前一节深入理解 Kafka 之 Producer介绍生产者的代码,本节介绍服务端的代码
网络
服务端的网络框架也是使用 NIO与生产者网络底层代码是复用,都是 org.apache.kafka.common.network.Selector。下面介绍时关于 NIO 方面会略过(详情查阅生产者的介绍),重点介绍网络结构
// kafka.Kafka.main, kafka 启动时调用
// kafka.server.KafkaServerStartable.startup
// kafka.server.KafkaServer
// request 和 respon channel 存储
// totalProcessorThreads 默认三个和 processer 线程数一致
// maxQueuedRequests 默认 500
val requestChannel = new RequestChannel(totalProcessorThreads, maxQueuedRequests)
// 启动流程,创建和启动很多组件
def startup() {
...
val canStartup = isStartingUp.compareAndSet(false, true)
if (canStartup) {
...
/* start scheduler */
kafkaScheduler.startup()
/* setup zookeeper */
// zk 相关
zkUtils = initZk()
/* Get or create cluster_id */
_clusterId = getOrGenerateClusterId(zkUtils)
info(s"Cluster ID = $clusterId")
notifyClusterListeners(kafkaMetricsReporters ++ reporters.asScala)
/* 数据读写清除管理 */
logManager = createLogManager(zkUtils.zkClient, brokerState)
logManager.startup()
/* generate brokerId */
config.brokerId = getBrokerId
this.logIdent = "[Kafka Server " + config.brokerId + "], "
metadataCache = new MetadataCache(config.brokerId)
// NIO 网络相关,接收请求、返回响应
socketServer = new SocketServer(config, metrics, kafkaMetricsTime)
socketServer.startup()
/* broker 管理 */
replicaManager = new ReplicaManager(config, metrics, time, kafkaMetricsTime, zkUtils, kafkaScheduler, logManager,
isShuttingDown, quotaManagers.follower)
replicaManager.startup()
/* start kafka controller */
kafkaController = new KafkaController(config, zkUtils, brokerState, kafkaMetricsTime, metrics, threadNamePrefix)
kafkaController.startup()
adminManager = new AdminManager(config, metrics, metadataCache, zkUtils)
/* start group coordinator */
groupCoordinator = GroupCoordinator(config, zkUtils, replicaManager, kafkaMetricsTime)
groupCoordinator.startup()
/* Get the authorizer and initialize it if one is specified.*/
authorizer = Option(config.authorizerClassName).filter(_.nonEmpty).map { authorizerClassName =>
val authZ = CoreUtils.createObject[Authorizer](authorizerClassName)
authZ.configure(config.originals())
authZ
}
/* 请求处理转发中心 */
apis = new KafkaApis(socketServer.requestChannel, replicaManager, adminManager, groupCoordinator,
kafkaController, zkUtils, config.brokerId, config, metadataCache, metrics, authorizer, quotaManagers, clusterId)
requestHandlerPool = new KafkaRequestHandlerPool(config.brokerId, socketServer.requestChannel, apis, config.numIoThreads)
Mx4jLoader.maybeLoad()
/* start dynamic config manager */
dynamicConfigHandlers = Map[String, ConfigHandler](ConfigType.Topic -> new TopicConfigHandler(logManager, config, quotaManagers),
ConfigType.Client -> new ClientIdConfigHandler(quotaManagers),
ConfigType.User -> new UserConfigHandler(quotaManagers),
ConfigType.Broker -> new BrokerConfigHandler(config, quotaManagers))
// Create the config manager. start listening to notifications
dynamicConfigManager = new DynamicConfigManager(zkUtils, dynamicConfigHandlers)
dynamicConfigManager.startup()
/* tell everyone we are alive */
val listeners = config.advertisedListeners.map {case(protocol, endpoint) =>
if (endpoint.port == 0)
(protocol, EndPoint(endpoint.host, socketServer.boundPort(protocol), endpoint.protocolType))
else
(protocol, endpoint)
}
kafkaHealthcheck = new KafkaHealthcheck(config.brokerId, listeners, zkUtils, config.rack,
config.interBrokerProtocolVersion)
kafkaHealthcheck.startup()
// Now that the broker id is successfully registered via KafkaHealthcheck, checkpoint it
checkpointBrokerId(config.brokerId)
/* register broker metrics */
registerStats()
brokerState.newState(RunningAsBroker)
shutdownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1)
startupComplete.set(true)
isStartingUp.set(false)
AppInfoParser.registerAppInfo(jmxPrefix, config.brokerId.toString)
info("started")
}
}
- SocketServer:接受网络请求
- KafkaRequestHandlerPool:处理 processer 读取数据封装好的 request 并返回 respon
- LogManager:数据管理
- log
- segment
- log
- KafkaApis:请求处理统一管理
- ReplicaManager:broker 节点管理
Accept
// socketServer = new SocketServer(config, metrics, kafkaMetricsTime)
// socketServer.startup()
// kafka.network.SocketServer
def startup() {
this.synchronized {
...
var processorBeginIndex = 0
// endpoints = server.properties 设置的 hostname:9092
endpoints.values.foreach { endpoint =>
val protocol = endpoint.protocolType
// numProcessorThreads 默认3,创建接收 read 事件的线程数
val processorEndIndex = processorBeginIndex + numProcessorThreads
for (i <- processorBeginIndex until processorEndIndex)
// 创建 read 事件的线程数,下面介绍 processors创建和功能
// 请求由 Acceptor 建立连接,连接后分发到 processors 来处理后续 read
processors(i) = newProcessor(i, connectionQuotas, protocol)
// 新建 Acceptor 线程,负责整个服务端 accept 请求
val acceptor = new Acceptor(endpoint, sendBufferSize, recvBufferSize, brokerId,
processors.slice(processorBeginIndex, processorEndIndex), connectionQuotas)
acceptors.put(endpoint, acceptor)
// 启动 acceptor
Utils.newThread("kafka-socket-acceptor-%s-%d".format(protocol.toString, endpoint.port), acceptor, false).start()
// 线程同步,等待 acceptor 线程启动
acceptor.awaitStartup()
...
}
// kafka.network.Acceptor
private[kafka] class Acceptor{
// nio 服务端 selector
private val nioSelector = NSelector.open()
// nio 服务端 channel
val serverChannel = openServerSocket(endPoint.host, endPoint.port)
this.synchronized {
// 启动处理 read 事件的 process 线程,默认三个
processors.foreach { processor =>
Utils.newThread("kafka-network-thread-%d-%s-%d".format(brokerId, endPoint.protocolType.toString, processor.id), processor, false).start()
}
}
def run() {
// 注册 OP_ACCEPT,表示只处理 ACCEPT
serverChannel.register(nioSelector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)
startupComplete()
try {
var currentProcessor = 0
// 死循环
while (isRunning) {
try {
val ready = nioSelector.select(500)
if (ready > 0) {
// 有 ACCEPT 事件
val keys = nioSelector.selectedKeys()
val iter = keys.iterator()
while (iter.hasNext && isRunning) {
try {
val key = iter.next
iter.remove()
if (key.isAcceptable)
// 处理 ACCEPT 事件
// processors = Array[Processor]
// 此处表示选择 currentProcessor 序号的Processor 来处理channel后续事件
accept(key, processors(currentProcessor))
else
throw new IllegalStateException("Unrecognized key state for acceptor thread.")
// 轮训将 channel 发送到 processors 线程中
currentProcessor = (currentProcessor + 1) % processors.length
...
}
SocketServer 启动时创建 Acceptor,Acceptor 作为 NIO server 端只接收 OP_ACCEPT 事件。
SocketServer 启动时创建 Processor 线程组,Acceptor 启动时也启动 Processor 线程组中的每一个线程。
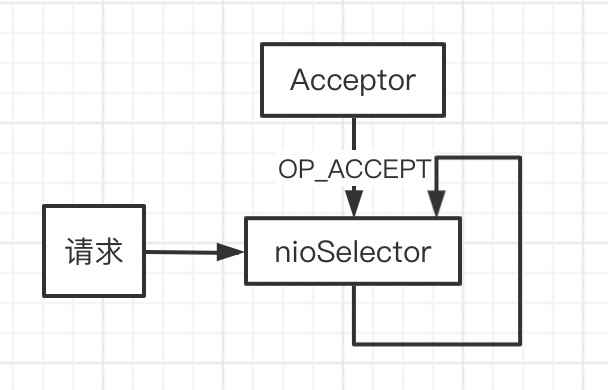
processors
// accept(key, processors(currentProcessor))
// kafka.network.Acceptor
// 处理 accept 事件
def accept(key: SelectionKey, processor: Processor) {
val serverSocketChannel = key.channel().asInstanceOf[ServerSocketChannel]
val socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept()
try {
connectionQuotas.inc(socketChannel.socket().getInetAddress)
// 服务端 channel 设置非阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false)
socketChannel.socket().setTcpNoDelay(true)
socketChannel.socket().setKeepAlive(true)
if (sendBufferSize != Selectable.USE_DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE)
socketChannel.socket().setSendBufferSize(sendBufferSize)
// channel 交给 processor 线程处理
// 此处的 processor 根据 index 每次轮训
processor.accept(socketChannel)
}
}
Acceptor 处理 accept 事件获取到 channel,此 channel 后续操作交由 processor 线程处理。
// processors(i) = newProcessor(i, connectionQuotas, protocol)
// kafka.network.SocketServer
protected[network] def newProcessor(id: Int, connectionQuotas: ConnectionQuotas, protocol: SecurityProtocol): Processor = {
new Processor(id,
time,
config.socketRequestMaxBytes,
requestChannel,
connectionQuotas,
config.connectionsMaxIdleMs,
protocol,
config.values,
metrics
)
}
// kafka.network.Processor
// Processor 处理某个连接的所有请求,默认有3个线程,每个线程都有单独的 selector
private[kafka] class Processor{
// 存储请求
private val newConnections = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue[SocketChannel]()
// 创建 selector
private val selector = new KSelector()
def accept(socketChannel: SocketChannel) {
// 添加新的 channel
newConnections.add(socketChannel)
wakeup()
}
override def run() {
startupComplete()
while (isRunning) {
try {
// 新的 channel 注册到 selector
configureNewConnections()
// 处理响应,写事件;requestHandler 写入 respon
processNewResponses()
// 获取事件并处理;与生产者代码相同,不展开了
poll()
// 处理 接收完成 事件
processCompletedReceives()
// 处理 发送完成 事件
processCompletedSends()
// 处理 连接断开 事件
processDisconnected()
}
// 新的 channel 注册到 selector
private def configureNewConnections() {
while (!newConnections.isEmpty) {
val channel = newConnections.poll()
try {
debug(s"Processor $id listening to new connection from ${channel.socket.getRemoteSocketAddress}")
val localHost = channel.socket().getLocalAddress.getHostAddress
val localPort = channel.socket().getLocalPort
val remoteHost = channel.socket().getInetAddress.getHostAddress
val remotePort = channel.socket().getPort
val connectionId = ConnectionId(localHost, localPort, remoteHost, remotePort).toString
// channel 注册到 selector 并添加 OP_READ 事件
selector.register(connectionId, channel)
...
}
}
到此为止,我们了解的流程:
Acceptor处理accept事件,得到新的连接 channel;- 新的 channel 通过轮训的方式发送到某个 Processor 线程
- Processor 线程得到新的 channel ,将其添加到
selector并注册OP_READ
接下来我们继续研究 Processor 如何处理 OP_READ
// kafka.network.Processor
poll() // 读取 OP_READ 事件的数据得到 receive(不展开,有兴趣看上节生产者代码)
/**
* 接收读取完毕后的处理
*/
private def processCompletedReceives() {
selector.completedReceives.asScala.foreach { receive =>
try {
val channel = selector.channel(receive.source)
val session = RequestChannel.Session(new KafkaPrincipal(KafkaPrincipal.USER_TYPE, channel.principal.getName),
channel.socketAddress)
val req = RequestChannel.Request(processor = id, connectionId = receive.source, session = session, buffer = receive.payload, startTimeMs = time.milliseconds, securityProtocol = protocol)
// 读取到的 receive 封装成 Request 添加到 requestChannel
requestChannel.sendRequest(req)
// 接收读取完毕后,当前 channel 移除在 selector 上注册的 OP_READ 事件
selector.mute(receive.source)
}
...
}
Processor 流程到先到这里,它处理 channel 的 read 事件读取数据,并将数据封装成 Request 添加到 requestChannel
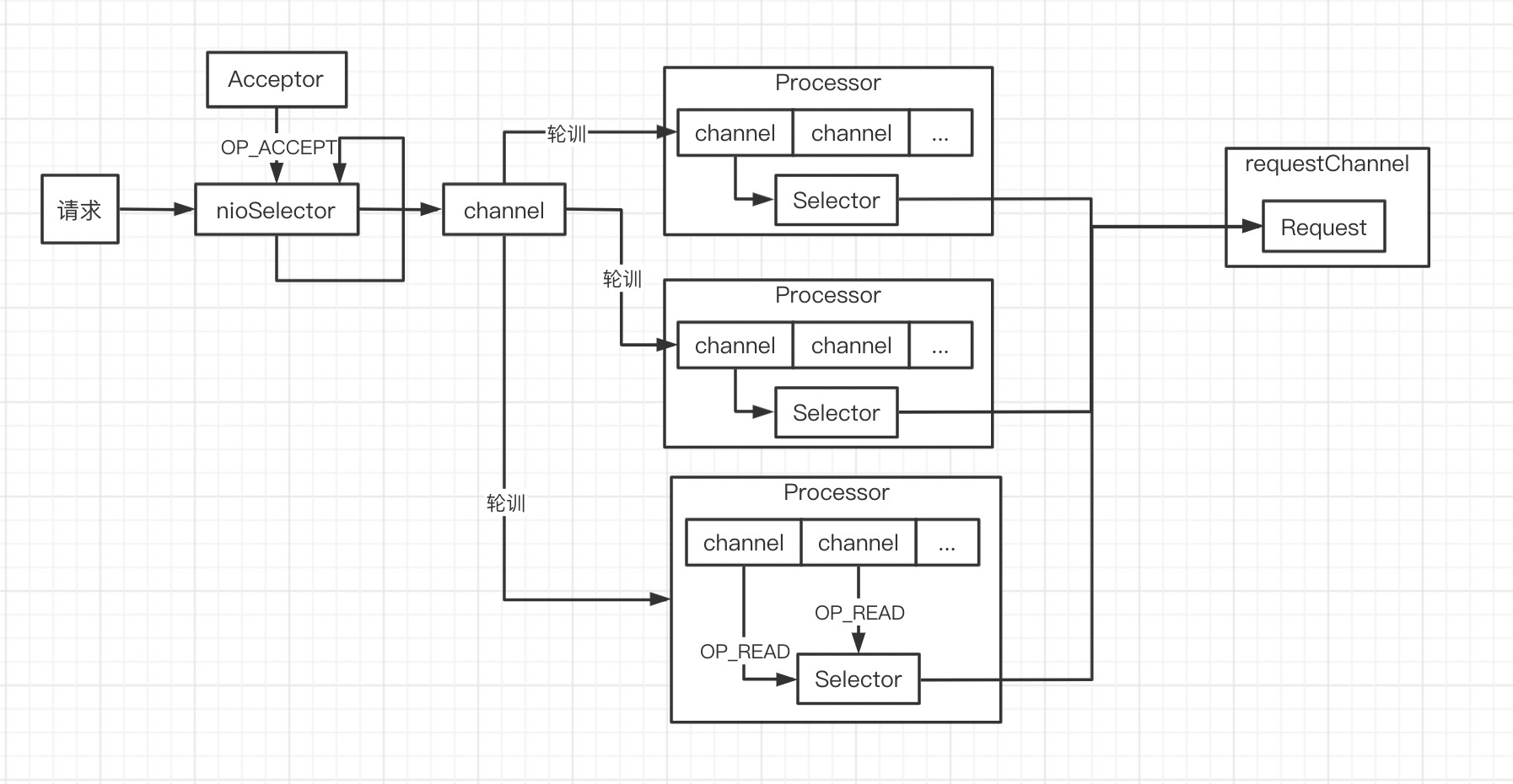
RequestChannel
// val requestChannel = new RequestChannel(totalProcessorThreads, maxQueuedRequests)
// kafka.network.RequestChannel
class RequestChannel(val numProcessors: Int, val queueSize: Int){
private var responseListeners: List[(Int) => Unit] = Nil
// processer 线程读取到数据封装 request 添加到此队列
private val requestQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue[RequestChannel.Request](queueSize)
// 与 processer 线程数相同的 响应队列,write data
private val responseQueues = new Array[BlockingQueue[RequestChannel.Response]](numProcessors)
// 创建 responseQueues
for(i <- 0 until numProcessors)
responseQueues(i) = new LinkedBlockingQueue[RequestChannel.Response]()
// requestChannel.sendRequest(req)
// requestQueue 线程安全,但会阻塞
// 当 requestQueue 没有空间时(默认500),阻塞直到有空间
def sendRequest(request: RequestChannel.Request) {
requestQueue.put(request)
}
}
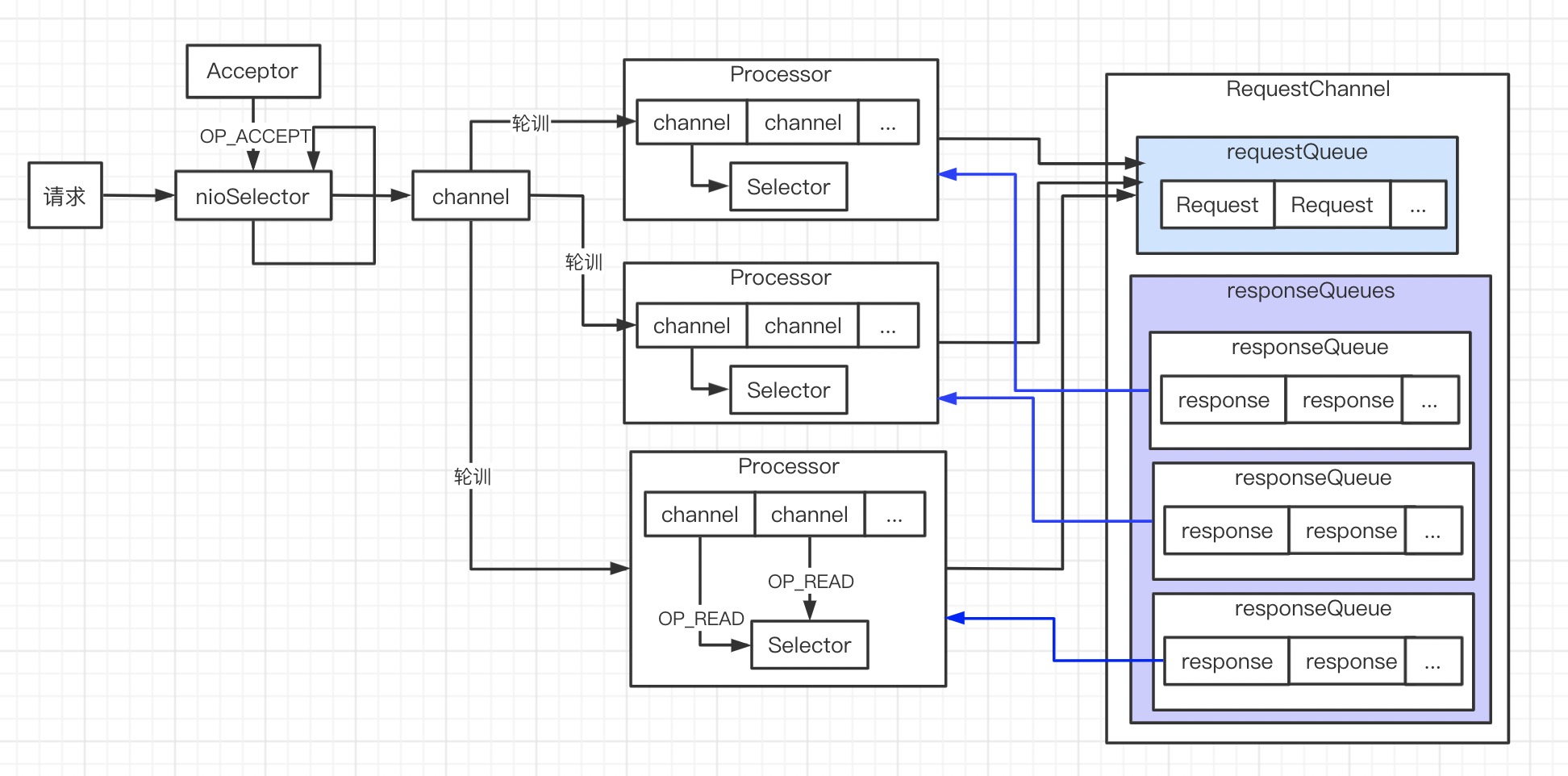
KafkaRequestHandlerPool
// requestHandlerPool = new KafkaRequestHandlerPool(config.brokerId, socketServer.requestChannel, apis, config.numIoThreads)
// kafka.server.KafkaRequestHandlerPool
class KafkaRequestHandlerPool{
// numThreads 线程数默认8个
val threads = new Array[Thread](numThreads)
val runnables = new Array[KafkaRequestHandler](numThreads)
for(i <- 0 until numThreads) {
// 默认启动8个线程
runnables(i) = new KafkaRequestHandler(i, brokerId, aggregateIdleMeter, numThreads, requestChannel, apis)
threads(i) = Utils.daemonThread("kafka-request-handler-" + i, runnables(i))
threads(i).start()
}
// kafka.server.KafkaRequestHandler
// 处理 requestQueue
class KafkaRequestHandler{
this.logIdent = "[Kafka Request Handler " + id + " on Broker " + brokerId + "], "
def run() {
while(true) {
try {
var req : RequestChannel.Request = null
// 死循环直到从 requestChannel 获取到 request
while (req == null) {
// We use a single meter for aggregate idle percentage for the thread pool.
// Since meter is calculated as total_recorded_value / time_window and
// time_window is independent of the number of threads, each recorded idle
// time should be discounted by # threads.
val startSelectTime = SystemTime.nanoseconds
// 若 requestChannel 没有 request 会 block
req = requestChannel.receiveRequest(300)
val idleTime = SystemTime.nanoseconds - startSelectTime
aggregateIdleMeter.mark(idleTime / totalHandlerThreads)
}
if(req eq RequestChannel.AllDone) {
debug("Kafka request handler %d on broker %d received shut down command".format(
id, brokerId))
return
}
req.requestDequeueTimeMs = SystemTime.milliseconds
trace("Kafka request handler %d on broker %d handling request %s".format(id, brokerId, req))
// handle and respon
apis.handle(req)
...
}
requestHandlerPool 默认创建8个线程从 requestChannel 获取 request ,最终由 apis 处理并返回 respon。
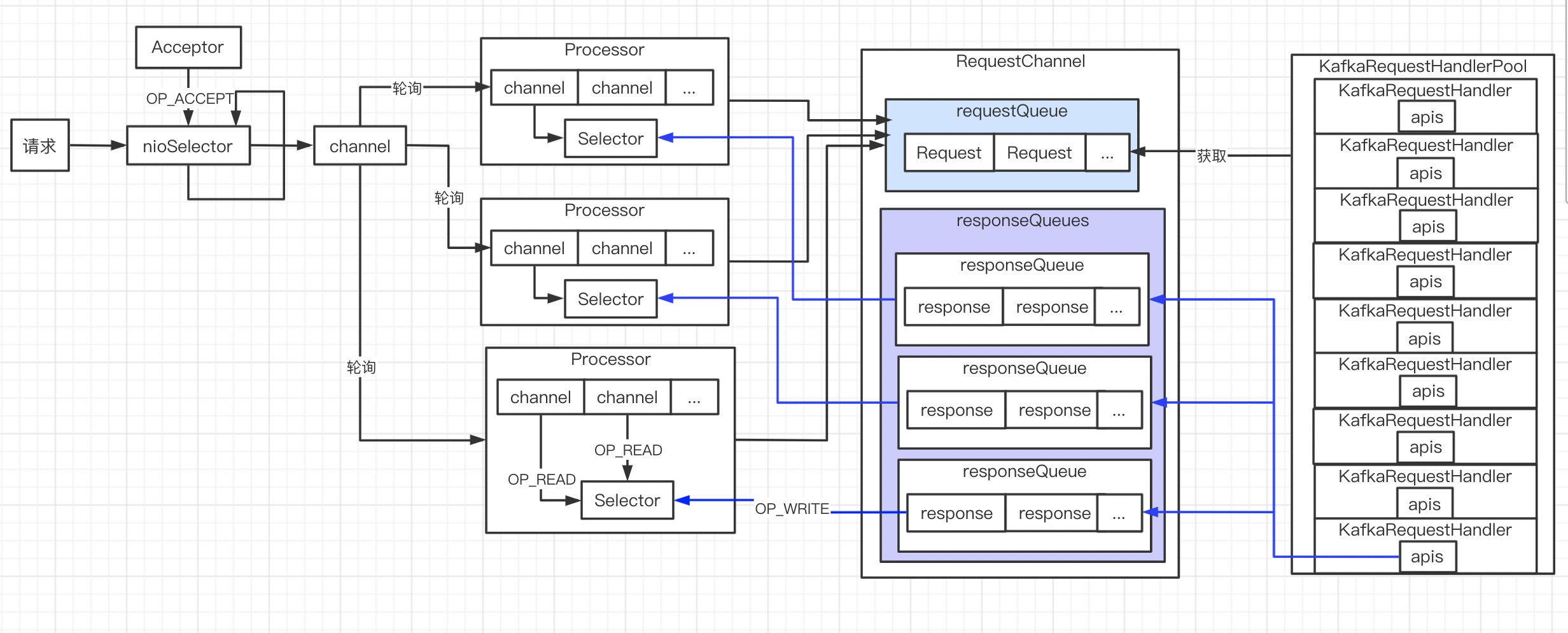
到此,网络相关的脉络都清晰了
- Acceptor 线程处理 connect 请求
- Processor 处理 channel 的read ,并封装成 request 放到
RequestChannel消息队列 - KafkaRequestHandler 从
RequestChannel消息队列获取 request,并将 respon 放入 responseQueues - Processor 从 responseQueues 获取响应,返回给客户端。
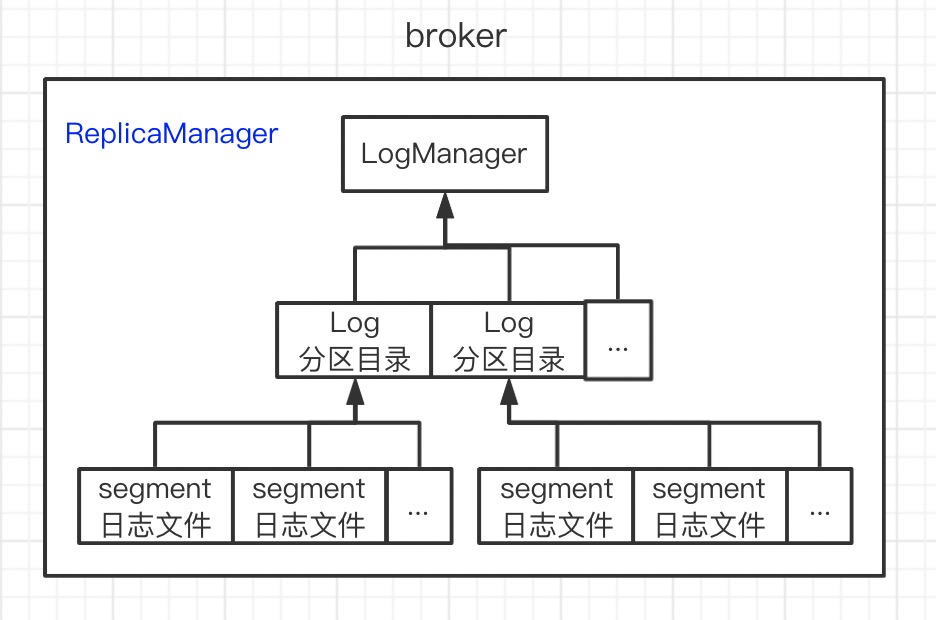
Log
kafka 中的一条数据称为 log,以 topic 概念组织起来。但 topic 只是个逻辑概念,topic 下的分区才是真实存在的。分区是磁盘上真实存在的目录,目录下包括很多的日志文件,每个日志文件就是一个 segment。
kafka 是一个集群,每个 broker 中的log 由 ReplicaManager 控制:读、写、副本同步。
logManager
// logManager.startup()
// kafka.log.LogManager
class LogManager{
val InitialTaskDelayMs = 30*1000
// 每个分区对应一个 log 对象,log 对象操纵数据
private val logs = new Pool[TopicAndPartition, Log]()
// logDirs 是 kafka 配置文件中的 data 目录
// 校验保存数据的目录是否有效
createAndValidateLogDirs(logDirs)
// 加载log(每个分区目录独有)
loadLogs()
private def loadLogs(): Unit = {
...
for (dir <- this.logDirs) {
// ioThreads 默认1
val pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(ioThreads)
threadPools.append(pool)
...
var recoveryPoints = Map[TopicAndPartition, Long]()
try {
// 重读 recovery-point-offset-checkpoint 文件 恢复
recoveryPoints = this.recoveryPointCheckpoints(dir).read
}
...
val jobsForDir = for {
// dirContent = 数据目录下的所有文件
dirContent <- Option(dir.listFiles).toList
// logDir = 分区目录
logDir <- dirContent if logDir.isDirectory
} yield {
CoreUtils.runnable {
debug("Loading log '" + logDir.getName + "'")
// 从目录名称解析出分区名 xx-2 表示 xx topic 2分区
val topicPartition = Log.parseTopicPartitionName(logDir)
val config = topicConfigs.getOrElse(topicPartition.topic, defaultConfig)
val logRecoveryPoint = recoveryPoints.getOrElse(topicPartition, 0L)
// 重新构建 log 对象
val current = new Log(logDir, config, logRecoveryPoint, scheduler, time)
// 保存log 对象
val previous = this.logs.put(topicPartition, current)
...
}
// kafka.log.Log
class Log{
// 目录下每组文件称为 segment(数据+索引),一个log 包含很多 segment
// map 结构<segment baseoffset, segment>
private val segments: ConcurrentNavigableMap[java.lang.Long, LogSegment] = new ConcurrentSkipListMap[java.lang.Long, LogSegment]
// 加载 segment
loadSegments() = {
...
// 数据文件中重新构建 segment
val segment = new LogSegment(dir = dir,
startOffset = start,
indexIntervalBytes = config.indexInterval,
maxIndexSize = config.maxIndexSize,
rollJitterMs = config.randomSegmentJitter,
time = time,
fileAlreadyExists = true)
...
}
}
// kafka.log.LogManager
// 主要是清理数据线程
def startup() {
/* Schedule the cleanup task to delete old logs */
if(scheduler != null) {
// cleanupLogs 清理过期数据,5分钟清理一次
// 筛选出过期 segment 后异步删除
info("Starting log cleanup with a period of %d ms.".format(retentionCheckMs))
scheduler.schedule("kafka-log-retention",
cleanupLogs,
delay = InitialTaskDelayMs,
period = retentionCheckMs,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
info("Starting log flusher with a default period of %d ms.".format(flushCheckMs))
// flushDirtyLogs 默认不刷磁盘,由操纵系统 page cache 自动刷
scheduler.schedule("kafka-log-flusher",
flushDirtyLogs,
delay = InitialTaskDelayMs,
period = flushCheckMs,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
// 恢复
scheduler.schedule("kafka-recovery-point-checkpoint",
checkpointRecoveryPointOffsets,
delay = InitialTaskDelayMs,
period = flushCheckpointMs,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
}
}
LogManager 启动时扫描每个数据路径下分区目录,每个分区构建出 log 对象;构建 log 对象时,扫描每个分区下的数据文件构建 segment。 三者之间的关系加上 ReplicaManager 如下所示
log
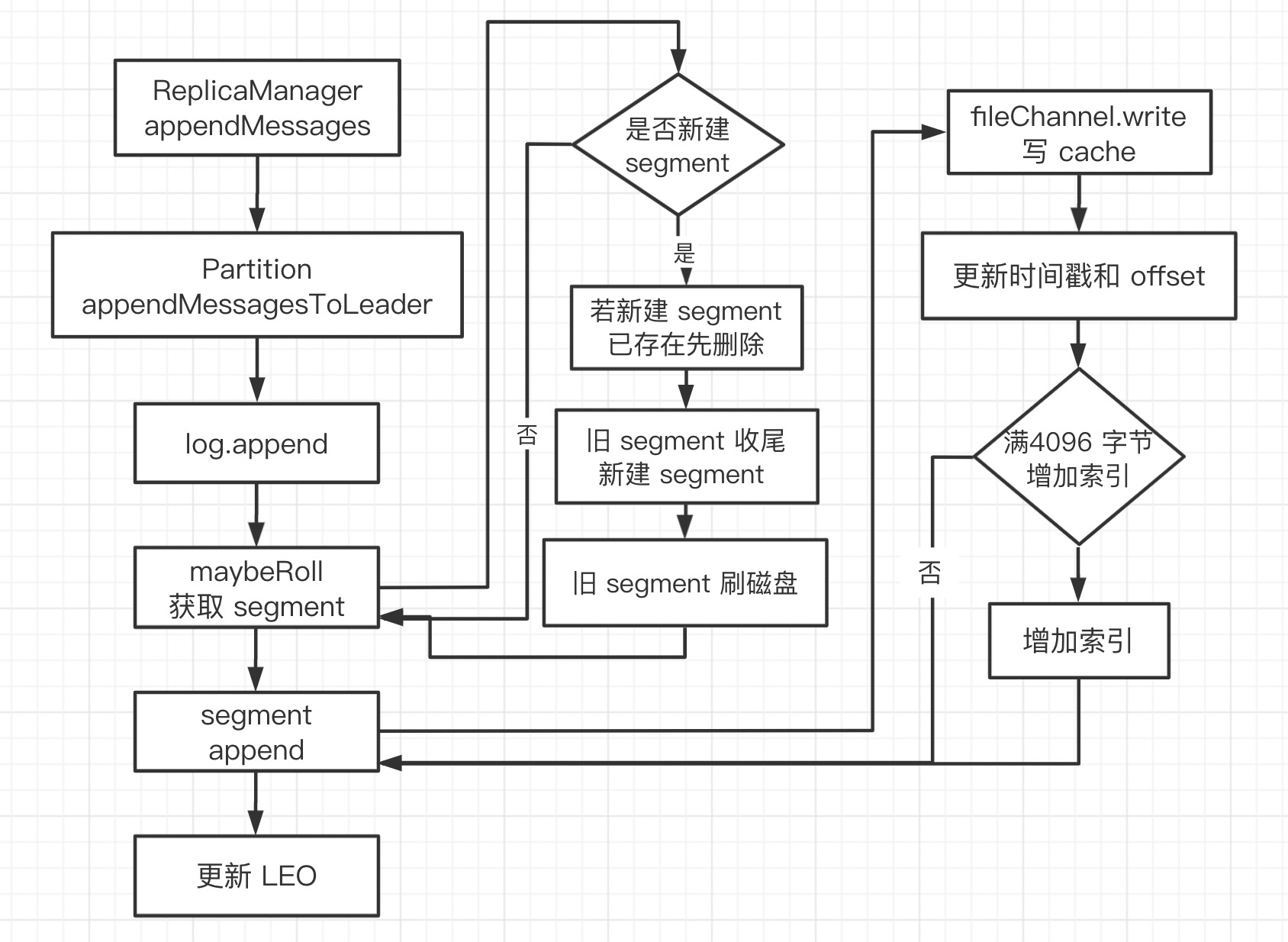
Log 负责 record append 操作。我们把思绪往前拉:KafkaRequestHandler 从 RequestChannel 获取 request 并交给 apis 处理。
// apis.handle(req)
// 生产者发送请求时:KafkaApis.handleProducerRequest
// replicaManager.appendMessages
// -> partition.appendMessagesToLeader
// -> log.append
// -> segment.append
由以上流程可知层级关系:
- replicaManager 管理整个 broker 上所有的 partition
- partition:分区的数据结构
- log
- segment:
// kafka.log.Log
def append(messages: ByteBufferMessageSet, assignOffsets: Boolean = true): LogAppendInfo = {
val appendInfo = analyzeAndValidateMessageSet(messages)
...
try {
// they are valid, insert them in the log
// 锁
lock synchronized {
if (assignOffsets) {
// assign offsets to the message set
// 获取当前offset
val offset = new LongRef(nextOffsetMetadata.messageOffset)
appendInfo.firstOffset = offset.value
val now = time.milliseconds
val validateAndOffsetAssignResult = try {
validMessages.validateMessagesAndAssignOffsets(offset,
now,
appendInfo.sourceCodec,
appendInfo.targetCodec,
config.compact,
config.messageFormatVersion.messageFormatVersion,
config.messageTimestampType,
config.messageTimestampDifferenceMaxMs)
} catch {
case e: IOException => throw new KafkaException("Error in validating messages while appending to log '%s'".format(name), e)
}
validMessages = validateAndOffsetAssignResult.validatedMessages
appendInfo.maxTimestamp = validateAndOffsetAssignResult.maxTimestamp
appendInfo.offsetOfMaxTimestamp = validateAndOffsetAssignResult.offsetOfMaxTimestamp
appendInfo.lastOffset = offset.value - 1
...
// check messages set size may be exceed config.segmentSize
if (validMessages.sizeInBytes > config.segmentSize) {
throw new RecordBatchTooLargeException("Message set size is %d bytes which exceeds the maximum configured segment size of %d."
.format(validMessages.sizeInBytes, config.segmentSize))
}
// maybe roll the log if this segment is full
// 获取 segment:已存在/新建
val segment = maybeRoll(messagesSize = validMessages.sizeInBytes,
maxTimestampInMessages = appendInfo.maxTimestamp)
// now append to the log
// segment append
segment.append(firstOffset = appendInfo.firstOffset, largestTimestamp = appendInfo.maxTimestamp,
offsetOfLargestTimestamp = appendInfo.offsetOfMaxTimestamp, messages = validMessages)
// increment the log end offset
// msg添加成功,增加当前 log(分区) 的offset
// 即更新 LEO
updateLogEndOffset(appendInfo.lastOffset + 1)
...
//
private def maybeRoll(messagesSize: Int, maxTimestampInMessages: Long): LogSegment = {
val segment = activeSegment
val now = time.milliseconds
val reachedRollMs = segment.timeWaitedForRoll(now, maxTimestampInMessages) > config.segmentMs - segment.rollJitterMs
if (segment.size > config.segmentSize - messagesSize ||
(segment.size > 0 && reachedRollMs) ||
segment.index.isFull || segment.timeIndex.isFull) {
// 当前 segmentsize + msgsize > 设定 segment大小(默认1G),新建
// 间隔多长时间新建 segment 默认不启用
// 索引文件超过阈值,一般不会发送,因为数据文件会先超
debug(s"Rolling new log segment in $name (log_size = ${segment.size}/${config.segmentSize}}, " +
s"index_size = ${segment.index.entries}/${segment.index.maxEntries}, " +
s"time_index_size = ${segment.timeIndex.entries}/${segment.timeIndex.maxEntries}, " +
s"inactive_time_ms = ${segment.timeWaitedForRoll(now, maxTimestampInMessages)}/${config.segmentMs - segment.rollJitterMs}).")
roll()
} else {
// 返回已有的 segment
segment
}
}
// 新建 segment
def roll(): LogSegment = {
val start = time.nanoseconds
lock synchronized {
val newOffset = logEndOffset
val logFile = logFilename(dir, newOffset)
val indexFile = indexFilename(dir, newOffset)
val timeIndexFile = timeIndexFilename(dir, newOffset)
// 若新建 segment 的文件已存在,则先删除
for(file <- List(logFile, indexFile, timeIndexFile); if file.exists) {
warn("Newly rolled segment file " + file.getName + " already exists; deleting it first")
file.delete()
}
// 之前的 segment 做收尾工作,准备刷磁盘
segments.lastEntry() match {
case null =>
case entry => {
val seg = entry.getValue
seg.onBecomeInactiveSegment()
seg.index.trimToValidSize()
seg.timeIndex.trimToValidSize()
seg.log.trim()
}
}
val segment = new LogSegment(dir,
startOffset = newOffset,
indexIntervalBytes = config.indexInterval,
maxIndexSize = config.maxIndexSize,
rollJitterMs = config.randomSegmentJitter,
time = time,
fileAlreadyExists = false,
initFileSize = initFileSize,
preallocate = config.preallocate)
// 添加 segment
val prev = addSegment(segment)
if(prev != null)
throw new KafkaException("Trying to roll a new log segment for topic partition %s with start offset %d while it already exists.".format(name, newOffset))
// We need to update the segment base offset and append position data of the metadata when log rolls.
// The next offset should not change.
updateLogEndOffset(nextOffsetMetadata.messageOffset)
// 新建一个 segment时,前一个segment 会异步刷磁盘
// kafka 专门定时刷磁盘的线程,但默认不开启
// 索引文件刷磁盘只会在这里触发
// log 文件写 fileChannel 后,由操纵系统触发刷写/在这里触发
scheduler.schedule("flush-log", () => flush(newOffset), delay = 0L)
info("Rolled new log segment for '" + name + "' in %.0f ms.".format((System.nanoTime - start) / (1000.0*1000.0)))
segment
}
}
LogSegment
// kafka.log.LogSegment
// log 片段,每个片段包含两部分:log 和 索引
def append(firstOffset: Long, largestTimestamp: Long, offsetOfLargestTimestamp: Long, messages: ByteBufferMessageSet) {
if (messages.sizeInBytes > 0) {
trace("Inserting %d bytes at offset %d at position %d with largest timestamp %d at offset %d"
.format(messages.sizeInBytes, firstOffset, log.sizeInBytes(), largestTimestamp, offsetOfLargestTimestamp))
val physicalPosition = log.sizeInBytes()
if (physicalPosition == 0)
rollingBasedTimestamp = Some(largestTimestamp)
// msg 刷到磁盘(内存)
log.append(messages)
// Update the in memory max timestamp and corresponding offset.
// 更新 time 和 offset
if (largestTimestamp > maxTimestampSoFar) {
maxTimestampSoFar = largestTimestamp
offsetOfMaxTimestamp = offsetOfLargestTimestamp
}
// append an entry to the index (if needed)
// 更新索引,log 增加 4096 字节,增加一条索引
if(bytesSinceLastIndexEntry > indexIntervalBytes) {
// 增加索引
// physicalPosition = msg 在文件中的 offset
index.append(firstOffset, physicalPosition)
timeIndex.maybeAppend(maxTimestampSoFar, offsetOfMaxTimestamp)
bytesSinceLastIndexEntry = 0
}
// 记录 log 增加了多少字节
bytesSinceLastIndexEntry += messages.sizeInBytes
}
}
// kafka.log.FileMessageSet
def append(messages: ByteBufferMessageSet) {
val written = messages.writeFullyTo(channel)
_size.getAndAdd(written)
}
// kafka.message.ByteBufferMessageSet
// fileChannel 写 msg;os page cache
def writeFullyTo(channel: GatheringByteChannel): Int = {
buffer.mark()
var written = 0
while (written < sizeInBytes)
// 写
written += channel.write(buffer)
buffer.reset()
written
}
副本
kafka 支持多副本,在源码中 broker 也称为 ReplicaManager。分区的 follower 节点 从 leader 节点拉取数据流程如下图所示
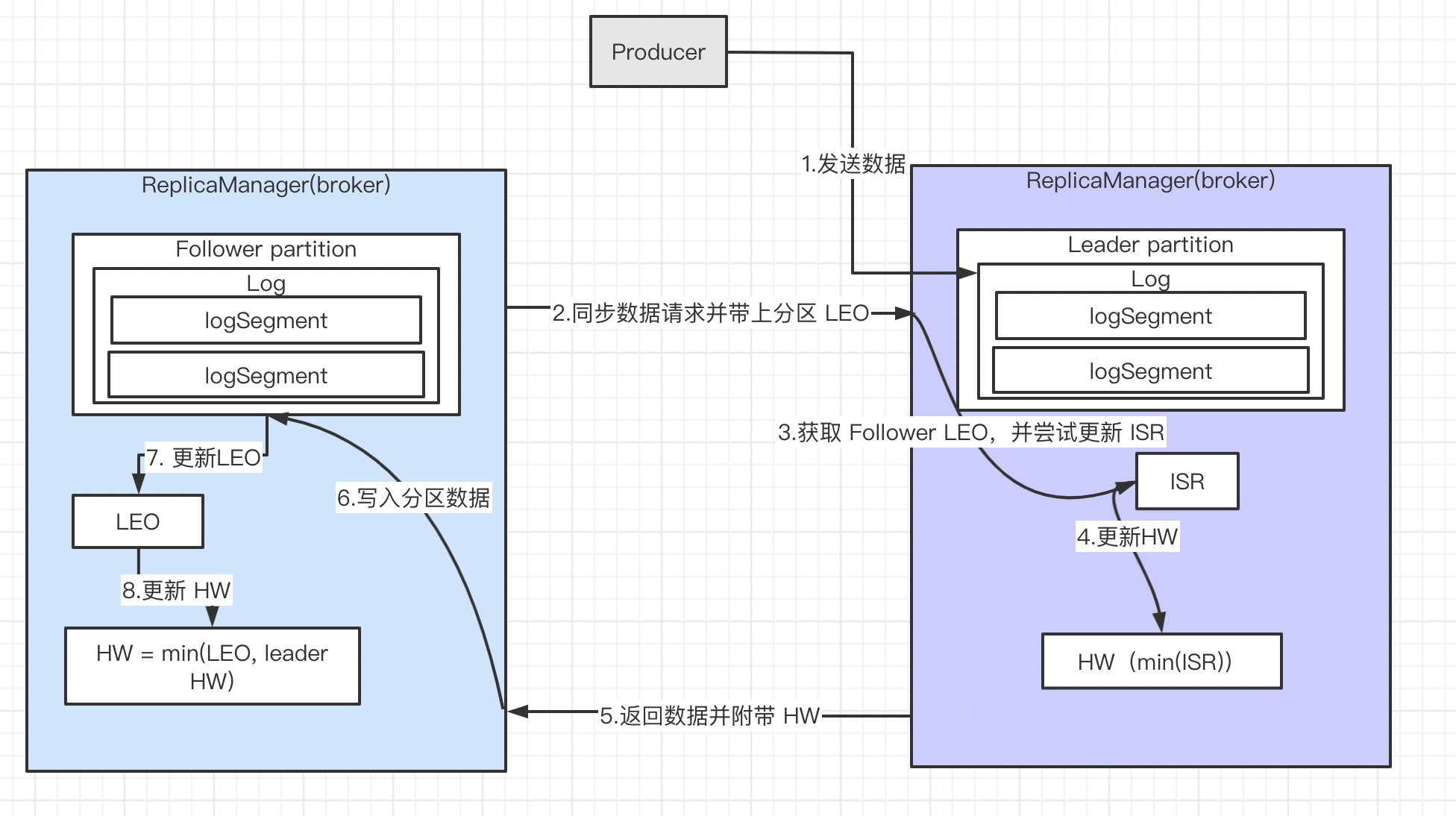
leader partition 接收 producer 数据写入 logsegment 并更新 LEO 的流程,这里不介绍了,是上一节 log 的写入流程。 从 follower partiton 如何发起 数据同步开始
ReplicaFetcherManager
// kafka.server.ReplicaManager
val replicaFetcherManager = new ReplicaFetcherManager(config, this, metrics, jTime, threadNamePrefix, quotaManager)
// ReplicaManager 发现有分区是 Follower 角色时,
// 会将当前分区添加到 ReplicaFetcherManager,等待从 Leader 分区拉取数据
replicaFetcherManager.addFetcherForPartitions(partitionsToMakeFollowerWithLeaderAndOffset)
// kafka.server.AbstractFetcherManager
// 从其他 broker 拉取数据线程数,默认一个 broker 一个线程(num.replica.fetchers)
// 若一个 broker 有好几个 leader partition,此线程一起拉
// 此处可知,kafka 集群节点不宜太多,不然线程太大
private val fetcherThreadMap = new mutable.HashMap[BrokerAndFetcherId, AbstractFetcherThread]
def addFetcherForPartitions(partitionAndOffsets: Map[TopicPartition, BrokerAndInitialOffset]) {
mapLock synchronized {
// 由于num.replica.fetchers 默认为1,此处表示按 broker 分组
val partitionsPerFetcher = partitionAndOffsets.groupBy{ case(topicAndPartition, brokerAndInitialOffset) =>
BrokerAndFetcherId(brokerAndInitialOffset.broker, getFetcherId(topicAndPartition.topic, topicAndPartition.partition))}
// brokerAndFetcherId = broker + (拉取数据的topic 分区序列号)
for ((brokerAndFetcherId, partitionAndOffsets) <- partitionsPerFetcher) {
var fetcherThread: AbstractFetcherThread = null
fetcherThreadMap.get(brokerAndFetcherId) match {
// broker 已存在拉取数据线程,直接复用
case Some(f) => fetcherThread = f
case None =>
// 若不存在新建拉取数据线程
fetcherThread = createFetcherThread(brokerAndFetcherId.fetcherId, brokerAndFetcherId.broker)
fetcherThreadMap.put(brokerAndFetcherId, fetcherThread)
// 启动 dowork
fetcherThread.start
}
// 添加要拉取的分区,并带上自身 LEO
fetcherThreadMap(brokerAndFetcherId).addPartitions(partitionAndOffsets.map { case (tp, brokerAndInitOffset) =>
tp -> brokerAndInitOffset.initOffset
...
// 新建拉取数据线程
override def createFetcherThread(fetcherId: Int, sourceBroker: BrokerEndPoint): AbstractFetcherThread = {
val threadName = threadNamePrefix match {
case None =>
"ReplicaFetcherThread-%d-%d".format(fetcherId, sourceBroker.id)
case Some(p) =>
"%s:ReplicaFetcherThread-%d-%d".format(p, fetcherId, sourceBroker.id)
}
new ReplicaFetcherThread(threadName, fetcherId, sourceBroker, brokerConfig,
replicaMgr, metrics, time, quotaManager)
}
// kafka.server.AbstractFetcherThread
// 拉取数据线程工作
override def doWork() {
// run 函数中 while 一直在拉取数据
// 若无数据可拉,leader partition 会延迟,
// 使 follower partition 不会一直在请求空数据
val fetchRequest = inLock(partitionMapLock) {
// 拉取数据
val fetchRequest = buildFetchRequest(partitionStates.partitionStates.asScala.map { state =>
state.topicPartition -> state.value
})
...
fetchRequest
}
if (!fetchRequest.isEmpty)
// 发送拉取数据请求
processFetchRequest(fetchRequest)
}
private def processFetchRequest(fetchRequest: REQ) {
...
responseData = fetch(fetchRequest)
...
// 从 leader partition 拉取到的数据后
if (responseData.nonEmpty) {
...
// 处理拉取的数据
processPartitionData(topicPartition, currentPartitionFetchState.offset, partitionData)
...
}
}
// 处理从 leader patition 拉取到的数据
def processPartitionData(){
// 拉取到的数据写入 log,与之前生产者写入 leader partition 流程一致,
// 写入成功更新自身 LEO
replica.log.get.append(messageSet, assignOffsets = false)
// 更新 follower 的 HW, min(leader HW, 自身 LEO)
val followerHighWatermark = replica.logEndOffset.messageOffset.min(partitionData.highWatermark)
// 本身作为 follower 是可以不用保留 HW
// 但若是 leader 节点故障,follower 有可能会成为 leader
// 这样情况下保存 HW 是必要的
replica.highWatermark = new LogOffsetMetadata(followerHighWatermark)
...
}
// kafka.server.ReplicaFetcherThread
// 发送拉取数据请求
protected def fetch(fetchRequest: FetchRequest): Seq[(TopicPartition, PartitionData)] = {
// ApiKeys.FETCH 拉取数据标识符
val clientResponse = sendRequest(ApiKeys.FETCH, Some(fetchRequestVersion), fetchRequest.underlying)
new FetchResponse(clientResponse.responseBody).responseData.asScala.toSeq.map { case (key, value) =>
key -> new PartitionData(value)
}
}
ReplicaManager
// kafka.server.KafkaApis
// case ApiKeys.FETCH => handleFetchRequest(request) //处理 拉取数据 的请求
// -> replicaManager.fetchMessages()
// kafka.server.ReplicaManager
def fetchMessages(timeout: Long,
replicaId: Int,
fetchMinBytes: Int,
fetchMaxBytes: Int,
hardMaxBytesLimit: Boolean,
fetchInfos: Seq[(TopicAndPartition, PartitionFetchInfo)],
quota: ReplicaQuota = UnboundedQuota,
responseCallback: Seq[(TopicAndPartition, FetchResponsePartitionData)] => Unit) {
...
// 获取要拉取的数据并附带 leader 的 HW
val logReadResults = readFromLocalLog(
replicaId = replicaId,
fetchOnlyFromLeader = fetchOnlyFromLeader,
readOnlyCommitted = fetchOnlyCommitted,
fetchMaxBytes = fetchMaxBytes,
hardMaxBytesLimit = hardMaxBytesLimit,
readPartitionInfo = fetchInfos,
quota = quota)
if(Request.isValidBrokerId(replicaId))
// 更新 leader partition ISR 和 HW
updateFollowerLogReadResults(replicaId, logReadResults)
...
// respond immediately if 1) fetch request does not want to wait
// 2) fetch request does not require any data
// 3) has enough data to respond
// 4) some error happens while reading data
// timeout <= 0 没数据也不需要等待
// bytesReadable >= fetchMinBytes 只要有拉取数据就返回
if (timeout <= 0 || fetchInfos.isEmpty || bytesReadable >= fetchMinBytes || errorReadingData) {
val fetchPartitionData = logReadResults.map { case (tp, result) =>
tp -> FetchResponsePartitionData(result.errorCode, result.hw, result.info.messageSet)
}
responseCallback(fetchPartitionData)
} else {
// construct the fetch results from the read results
// 若没有数据拉取,需等待会再返回
...
// replica.fetch.wait.max.ms 默认 500ms
val delayedFetch = new DelayedFetch(timeout, fetchMetadata, this, quota, responseCallback)
// create a list of (topic, partition) pairs to use as keys for this delayed fetch operation
val delayedFetchKeys = fetchPartitionStatus.map { case (tp, _) => new TopicPartitionOperationKey(tp) }
// try to complete the request immediately, otherwise put it into the purgatory;
// this is because while the delayed fetch operation is being created, new requests
// may arrive and hence make this operation completable.
delayedFetchPurgatory.tryCompleteElseWatch(delayedFetch, delayedFetchKeys)
}
}
// 读取数据
def readFromLocalLog(){
def read(){
val logReadInfo = localReplica.log match {
case Some(log) =>
val fetch = log.read(offset, adjustedFetchSize, maxOffsetOpt, minOneMessage)
case None =>
error(s"Leader for partition $tp does not have a local log")
}
// 返回除了 log ,还有leader partitoner HW
LogReadResult(logReadInfo, localReplica.highWatermark.messageOffset, fetchSize, readToEndOfLog, None)
}
readPartitionInfo.foreach { case (tp, fetchInfo) =>
// read log
val readResult = read(tp, fetchInfo, limitBytes, minOneMessage)
val messageSetSize = readResult.info.messageSet.sizeInBytes
// Once we read from a non-empty partition, we stop ignoring request and partition level size limits
if (messageSetSize > 0)
minOneMessage = false
limitBytes = math.max(0, limitBytes - messageSetSize)
// 读取到的多个 partition 数据整合到一起
result += (tp -> readResult)
}
result
}
// 更新 follower LEO 和 ISR列表
private def updateFollowerLogReadResults(replicaId: Int, readResults: Seq[(TopicAndPartition, LogReadResult)]) {
debug("Recording follower broker %d log read results: %s ".format(replicaId, readResults))
readResults.foreach { case (topicAndPartition, readResult) =>
getPartition(topicAndPartition.topic, topicAndPartition.partition) match {
case Some(partition) =>
// 更新
partition.updateReplicaLogReadResult(replicaId, readResult)
...
}
Partition
// kafka.cluster.Partition
// ISR 列表保存着 leader 和 follower
@volatile var inSyncReplicas: Set[Replica] = Set.empty[Replica]
def updateReplicaLogReadResult(replicaId: Int, logReadResult: LogReadResult) {
getReplica(replicaId) match {
case Some(replica) =>
// 更新 follower LEO
replica.updateLogReadResult(logReadResult)
// 尝试更新 ISR(也包含更新 HW),当前 follower 可能之前被移除 ISR
// 现在拉取数据,offset 追上来了,重新加入 ISR
maybeExpandIsr(replicaId)
// 尝试更新 ISR
def maybeExpandIsr(replicaId: Int) {
case Some(leaderReplica) =>
// leader partition 才有 ISR
val replica = getReplica(replicaId).get
val leaderHW = leaderReplica.highWatermark
if(!inSyncReplicas.contains(replica) &&
assignedReplicas.map(_.brokerId).contains(replicaId) &&
replica.logEndOffset.offsetDiff(leaderHW) >= 0) {
// 重新加入 ISR 条件:offset 大于等于 HW
...
// update ISR in ZK and cache
// 在 ZK 和 Cache 都要更新 ISR
updateIsr(newInSyncReplicas)
replicaManager.isrExpandRate.mark()
}
// HW 可能也要更新
maybeIncrementLeaderHW(leaderReplica)
}
// 以下两种情况,可能会更新
// ISR 列表变动时
// follower LEO 有变化
private def maybeIncrementLeaderHW(leaderReplica: Replica): Boolean = {
// HW = min(ISR 分区 offset 最小值)
val allLogEndOffsets = inSyncReplicas.map(_.logEndOffset)
val newHighWatermark = allLogEndOffsets.min(new LogOffsetMetadata.OffsetOrdering)
val oldHighWatermark = leaderReplica.highWatermark
isr-expiration
在 ReplicaManager 启动时,会开启维护 ISR 列表的线程
// kafka/server/ReplicaManager.scala
def startup() {
// 维护 ISR 列表的线程 10s
scheduler.schedule("isr-expiration", maybeShrinkIsr, period = config.replicaLagTimeMaxMs, unit = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
scheduler.schedule("isr-change-propagation", maybePropagateIsrChanges, period = 2500L, unit = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
}
private def maybeShrinkIsr(): Unit = {
// 每个 leader partitioner 都维护了 ISR
allPartitions.values.foreach(partition => partition.maybeShrinkIsr(config.replicaLagTimeMaxMs))
}
def maybeShrinkIsr(replicaMaxLagTimeMs: Long) {
// replicaMaxLagTimeMs 默认 10s
val leaderHWIncremented = inWriteLock(leaderIsrUpdateLock) {
leaderReplicaIfLocal() match {
case Some(leaderReplica) =>
val outOfSyncReplicas = getOutOfSyncReplicas(leaderReplica, replicaMaxLagTimeMs)
if(outOfSyncReplicas.nonEmpty) {
// 移除10s 没有拉取数据的 follower
val newInSyncReplicas = inSyncReplicas -- outOfSyncReplicas
// update ISR in zk and in cache
// 更新 ISR
updateIsr(newInSyncReplicas)
replicaManager.isrShrinkRate.mark()
// ISR 更改后,HW 可能也会更改
maybeIncrementLeaderHW(leaderReplica)
}
isr-expiration 线程定时10s 执行一次,遍历所有 leader partition 中 ISR 列表,移除超过10s 没有来拉取数据的 follower 。这样 ISR 列表里 follower 个数会变少,当 follower 的 offset 通过拉取数据追上来后又会重新加入 ISR。
副本切换
假设这么一种情况, leader 节点挂掉后,哪个 follower 节点会成为 leader 呢?
kafka 动态维护一组同步 leader 数据的副本(ISR),只有这个组的成员才有资格当选 leader,kafka 副本写入不被认为是已提交,直到所有的同步副本已经接收才认为。这组 ISR 保存在 zookeeper,正因为如此,在 ISR 中的任何副本都有资格当选 leader,这是kafka的使用模型,有多个分区和确保 leader 平衡是很重要的一个重要因素。有了这个模型,ISR 和 f+1 副本,kafka 的主题可以容忍 f 失败而不会丢失已提交的消息。
当所有节点都挂了?
- 等待在 ISR 中的副本起死回生并选择该副本作为 leader(希望它仍有所有数据)。
- 选择第一个副本 (不一定在 ISR),作为leader。
在 kafka 0.11 之前选择第二种,0.11 之后选择第一种。
集群管理
选举
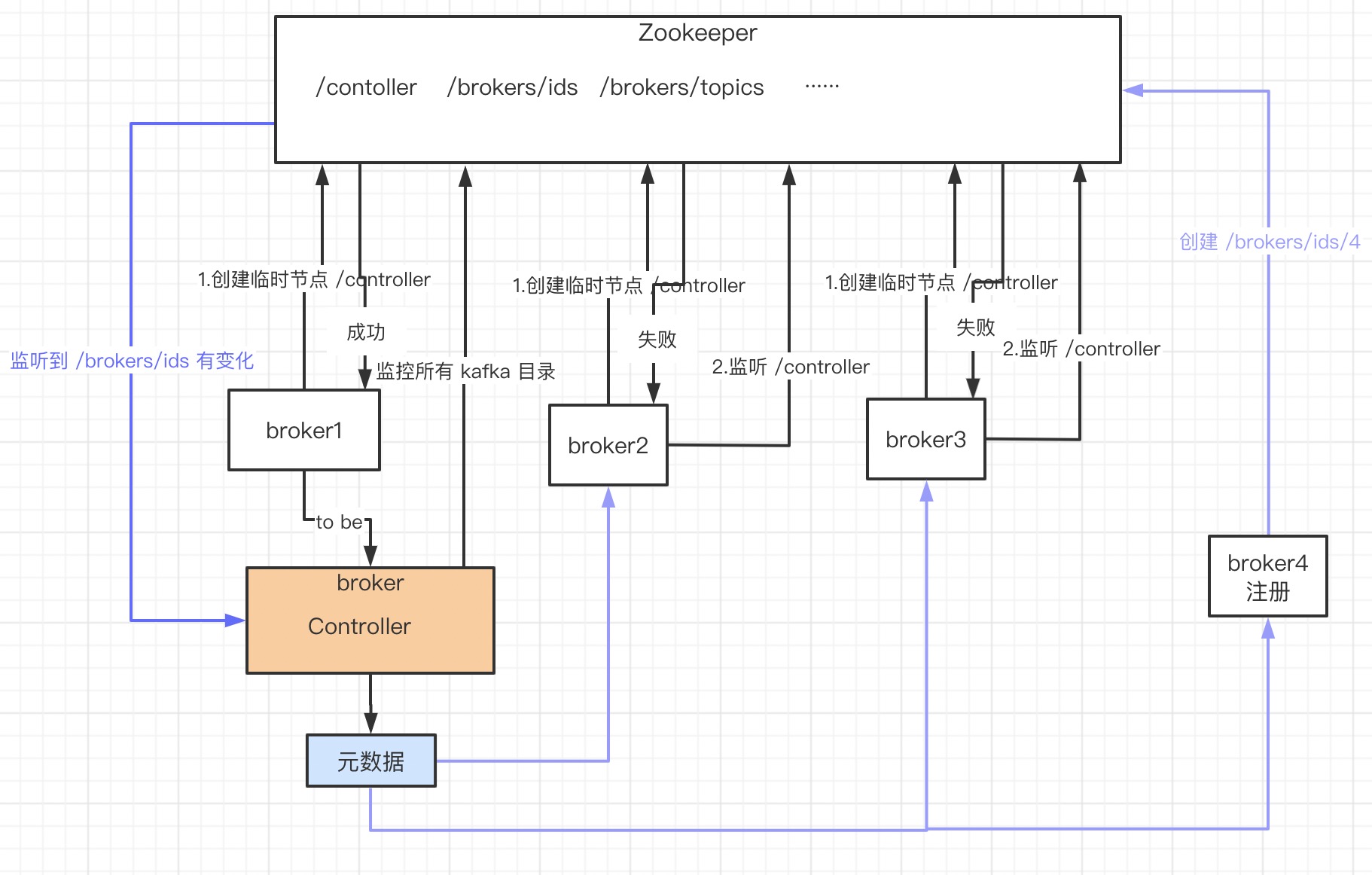
kafka 也是主从,Controller 管理元数据,并将元数据同步到所有 broker。每个 broker 在启动时都会竞选成为 Controller。
// kafka.server.ZookeeperLeaderElector
def startup {
inLock(controllerContext.controllerLock) {
// 监听 /controller,回调函数 LeaderChangeListener
// 若集群的 Controller 发生故障,/controller 节点会发生变化,
controllerContext.zkUtils.zkClient.subscribeDataChanges(electionPath, leaderChangeListener)
// 选举 Controller 过程
elect
}
}
def elect: Boolean = {
val timestamp = SystemTime.milliseconds.toString
// 在 /controller 写入的内容:brokerid,version,timestamp
// 哪个 broker 创建 /controller 成功,谁就是 Controller
// 这个过程就是 kafka 集群 Controller 选举
val electString = Json.encode(Map("version" -> 1, "brokerid" -> brokerId, "timestamp" -> timestamp))
// 获取 Controller broker id
leaderId = getControllerID
if(leaderId != -1) {
// 若有 Controller broker id,表示当前已经有 Controller
// 不继续选举过程
debug("Broker %d has been elected as leader, so stopping the election process.".format(leaderId))
return amILeader
}
// 继续选举过程
// electionPath = /controller
// 文件内容 = brokerid,version,timestamp
// 创建 /controller 临时节点
try {
val zkCheckedEphemeral = new ZKCheckedEphemeral(electionPath,
electString,
controllerContext.zkUtils.zkConnection.getZookeeper,
JaasUtils.isZkSecurityEnabled())
zkCheckedEphemeral.create()
info(brokerId + " successfully elected as leader")
// 创建临时节点成功,表示此 broker 成为 Controller
leaderId = brokerId
// 成为 Controller 之后,初始化工作 onControllerFailover
onBecomingLeader()
} catch {
case e: ZkNodeExistsException =>
// 此异常表示 /controller 节点已经生成,直接获取 Controller broker id
leaderId = getControllerID
选举过程很简单:哪个 broker 创建 /controller 成功,谁就是 Controller
Controller 管理整个集群的元数据,成为 Controller 后需要先初始化。
// kafka.controller.KafkaController
val controllerContext = new ControllerContext(zkUtils, config.zkSessionTimeoutMs)
// 分区管理
val partitionStateMachine = new PartitionStateMachine(this)
// broker 管理
val replicaStateMachine = new ReplicaStateMachine(this)
// /controller
private val controllerElector = new ZookeeperLeaderElector(controllerContext, ZkUtils.ControllerPath, onControllerFailover,
onControllerResignation, config.brokerId)
/* 当broker 成为 Controller 之后,回调函数
* 1、监听 zk目录,感知集群变化,管理元数据
* 2、增加 controller epoch,可预防脑裂(若集群出现两个 Controller,则epoch 大的才是需要的 Controller)
* 3、初始化集群元数据信息
* 4、
*/
def onControllerFailover() {
if(isRunning) {
info("Broker %d starting become controller state transition".format(config.brokerId))
//read controller epoch from zk
readControllerEpochFromZookeeper()
// increment the controller epoch
incrementControllerEpoch(zkUtils.zkClient)
// before reading source of truth from zookeeper, register the listeners to get broker/topic callbacks
// 监听 /admin/reassign_partitions,topic 分区增加/减少 PartitionsReassignedListener
registerReassignedPartitionsListener()
//监听 /isr_change_notification,ISR 列表变化,IsrChangeNotificationListener
registerIsrChangeNotificationListener()
registerPreferredReplicaElectionListener()
// 监听 /brokers/topics 和 /admin/delete_topics,topic 变化,TopicChangeListener
// 新建 topic 可以感知
partitionStateMachine.registerListeners()
// 监听 /brokers/ids,broker 变化,BrokerChangeListener
replicaStateMachine.registerListeners()
// 初始化集群元数据
initializeControllerContext()
...
Controller 通过监听 zk 节点感知集群变化,初始化数据大部分是从 zk 节点读取内容。
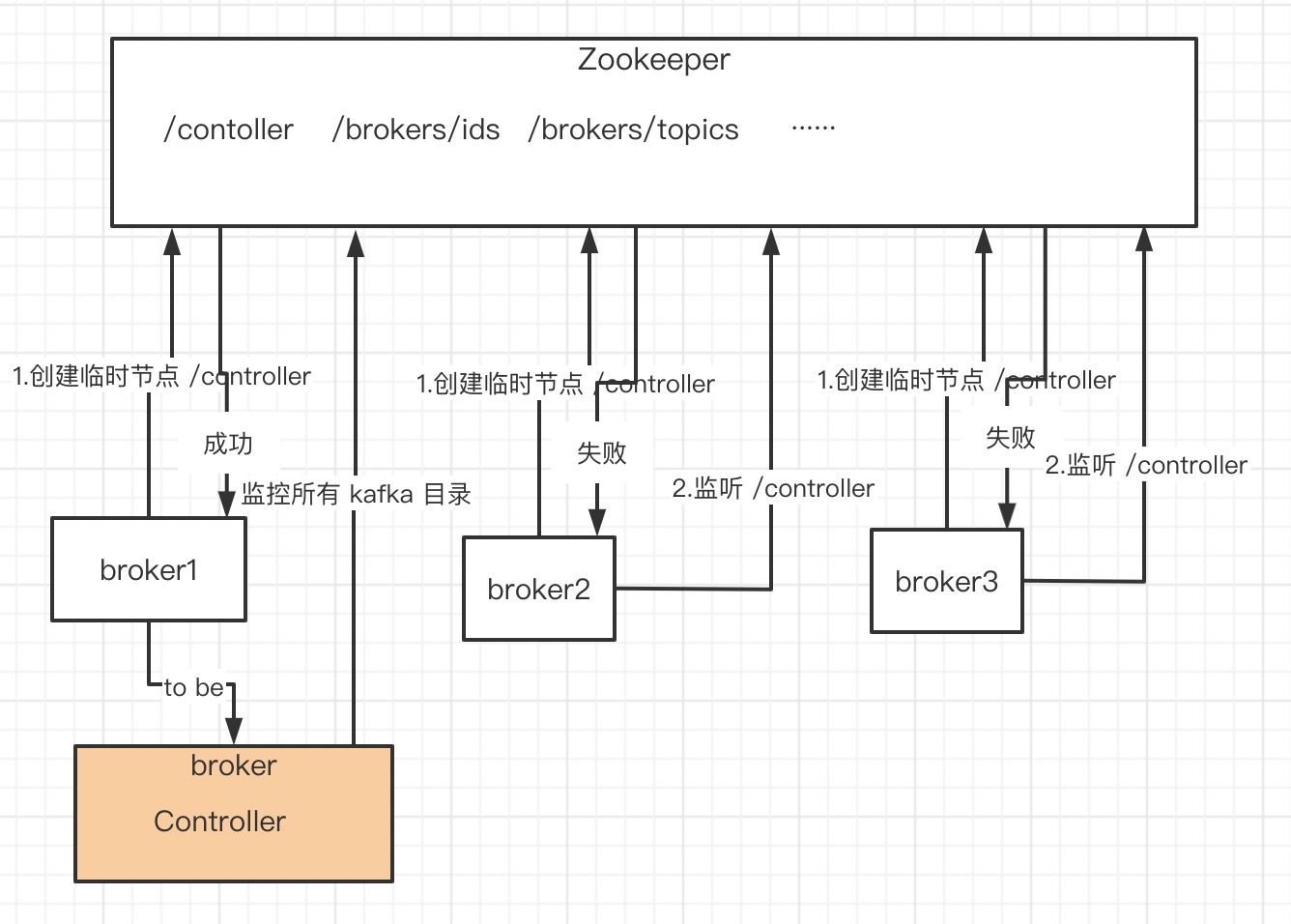
broker 注册
// kafkaHealthcheck.startup()
// -> kafka.server.KafkaHealthcheck.register()
// -> zkUtils.registerBrokerInZk
// kafka.utils.ZkUtils
def registerBrokerInZk(id: Int,
host: String,
port: Int,
advertisedEndpoints: collection.Map[SecurityProtocol, EndPoint],
jmxPort: Int,
rack: Option[String],
apiVersion: ApiVersion) {
// 节点路径:/brokers/ids/brokerid
val brokerIdPath = BrokerIdsPath + "/" + id
val timestamp = SystemTime.milliseconds.toString
val version = if (apiVersion >= KAFKA_0_10_0_IV1) 3 else 2
// 节点要写入的内容 jsonMap:ip、端口号、时间戳
var jsonMap = Map("version" -> version,
"host" -> host,
"port" -> port,
"endpoints" -> advertisedEndpoints.values.map(_.connectionString).toArray,
"jmx_port" -> jmxPort,
"timestamp" -> timestamp
)
rack.foreach(rack => if (version >= 3) jsonMap += ("rack" -> rack))
val brokerInfo = Json.encode(jsonMap)
// 创建临时节点
registerBrokerInZk(brokerIdPath, brokerInfo)
broker 注册很简单,就是在 /brokers/ids/ 目录写下自己的临时节点。broker 注册好之后,Controller 如何感知呢?
Controller 在启动时监听一些列目录,其中就有 /brokers/ids/ ,我们看看其回调函数。
// 监听 /brokers/ids,broker 变化,BrokerChangeListener
// replicaStateMachine.registerListeners()
// kafka.controller.ReplicaStateMachine.BrokerChangeListener
class BrokerChangeListener() extends IZkChildListener with Logging {
def handleChildChange(parentPath : String, currentBrokerList : java.util.List[String]) {
// 从zk 得到当前所有 broker
val curBrokers = currentBrokerList.map(_.toInt).toSet.flatMap(zkUtils.getBrokerInfo)
val curBrokerIds = curBrokers.map(_.id)
val liveOrShuttingDownBrokerIds = controllerContext.liveOrShuttingDownBrokerIds
// 当前brokers - 之前的brokers = 新增的 broker
val newBrokerIds = curBrokerIds -- liveOrShuttingDownBrokerIds
// 之前的brokers - 当前brokers = 挂掉的brokers
val deadBrokerIds = liveOrShuttingDownBrokerIds -- curBrokerIds
val newBrokers = curBrokers.filter(broker => newBrokerIds(broker.id))
controllerContext.liveBrokers = curBrokers
val newBrokerIdsSorted = newBrokerIds.toSeq.sorted
val deadBrokerIdsSorted = deadBrokerIds.toSeq.sorted
val liveBrokerIdsSorted = curBrokerIds.toSeq.sorted
info("Newly added brokers: %s, deleted brokers: %s, all live brokers: %s"
.format(newBrokerIdsSorted.mkString(","), deadBrokerIdsSorted.mkString(","), liveBrokerIdsSorted.mkString(",")))
newBrokers.foreach(controllerContext.controllerChannelManager.addBroker)
deadBrokerIds.foreach(controllerContext.controllerChannelManager.removeBroker)
if(newBrokerIds.nonEmpty)
// 有新增的 broker
// 更新自身元数据,并同步到所有 broker
controller.onBrokerStartup(newBrokerIdsSorted)
if(deadBrokerIds.nonEmpty)
// 有挂掉的 broker,流程与有新增相同,不在赘述
controller.onBrokerFailure(deadBrokerIdsSorted)
}
}
// kafkaController.onBrokerStartup
// -> partitionStateMachine.triggerOnlinePartitionStateChange()
// -> brokerRequestBatch.sendRequestsToBrokers(controller.epoch)
// kafka.controller.ControllerBrokerRequestBatch
def sendRequestsToBrokers(controllerEpoch: Int) {
...
// 发送请求,type = ApiKeys.UPDATE_METADATA_KEY
controller.sendRequest(broker, ApiKeys.UPDATE_METADATA_KEY, Some(version), updateMetadataRequest, null)
...
}
很显然,到这一步我们又要去 KafkaApis 代码了。
// case ApiKeys.UPDATE_METADATA_KEY => handleUpdateMetadataRequest(request)
// -> replicaManager.maybeUpdateMetadataCache(correlationId, updateMetadataRequest, metadataCache)
// -> metadataCache.updateCache(correlationId, updateMetadataRequest)
// -> 更新各种数据结构
Topic 新建
创建 topic 命令
./kafka-topic.sh create xxx
查看 kafka-topic.sh
# 可知执行 kafka.admin.TopicCommand
exec $(dirname $0)/kafka-run-class.sh kafka.admin.TopicCommand "$@"
// kafka.admin.TopicCommand
// createTopic(zkUtils, opts)
// AdminUtils.createTopic(zkUtils, topic, partitions, replicas, configs, rackAwareMode)
// kafka.admin.AdminUtils
def createTopic(zkUtils: ZkUtils,
topic: String,
partitions: Int,
replicationFactor: Int,
topicConfig: Properties = new Properties,
rackAwareMode: RackAwareMode = RackAwareMode.Enforced) {
val brokerMetadatas = getBrokerMetadatas(zkUtils, rackAwareMode)
// replicaAssignment = Map[Int, Seq[Int]] = Map[partitionindex,Seq[brokerid]
// 为 partition 分配 broker
// partition0: [broker1,broker2,broker3]
// partition1: [broker4,broker2,broker3]
// ...
val replicaAssignment = AdminUtils.assignReplicasToBrokers(brokerMetadatas, partitions, replicationFactor)
//
AdminUtils.createOrUpdateTopicPartitionAssignmentPathInZK(zkUtils, topic, replicaAssignment, topicConfig)
}
// writeTopicPartitionAssignment(zkUtils, topic, partitionReplicaAssignment, update)
private def writeTopicPartitionAssignment(zkUtils: ZkUtils, topic: String, replicaAssignment: Map[Int, Seq[Int]], update: Boolean) {
try {
// 得到 topic 在 zk 路径
val zkPath = getTopicPath(topic)
// 获取要写入 topic 节点的内容:{"version":1,"partitions":{"4":[76,77,78],"5":[77,79,75],"1":[78,79,75],"0":[77,78,79],"2":[79,75,76],"3":[75,76,77]}}
val jsonPartitionData = zkUtils.replicaAssignmentZkData(replicaAssignment.map(e => e._1.toString -> e._2))
if (!update) {
info("Topic creation " + jsonPartitionData.toString)
// 创建 topic 在 zk 路径,写入数据
zkUtils.createPersistentPath(zkPath, jsonPartitionData)
} else {
info("Topic update " + jsonPartitionData.toString)
zkUtils.updatePersistentPath(zkPath, jsonPartitionData)
}
debug("Updated path %s with %s for replica assignment".format(zkPath, jsonPartitionData))
} catch {
case e: ZkNodeExistsException => throw new TopicExistsException("topic %s already exists".format(topic))
case e2: Throwable => throw new AdminOperationException(e2.toString)
}
}
到此为止,创建 Topic 的过程,就是在 /brokers/topics 下新建 topic 节点,并写入分区所在的 brokerid。毫无疑问,接下来肯定是 Controller 监听到目录变化调用回调函数。
// 监听 /brokers/topics 和 /admin/delete_topics,topic 变化,TopicChangeListener
// partitionStateMachine.registerListeners()
总结
可以来看看 broker 运行至少需要多少个线程:
- 网络:1 + 3 +8
- 副本:(broker-1) + 2