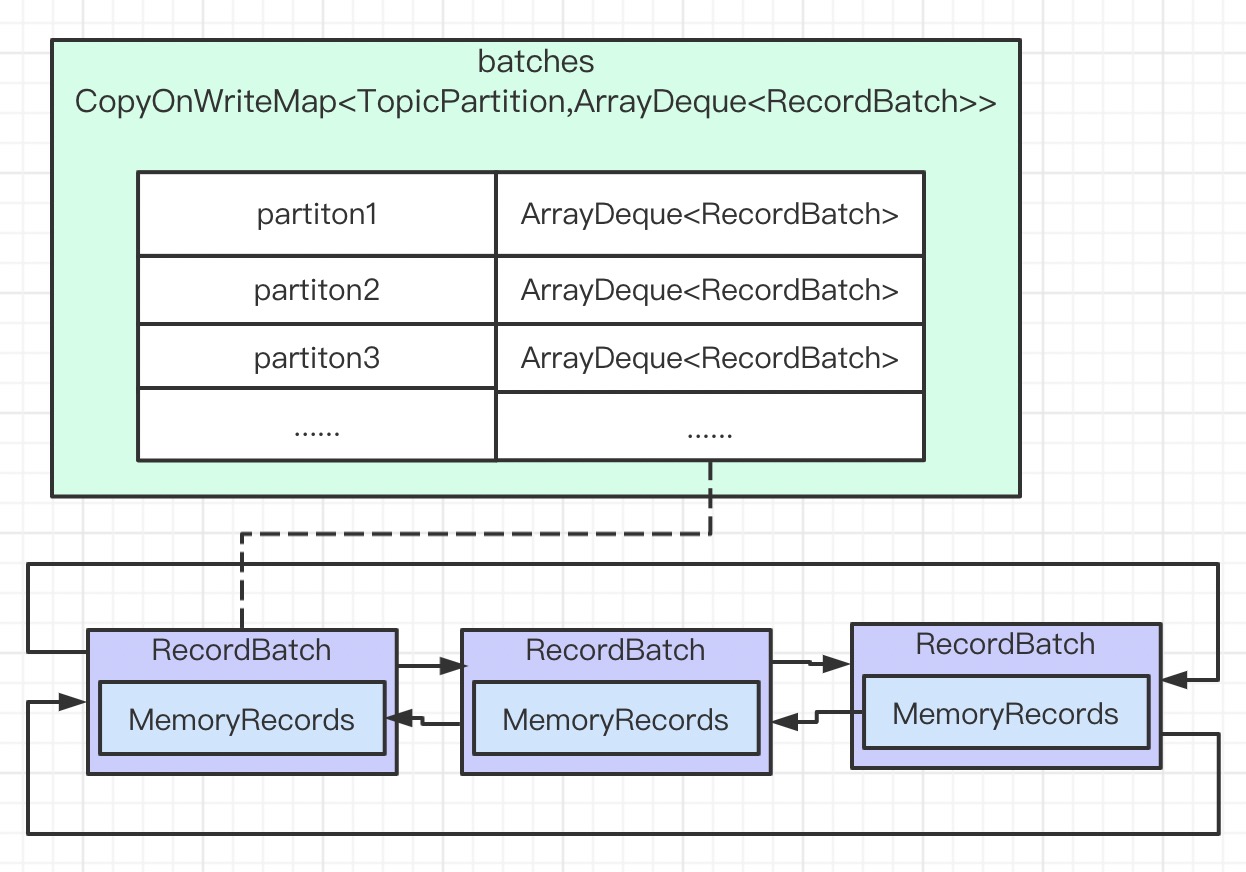
RecordAccumulator
Record 不是一条一条发送的,需要先添加到 RecordAccumulator 缓存中,然后再 batch 发送。
// org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.RecordAccumulator
public final class RecordAccumulator {
// 真正的缓存 CopyOnWriteMap
// Deque 是 ArrayDeque,当作为一个队列时,比 LinkedList 快
// 每个分区都有自己的Deque, 存的是 RecordBatch
// RecordBatch 才是 record 真正缓存和 batch 发送
private final ConcurrentMap<TopicPartition, Deque<RecordBatch>> batches;
/*
* record 添加到 缓冲区
* 线程安全,分段加锁提高性能
*/
public RecordAppendResult append(TopicPartition tp,
long timestamp,
byte[] key,
byte[] value,
Callback callback,
long maxTimeToBlock) throws InterruptedException {
try {
// getOrCreateDeque 获取当前分区缓存,线程安全,CopyOnWriteMap 后续介绍
Deque<RecordBatch> dq = getOrCreateDeque(tp);
// 第一次加锁
synchronized (dq) {
...
RecordAppendResult appendResult = tryAppend(timestamp, key, value, callback, dq);
if (appendResult != null)
return appendResult;
}// 解锁
// 走到这一步说明,上面的 tryAppend 返回null 即 RecordBatch 为 null
// // 可能有两种情况:没有RecordBatch,旧的RecordBatch 已写满要开辟新的 RecordBatch
// 内存池(后续介绍)开辟新的 RecordBatch,供添加缓存数据
// 开辟新批次的空间耗时,不加锁
int size = Math.max(this.batchSize, Records.LOG_OVERHEAD + Record.recordSize(key, value));
log.trace("Allocating a new {} byte message buffer for topic {} partition {}", size, tp.topic(), tp.partition());
ByteBuffer buffer = free.allocate(size, maxTimeToBlock);
// 第二次加锁
// 一:tryAppend 再次尝试添加
// 二:添加成功,说明已存在 RecordBatch,删除之前创建的 buffer
// 三:添加失败,利用之前创建的 buffer 新建 RecordBatch,然后添加
synchronized (dq) {
...
RecordAppendResult appendResult = tryAppend(timestamp, key, value, callback, dq);
if (appendResult != null) {
// 此时发现已有新批次的 RecordBatch,删除之前创建的 buffer
// 结合多线程场景去考虑
free.deallocate(buffer);
return appendResult;
}
// 新建 RecordBatch,并将 Record 添加
MemoryRecords records = MemoryRecords.emptyRecords(buffer, compression, this.batchSize);
RecordBatch batch = new RecordBatch(tp, records, time.milliseconds());
FutureRecordMetadata future = Utils.notNull(batch.tryAppend(timestamp, key, value, callback, time.milliseconds()));
// 分区队列中添加 RecordBatch,下次不用再创建
dq.addLast(batch);
incomplete.add(batch);
return new RecordAppendResult(future, dq.size() > 1 || batch.records.isFull(), true);
} // 解锁
...
}
}
batches 是真正的 Record 缓存数据结构,这里设计也是很精妙的。
// org.apache.kafka.common.utils.CopyOnWriteMap
// 读优化
// 这里为了提高队列的性能,使用的数据结构是 ArrayDeque ,即 V = ArrayQueue
public class CopyOnWriteMap<K, V> implements ConcurrentMap<K, V> {
/**
* 读 map 时没加
*/
public V get(Object k) {
return map.get(k);
}
/**
* 重点
* 写 map 时加锁,读写分离思路,适合读多写少的场景即多 get 少 put
* put:每个分区只会 put 一次,实际操作中分区数时有有限的
* 注意这里多开辟新的 map ,用于交换:https://www.cnblogs.com/hapjin/p/4840107.html
* 疑问:为什么这里要多复制一份而不是直接操作呢? 因为同个 map 同一时间有增删和遍历时,会报 ConcurrentModificationException
* 所以这里多复制一份,保证读原来的 map,写备份的 map 后替换原先的 map
*/
public synchronized V put(K k, V v) {
Map<K, V> copy = new HashMap<K, V>(this.map);
V prev = copy.put(k, v);
this.map = Collections.unmodifiableMap(copy);
return prev;
}
public synchronized V putIfAbsent(K k, V v) {
if (!containsKey(k))
return put(k, v);
else
return get(k);
}
}
到此我们可以得到 RecordAccumulator 的数据结构图。
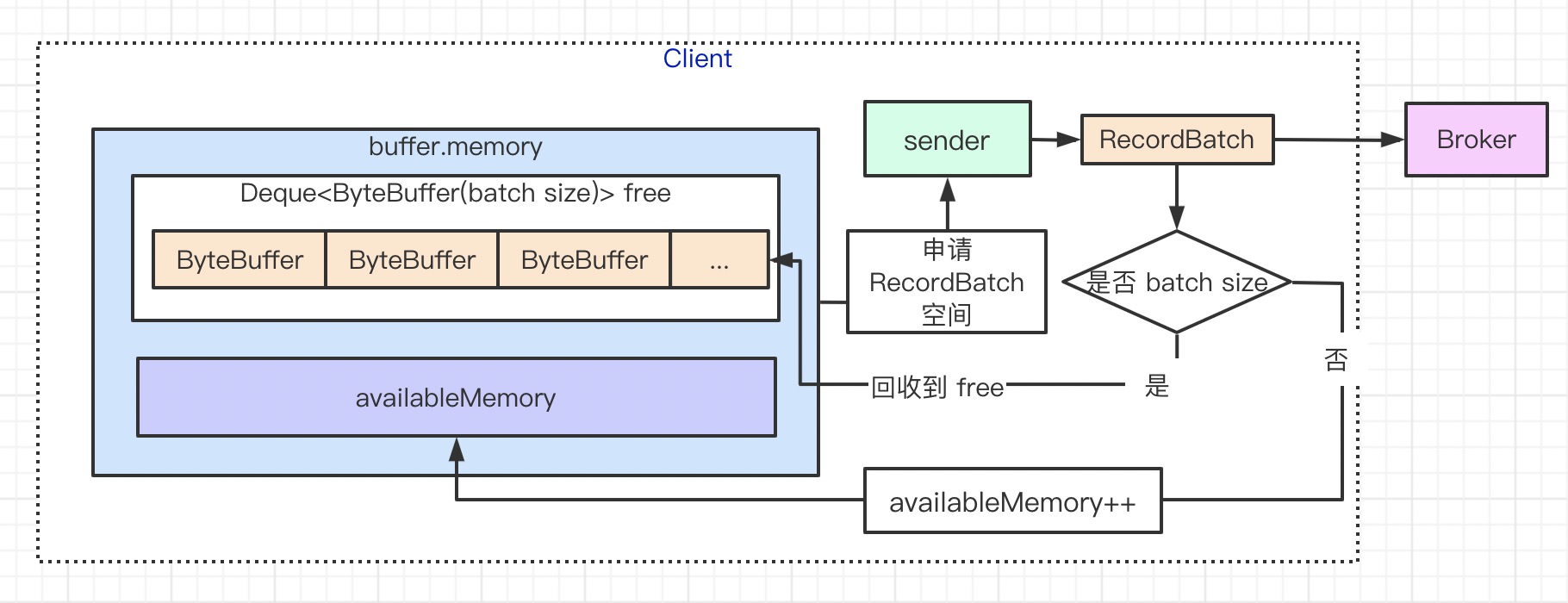
内存池
Producer 发送数据是攒批的,先缓存到 RecordBatch 然后再整体发送。RecordBatch 在 JVM 内存空间,Producer 吞吐很大必然会频繁创建 RecordBatch。对象频繁创建,在 JAVA 世界中不可避免的涉及到 GC,但 kafka 在这一步做了优化。下面一起看看在 Producer 端的内存池优化。
// 获取 RecordBatch 所需的内存空间
// ByteBuffer buffer = free.allocate(size, maxTimeToBlock);
// org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.BufferPool
public final class BufferPool {
// 可用的 ByteBuffer 队列
// ByteBuffer 是 默认 batch 大小的内存块
private final Deque<ByteBuffer> free;
// 需要等待开辟 ByteBuffer 的 batchs(没有可缓冲的内存,需要发送 batch 来释放)
private final Deque<Condition> waiters;
// Deque<ByteBuffer> + availableMemory = 缓存池大小,默认 32M
// availableMemory 可分配的内存大小
private long availableMemory;
public ByteBuffer allocate(int size, long maxTimeToBlockMs) throws InterruptedException {
// size 大于 总缓存池大小,直接报错,太大了放不下
if (size > this.totalMemory)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Attempt to allocate " + size
+ " bytes, but there is a hard limit of "
+ this.totalMemory
+ " on memory allocations.");
// 加锁
this.lock.lock();
try {
// 判断 size 是否为设置的 batch size 大小,
// 一般都是 batch 大小,除非一条 record 超过 batch size 则要大于 batch size
// 这里很关键,是内存池管理的体现:
// free:Deque<ByteBuffer> 是 ByteBuffer队列,且 ByteBuffer 大小=batch size
// 如果要申请的内存大小是 batch size,那么直接从 free 获取即可,无需创建新的 ByteBuffer 对象
if (size == poolableSize && !this.free.isEmpty())
return this.free.pollFirst();
// now check if the request is immediately satisfiable with the
// memory on hand or if we need to block
int freeListSize = this.free.size() * this.poolableSize;
if (this.availableMemory + freeListSize >= size) {
// 第一种情况:
// 当前可用的内存(availableMemory + free)大于申请的 size,开辟后返回
// 释放 free 中的 ByteBuffer 到 availableMemory,保证 availableMemory 空间大于申请的 size
freeUp(size);
this.availableMemory -= size;
lock.unlock();
return ByteBuffer.allocate(size);
} else {
// 第二种情况:
// 当前可用的内存(availableMemory + free)小于申请的 size
// 当前线程 block,直到(availableMemory + free)大于申请的 size,等待 释放
// 如果常常发生这种情况,建议加大缓冲区大小
int accumulated = 0;
ByteBuffer buffer = null;
Condition moreMemory = this.lock.newCondition();
long remainingTimeToBlockNs = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toNanos(maxTimeToBlockMs);
// 当前开辟 size ,内存空间不足,信息存入 waiters
this.waiters.addLast(moreMemory);
// 等待,直到 可用内存大于申请的 size
while (accumulated < size) {
long startWaitNs = time.nanoseconds();
long timeNs;
boolean waitingTimeElapsed;
try {
// wait
// 超时自动苏醒
// 有内存释放被唤醒
waitingTimeElapsed = !moreMemory.await(remainingTimeToBlockNs, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
this.waiters.remove(moreMemory);
throw e;
} finally {
long endWaitNs = time.nanoseconds();
timeNs = Math.max(0L, endWaitNs - startWaitNs);
this.waitTime.record(timeNs, time.milliseconds());
}
// 如果是超时等待,表示在规定的时间没有可用的内存,直接报错,默认 60s - 获取元数据时间
if (waitingTimeElapsed) {
this.waiters.remove(moreMemory);
throw new TimeoutException("Failed to allocate memory within the configured max blocking time " + maxTimeToBlockMs + " ms.");
}
remainingTimeToBlockNs -= timeNs;
// 到这一步,说明有内存释放
if (accumulated == 0 && size == this.poolableSize && !this.free.isEmpty()) {
// 申请内存size = batch size,把 free 中 ByteBuffer 返回
buffer = this.free.pollFirst();
accumulated = size;
} else {
// 累加 可用内存大小,accumulated
freeUp(size - accumulated);
int got = (int) Math.min(size - accumulated, this.availableMemory);
this.availableMemory -= got;
accumulated += got;
}
}
public void deallocate(ByteBuffer buffer, int size) {
lock.lock();
try {
if (size == this.poolableSize && size == buffer.capacity()) {
// 释放的内存大小 = batch size
// 清空 buffer,并添加到 free
// 内存池管理的体现:用完内存不释放,直接复用,减少 GC
buffer.clear();
this.free.add(buffer);
} else {
// 释放的内存大小 != batch size,直接释放等待 GC
this.availableMemory += size;
}
// 有内存释放,唤醒在等待内存开辟的 waiters
Condition moreMem = this.waiters.peekFirst();
if (moreMem != null)
// waitingTimeElapsed = !moreMemory.await(remainingTimeToBlockNs, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
moreMem.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
内存申请和释放主要代码如上所示,接下来理清设计:
- 缓冲池分为:free 和 availableMemory
- availableMemory 表示未分配可用的内存,主要是计算是否可分配 size 内存:分配时减少,释放时增加,回收靠 GC
- free :ByteBuffer 队列,ByteBuffer 大小 = batch size,一般恰好是每次开辟的大小,释放时清空数据重新添加到队列
按 batch size 大小划分 ByteBuffer,增大复用效果;不等于 batch size 的内存空间直接 GC,不会出现内存碎片问题。
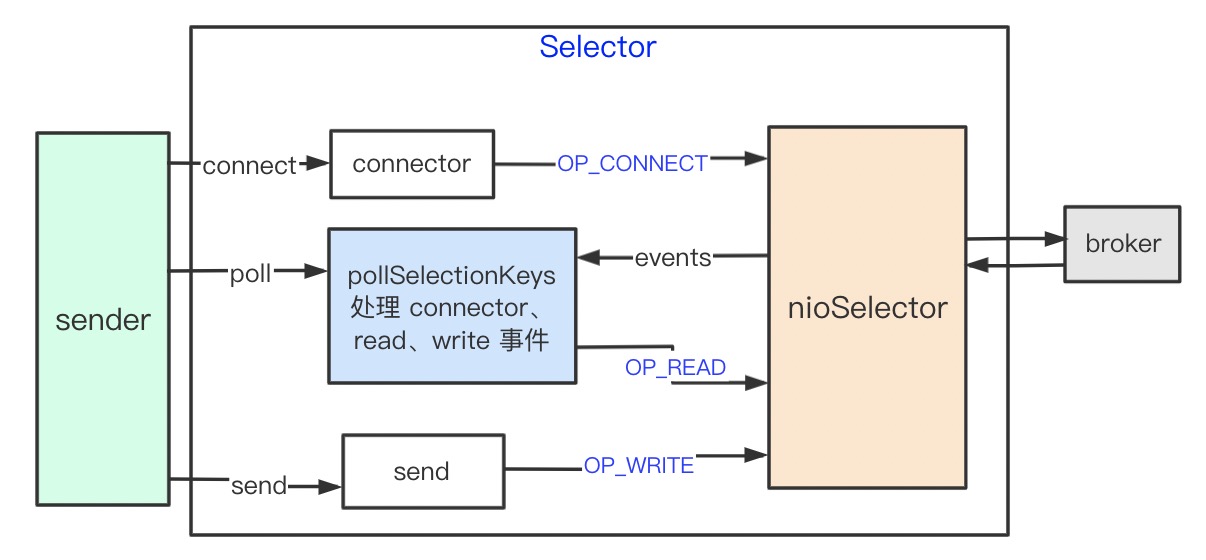
NIO
有了以上的知识后,我们可以将 record 加入到 batch 中,准备发送到 kafka broker。在发送之前,我们先分析 kafka 的使用的网络框架 NIO,有助于后续分析 sender 线程。网络一般涉及三个过程:建立连接,发送数据,读响应。
// NetworkClient 是 kafka 网络请求实现类
// NetworkClient 主要是封装 NIO 中 selector 操作
// 下面主要分析 kafka 中 selector 操作,关于 NetworkClient 放到后续的 sender 线程一起分析
// org.apache.kafka.common.network.Selector
public class Selector implements Selectable {
// java nio,不了解的先去熟悉下
private final java.nio.channels.Selector nioSelector;
// 记录对 kafka broker 连接
private final Map<String, KafkaChannel> channels;
// 与 kafka broker 建立连接,id = kafka node
public void connect(String id, InetSocketAddress address, int sendBufferSize, int receiveBufferSize) throws IOException {
...
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
// 设置非阻塞模式
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
Socket socket = socketChannel.socket();
socket.setKeepAlive(true);
if (sendBufferSize != Selectable.USE_DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE)
socket.setSendBufferSize(sendBufferSize);
if (receiveBufferSize != Selectable.USE_DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE)
socket.setReceiveBufferSize(receiveBufferSize);
// tcp 优化
socket.setTcpNoDelay(true);
boolean connected;
try {
// 尝试建立连接
connected = socketChannel.connect(address);
} catch (UnresolvedAddressException e) {
socketChannel.close();
throw new IOException("Can't resolve address: " + address, e);
} catch (IOException e) {
socketChannel.close();
throw e;
}
// channel 加到 nio selector,并添加 OP_CONNECT 事件
// 后续 chanel 建立连接后,由 nio selector 返回 connect 事件
SelectionKey key = socketChannel.register(nioSelector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
// id = kafka node;kafkaChannel 只是对 java channel 的封装
KafkaChannel channel = channelBuilder.buildChannel(id, key, maxReceiveSize);
// 后续处理时可通过 key.attachment 得到 channel
key.attach(channel);
// 记录 kafka node 对应的 channel
this.channels.put(id, channel);
...
}
// 发送数据
public void send(Send send) {
// 通过send 获取 kafka node 得到对应的 channel
KafkaChannel channel = channelOrFail(send.destination());
try {
// channel 发送数据,此时只是为 channel 添加 OP_WRITE,并未真正发送
channel.setSend(send);
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
this.failedSends.add(send.destination());
close(channel);
}
}
// sender 线程中会定时调用获取 event
// 读取 nio selector event,time 表示是否需要阻塞等待事件发生
public void poll(long timeout) throws IOException {
...
// block 直到有事件
// 注意此时会 wait,那么会导致 sender 线程也会休眠,需要调用 sender.wakeup 唤醒
int readyKeys = select(timeout);
long endSelect = time.nanoseconds();
this.sensors.selectTime.record(endSelect - startSelect, time.milliseconds());
// 有需要响应的事件
if (readyKeys > 0 || !immediatelyConnectedKeys.isEmpty()) {
pollSelectionKeys(this.nioSelector.selectedKeys(), false, endSelect);
pollSelectionKeys(immediatelyConnectedKeys, true, endSelect);
}
// 处理服务端返回的响应,stagedReceives
addToCompletedReceives();
...
}
// 处理 nio selector 返回的事件
// connect
// read
// write
private void pollSelectionKeys(Iterable<SelectionKey> selectionKeys,
boolean isImmediatelyConnected,
long currentTimeNanos) {
// eventKeys
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
KafkaChannel channel = channel(key);
...
try {
// 处理 connect ,与 kafka node 已建立连接:OP_CONNECT
if (isImmediatelyConnected || key.isConnectable()) {
// 连接建立完成后,channel 上对应的key 去除 OP_CONNECT,添加 OP_READ 事件
if (channel.finishConnect()) {
// 记录当前 kafka node 已建立连接
this.connected.add(channel.id());
this.sensors.connectionCreated.record();
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
log.debug("Created socket with SO_RCVBUF = {}, SO_SNDBUF = {}, SO_TIMEOUT = {} to node {}",
socketChannel.socket().getReceiveBufferSize(),
socketChannel.socket().getSendBufferSize(),
socketChannel.socket().getSoTimeout(),
channel.id());
} else
continue;
}
...
// 处理 read:在建立连接后已添加 OP_READ 事件
if (channel.ready() && key.isReadable() && !hasStagedReceive(channel)) {
NetworkReceive networkReceive;
while ((networkReceive = channel.read()) != null)
addToStagedReceives(channel, networkReceive);
}
// 处理 write:OP_WRITE (send(Send send))
if (channel.ready() && key.isWritable()) {
// channel.setSend(send); 为 chanel 添加 send
// 通过 chanel 发送数据:RecordBatchs
Send send = channel.write();
if (send != null) {
this.completedSends.add(send);
this.sensors.recordBytesSent(channel.id(), send.size());
}
}
// 关闭连接
if (!key.isValid()) {
close(channel);
this.disconnected.add(channel.id());
}
...
}
}
之前没有接触过 NIO,可能不太理解上面的代码,附图梳理下脉络
read
当使用 NIO ,由于 buffer 大小不匹配问题,必然会碰到粘包或拆包的问题。假设两个响应返回 “hello word” 和 “flink kafka”,有可能是返回(一个返回就好触发一个 read event)
- “hello word”
- “flink “
- “kafka”
这叫拆包,也有可能返回
- “hello wordflink”
- “kafka”
这叫粘包
kafka 的解决方案是相当于在原有 data 基础上增加 header,header 只包含 data size,很朴素和通用方案。两个数据包变成 10”hello word”,11”flink kafka”。此时读取方式变为先读取4字节 size,然后再开辟 size 大小的 buffer 存data,死循环直到 data buffer 读满
// org.apache.kafka.common.network.Selector
if (channel.ready() && key.isReadable() && !hasStagedReceive(channel)) {
NetworkReceive networkReceive;
// read receive返回null 表示当前响应包为读取完毕,等待下个 read event再读
while ((networkReceive = channel.read()) != null)
// receive complete 才算响应读取完毕
// receive 添加到 stagedReceives
addToStagedReceives(channel, networkReceive);
}
// org.apache.kafka.common.network.KafkaChannel
public NetworkReceive read() throws IOException {
NetworkReceive result = null;
if (receive == null) {
receive = new NetworkReceive(maxReceiveSize, id);
}
// read
receive(receive);
// size 和 data 都读取完毕,才算 complete
if (receive.complete()) {
receive.payload().rewind();
result = receive;
receive = null;
}
return result;
}
private long receive(NetworkReceive receive) throws IOException {
return receive.readFrom(transportLayer);
}
public long readFromReadableChannel(ReadableByteChannel channel) throws IOException {
int read = 0;
// 读取 size;
if (size.hasRemaining()) {
int bytesRead = channel.read(size);
if (bytesRead < 0)
throw new EOFException();
read += bytesRead;
if (!size.hasRemaining()) {
size.rewind();
int receiveSize = size.getInt();
...
// 读取到size,可知 data 长度,申请存放 data 所需的 buffer
this.buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(receiveSize);
}
}
// 读取 data;每次进来都必会读取 buffer
if (buffer != null) {
int bytesRead = channel.read(buffer);
if (bytesRead < 0)
throw new EOFException();
read += bytesRead;
}
return read;
}
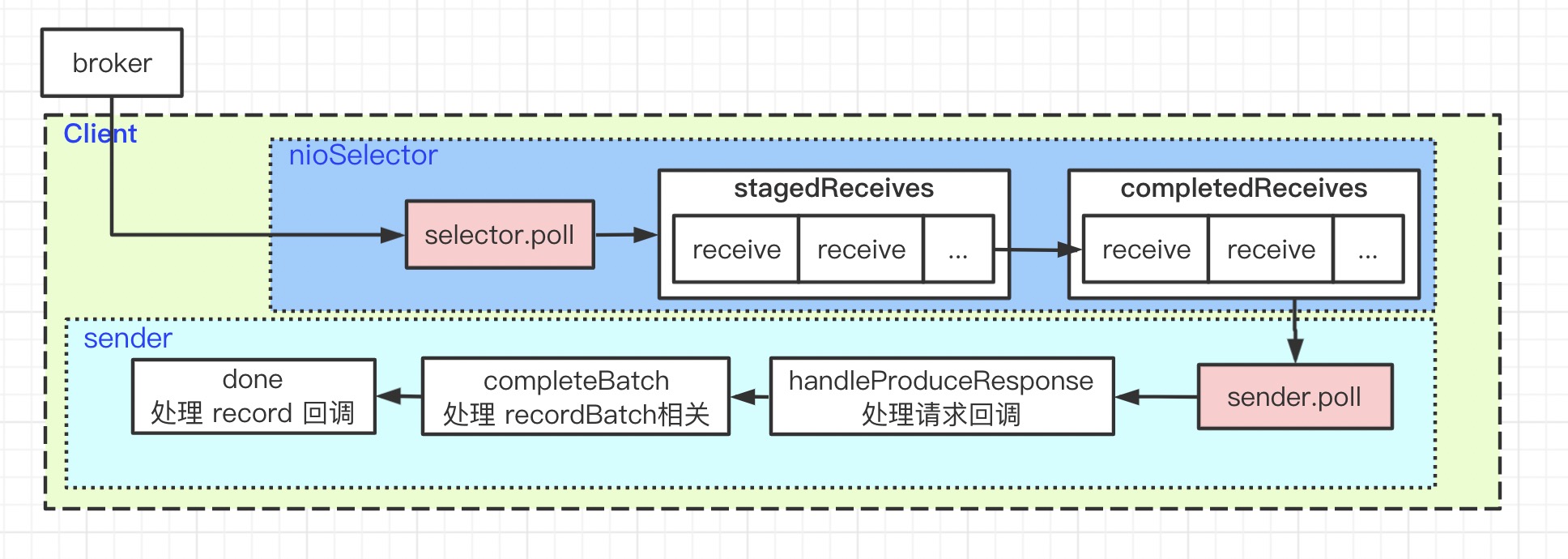
Sender
到此我们具备了发送 rocordBatch 的环境,开始向服务端发送流程。
// org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.KafkaProducer
// 满足 batch 发送条件,唤醒 sender 发送数据
this.sender.wakeup(); // 记得为什么这里要唤醒吗?selector.poll 有可能会 wait
// 后台线程发送请求
// org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.Sender
public class Sender implements Runnable {
private final KafkaClient client;
// while(run)
void run(long now) {
Cluster cluster = metadata.fetch();
// 从缓冲池 accumulator 筛选出满足 batch send 的 kafka nodes
RecordAccumulator.ReadyCheckResult result = this.accumulator.ready(cluster, now);
// 如果有 topic 的元数据信息位获取,设置元数据标识
if (!result.unknownLeaderTopics.isEmpty()) {
for (String topic : result.unknownLeaderTopics)
this.metadata.add(topic);
this.metadata.requestUpdate();
}
// 从需要发送的 kafka nodes 中移除没有准备好连接的 node,判断条件
// 元数据包含当前 kafka node
// 与当前 kafka node connection 已建立
// 与当前 kafka node channel 已建立
// 发送 batch 请求数未超过指定的最大值(默认5),生产中一般设置为1,保证数据不乱序
Iterator<Node> iter = result.readyNodes.iterator();
long notReadyTimeout = Long.MAX_VALUE;
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Node node = iter.next();
// ready 中如果发现未连接会去初始化连接 selector.connect
if (!this.client.ready(node, now)) {
iter.remove();
notReadyTimeout = Math.min(notReadyTimeout, this.client.connectionDelay(node, now));
}
}
// 从准备好发送的 kafkanodes 中,获取需要发送的 recordBatch
// 第一次调用时,与 kafka node 的连接都没有建立,此时 result.readyNodes 为空
// 在 poll 函数发现 connect 事件,此时会发起连接,那么下次再准备发送时就可以了
Map<Integer, List<RecordBatch>> batches = this.accumulator.drain(cluster,
result.readyNodes,
this.maxRequestSize,
now);
if (guaranteeMessageOrder) {
// Mute all the partitions drained
for (List<RecordBatch> batchList : batches.values()) {
for (RecordBatch batch : batchList)
this.accumulator.mutePartition(batch.topicPartition);
}
}
// 处理超时的发送
List<RecordBatch> expiredBatches = this.accumulator.abortExpiredBatches(this.requestTimeout, now);
...
// 创建请求:将要发送的 recordbatch 封装成ClientRequest
// 每个requests 都有个回调函数(handleProduceResponse),在收到响应时调用
List<ClientRequest> requests = createProduceRequests(batches, now);
long pollTimeout = Math.min(result.nextReadyCheckDelayMs, notReadyTimeout);
if (result.readyNodes.size() > 0) {
log.trace("Nodes with data ready to send: {}", result.readyNodes);
log.trace("Created {} produce requests: {}", requests.size(), requests);
pollTimeout = 0;
}
// 发送数据,这里只是在 select 注册 op_write,并在 channel 添加 send
for (ClientRequest request : requests)
client.send(request, now);
// 如果需要有数据发送,select.poll(0),不等待直接返回,因为有数据要发送
// 如果没有需要发送的数据,select.poll(timeout),距离下次有数据要发送的间隔(linger ms)
this.client.poll(pollTimeout, now);
}
}
sender 线程逻辑很清晰:
- while 以下步骤
- 检查缓冲区中满足发送条件的 recordBatch
- 检查要发送的 recordBatch 的元数据是否已准备
- 删除未建立连接的 kafka node(未连接时会发起连接事件)
- 获取已建立连接 kafka node 的 recordBatch
- 将 recordBatchs 封装成 ClientRequest
- 发送 ClientRequest
- poll
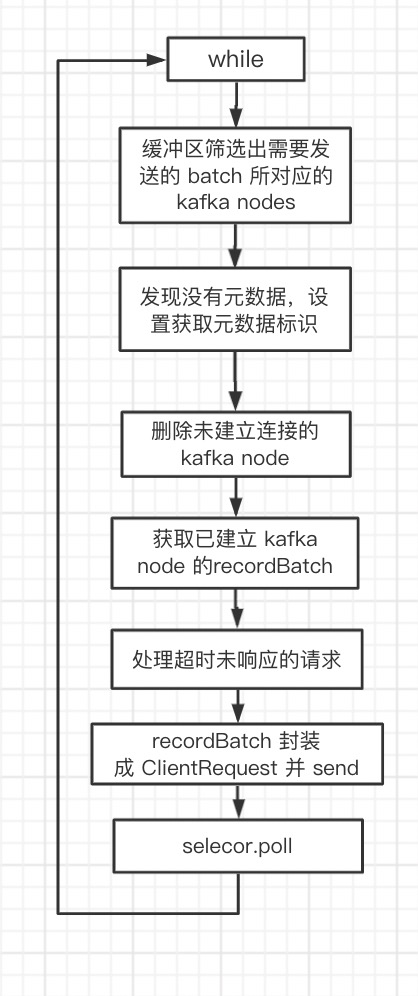
发起连接
程序刚运行的时候肯定是没有建立连接,当发现有 recordbatch 需要发送时会先判断是否已连接。
// this.client.ready(node, now)
// org.apache.kafka.clients.NetworkClient
public boolean ready(Node node, long now) {
if (node.isEmpty())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot connect to empty node " + node);
// entry
if (isReady(node, now))
return true;
// 未连接或失去连接,初始化
if (connectionStates.canConnect(node.idString(), now))
// selector.connect: OP_CONNECT
initiateConnect(node, now);
return false;
}
/**
* 检查是否可以向当前 kafka node 发送消息:
* 元数据包含当前 kafka node
* 与当前 kafka node connection 已建立
* 与当前 kafka node channel 已建立
* 发送 batch 请求数未超过指定的最大值(默认5)
*/
public boolean isReady(Node node, long now) {
// if we need to update our metadata now declare all requests unready to make metadata requests first
// priority
return !metadataUpdater.isUpdateDue(now) && canSendRequest(node.idString());
}
ClientRequest
要发送的 recordBatch 封装成 ClientRequest
// List<ClientRequest> requests = createProduceRequests(batches, now);
// org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.Sender
private List<ClientRequest> createProduceRequests(Map<Integer, List<RecordBatch>> collated, long now) {
List<ClientRequest> requests = new ArrayList<ClientRequest>(collated.size());
for (Map.Entry<Integer, List<RecordBatch>> entry : collated.entrySet())
// 创建请求:acks 非常重要,requestTimeout 默认 30s
// 将同个 node 上的多个 batch组装在一起
requests.add(produceRequest(now, entry.getKey(), acks, requestTimeout, entry.getValue()));
return requests;
}
private ClientRequest produceRequest(long now, int destination, short acks, int timeout, List<RecordBatch> batches) {
Map<TopicPartition, ByteBuffer> produceRecordsByPartition = new HashMap<TopicPartition, ByteBuffer>(batches.size());
final Map<TopicPartition, RecordBatch> recordsByPartition = new HashMap<TopicPartition, RecordBatch>(batches.size());
for (RecordBatch batch : batches) {
TopicPartition tp = batch.topicPartition;
produceRecordsByPartition.put(tp, batch.records.buffer());
recordsByPartition.put(tp, batch);
}
ProduceRequest request = new ProduceRequest(acks, timeout, produceRecordsByPartition);
// recordBatch 数据存到 RequestSend 数据结构
RequestSend send = new RequestSend(Integer.toString(destination),
// ApiKeys.PRODUCE 标识符,服务端会根据这个标识符处理
this.client.nextRequestHeader(ApiKeys.PRODUCE),
request.toStruct());
// 设置请求结束的回调函数,后续在响应会用到
RequestCompletionHandler callback = new RequestCompletionHandler() {
public void onComplete(ClientResponse response) {
handleProduceResponse(response, recordsByPartition, time.milliseconds());
}
};
return new ClientRequest(now, acks != 0, send, callback);
}
响应
// this.client.poll(pollTimeout, now);
// org.apache.kafka.clients.NetworkClient
public List<ClientResponse> poll(long timeout, long now) {
// 是否需要更新元数据
long metadataTimeout = metadataUpdater.maybeUpdate(now);
try {
// selector.poll,处理 OP_CONNECT、OP_WRITE、OP_READ 事件
// OP_READ 通过 nio read -> completedReceives
this.selector.poll(Utils.min(timeout, metadataTimeout, requestTimeoutMs));
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("Unexpected error during I/O", e);
}
// process completed actions
long updatedNow = this.time.milliseconds();
List<ClientResponse> responses = new ArrayList<>();
// 处理已发送的 send(recordBatch)
// responses.add(new ClientResponse(request, now, false, null));
handleCompletedSends(responses, updatedNow);
// 处理返回的响应
// responses.add(new ClientResponse(req, now, false, body));
handleCompletedReceives(responses, updatedNow);
handleDisconnections(responses, updatedNow);
handleConnections();
// 处理超时的请求
handleTimedOutRequests(responses, updatedNow);
// invoke callbacks
for (ClientResponse response : responses) {
if (response.request().hasCallback()) {
try {
// 回调请求的 callback,handleProduceResponse
response.request().callback().onComplete(response);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Uncaught error in request completion:", e);
}
}
}
return responses;
}
- 发送结束的响应
// org.apache.kafka.clients.NetworkClient
private void handleCompletedSends(List<ClientResponse> responses, long now) {
// completedSends.add(send); selector write 时加入
for (Send send : this.selector.completedSends()) {
ClientRequest request = this.inFlightRequests.lastSent(send.destination());
if (!request.expectResponse()) {
// ack = 0,才会构建 send 结束响应,这种方式不需要服务端返回结果
this.inFlightRequests.completeLastSent(send.destination());
// responseBody 为 null
responses.add(new ClientResponse(request, now, false, null));
}
}
}
- 服务端返回的响应
private void handleCompletedReceives(List<ClientResponse> responses, long now) {
for (NetworkReceive receive : this.selector.completedReceives()) {
String source = receive.source();
ClientRequest req = inFlightRequests.completeNext(source);
// receive 的二进制解析成可识别的数据
Struct body = parseResponse(receive.payload(), req.request().header());
if (!metadataUpdater.maybeHandleCompletedReceive(req, now, body))
// responseBody 有值
responses.add(new ClientResponse(req, now, false, body));
}
}
- 超时请求的响应
private void processDisconnection(List<ClientResponse> responses, String nodeId, long now) {
connectionStates.disconnected(nodeId, now);
for (ClientRequest request : this.inFlightRequests.clearAll(nodeId)) {
log.trace("Cancelled request {} due to node {} being disconnected", request, nodeId);
if (!metadataUpdater.maybeHandleDisconnection(request))
// responseBody 为 null 且 disconnected 为 true
responses.add(new ClientResponse(request, now, true, null));
}
}
- 处理响应
// org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.Sender
// 请求回调
private void handleProduceResponse(ClientResponse response, Map<TopicPartition, RecordBatch> batches, long now) {
// batches = 发送请求时携带的 recordBatch
// completeBatch
int correlationId = response.request().request().header().correlationId();
if (response.wasDisconnected()) {
// 失去连接
log.trace("Cancelled request {} due to node {} being disconnected", response, response.request()
.request()
.destination());
// Errors = Errors.NETWORK_EXCEPTION,
for (RecordBatch batch : batches.values())
completeBatch(batch, Errors.NETWORK_EXCEPTION, -1L, Record.NO_TIMESTAMP, correlationId, now);
} else {
log.trace("Received produce response from node {} with correlation id {}",
response.request().request().destination(),
correlationId);
if (response.hasResponse()) {
// ack != 0
ProduceResponse produceResponse = new ProduceResponse(response.responseBody());
for (Map.Entry<TopicPartition, ProduceResponse.PartitionResponse> entry : produceResponse.responses().entrySet()) {
// 每个 batch 处理
TopicPartition tp = entry.getKey();
ProduceResponse.PartitionResponse partResp = entry.getValue();
Errors error = Errors.forCode(partResp.errorCode);
RecordBatch batch = batches.get(tp);
completeBatch(batch, error, partResp.baseOffset, partResp.timestamp, correlationId, now);
}
this.sensors.recordLatency(response.request().request().destination(), response.requestLatencyMs());
this.sensors.recordThrottleTime(response.request().request().destination(),
produceResponse.getThrottleTime());
} else {
// ack = 0
for (RecordBatch batch : batches.values())
completeBatch(batch, Errors.NONE, -1L, Record.NO_TIMESTAMP, correlationId, now);
}
}
}
// recordBatch 处理
private void completeBatch(RecordBatch batch, Errors error, long baseOffset, long timestamp, long correlationId, long now) {
if (error != Errors.NONE && canRetry(batch, error)) { // 有异常且可以重新发送
// retry
log.warn("Got error produce response with correlation id {} on topic-partition {}, retrying ({} attempts left). Error: {}",
correlationId,
batch.topicPartition,
this.retries - batch.attempts - 1,
error);
// 重新加入 缓冲区
this.accumulator.reenqueue(batch, now);
} else {
// 无异常
// 有异常且不可以重新发送
RuntimeException exception;
if (error == Errors.TOPIC_AUTHORIZATION_FAILED)
exception = new TopicAuthorizationException(batch.topicPartition.topic());
else
exception = error.exception();
// record 回调函数
batch.done(baseOffset, timestamp, exception);
// recordBatch 发送结束,内存池回收该内存
this.accumulator.deallocate(batch);
...
}
// record 回调 producer.send(,callback)
public void done(long baseOffset, long timestamp, RuntimeException exception) {
// thunks = records
for (int i = 0; i < this.thunks.size(); i++) {
try {
Thunk thunk = this.thunks.get(i);
if (exception == null) {
// If the timestamp returned by server is NoTimestamp, that means CreateTime is used. Otherwise LogAppendTime is used.
RecordMetadata metadata = new RecordMetadata(this.topicPartition, baseOffset, thunk.future.relativeOffset(),
timestamp == Record.NO_TIMESTAMP ? thunk.future.timestamp() : timestamp,
thunk.future.checksum(),
thunk.future.serializedKeySize(),
thunk.future.serializedValueSize());
// 无异常时 record 回调函数
thunk.callback.onCompletion(metadata, null);
} else {
// 有异常时 record 回调函数
thunk.callback.onCompletion(null, exception);
}
}
}