HashMap
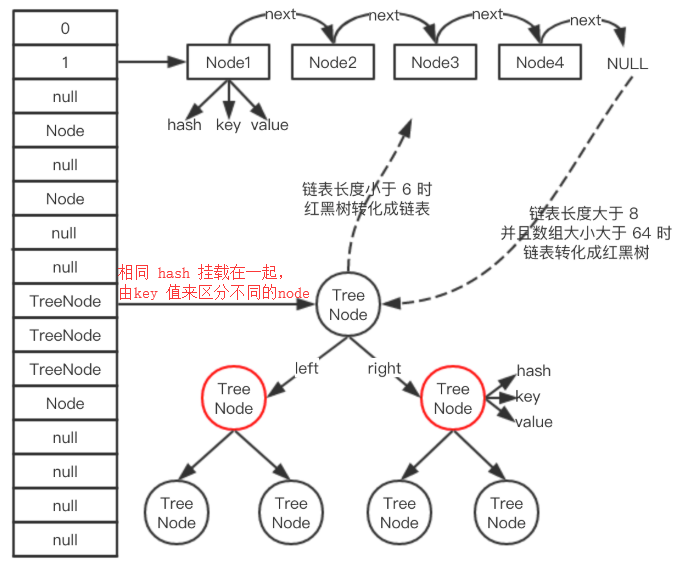
HashMap 底层的数据结构主要是:
数组+单链表+红黑树;其中当链表的长度大于等于8时,并且整个数组大小大于64,链表会转化成红黑树,当红黑树大小小于等于6时,红黑树会转化成链表。
底层是 Node 数组 + 链表/红黑数,键值hash 后按位与上(数组长度 - 1) 就是数组序列号, key 可为空。HashMap 的存储过程:
- key hash得到 hash 值
- 根据hash 值找到在map 数组中的下标,查看当前数组下标是否有 node
- 如果没有node,直接新建node 赋值;
- 如果有node 表示 hash 冲突,则需要链表/红黑树来存储相同 hash 不同key 的node
- 查看 node 数组是否需要扩容
transient Node<K,V>[] table;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
空构造函数
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted
}
// 空 map 新增一个自动增长为 16
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
put
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// 找到 hash 对应的 数组下标 i 和 node p
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
// p 为空直接添加
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
// p 不为空,表示有node,存在hash 冲突
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
// hash 、key 都相同,说明键值是一样,根据onlyIfAbsent 是否直接覆盖
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
// 红黑树插入
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
// 单链表直接插入到最后
// 如果中间找到相同key 的 node,根据onlyIfAbsent 是否直接覆盖
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
// onlyIfAbsent = false 表示覆盖
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
// 扩容
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
// 扩容
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
// size 已经大于 1<<30 ,不能再扩容,加大 threshold
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
// 在可扩容的范围下 size *2,threshold*2
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
// 原本为0,扩容成16,threshold = 16*0.75=12
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
// node 数组增大后,hash 得到的 数组 index 变了,涉及 node 复制
......
}
return newTab;
}
- 空值,size 增长到 16
- 有值,size < (1« 30)
- (size 2) < (1« 30),size >= 16 : size * 2 直接翻倍,threshold2
- (size 2) < (1« 30),size < 16 : size * 2 直接翻倍,threshold = size * 20.75
- (size *2) >= (1« 30),size * 2 直接翻倍,threshold=Integer.MAX_VALUE
- 有值,size >= (1« 30),不扩容,但增大 threshold=Integer.MAX_VALUE
get
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
// 由 key 得到 hash ,去查询
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
// map 不为空,且tab[hash] 上有 node
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
// 找到对应node 的条件是 key 相同
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
// 红黑树查找
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do {
// 普通链表查找
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
删除
public V remove(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ?
null : e.value;
}
final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,
boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
// key hash 得到 数组 index
Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
// 直接在 node 数组上取到
node = p;
else if ((e = p.next) != null) {
if (p instanceof TreeNode)
// 红黑树中获取
node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else {
do {
// 链表中获取
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key ||
(key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
node = e;
break;
}
p = e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value ||
(value != null && value.equals(v)))) {
if (node instanceof TreeNode)
// 红黑树删除
((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable);
else if (node == p)
// 链表删除,直接删表头
tab[index] = node.next;
else
// 删表中间
p.next = node.next;
++modCount;
--size;
afterNodeRemoval(node);
return node;
}
}
return null;
}
删除 node,并不会涉及到删除 node数组
链表 -> 红黑树的条件是长度大于8:链表查询复杂度是 O(n),红黑树查询复杂度是O(lon(n));在数据不多时,链表也是很快;当数据增多时转化为红黑树,但红黑树需要消耗空间是链表2倍。如果长度大于8 说明 hash 算法可能是有问题的,而且遇到大于8 的概率是很低很低,一般不会使用到红黑树。
TreeMap
treemap 按key 有序排列, 底层就是红黑树,利用红黑树左小右大的特性,可以实现按 key 大小存储。
// key 大小比较器
private final Comparator<? super K> comparator;
private transient Entry<K,V> root;
private transient int size = 0;
private transient int modCount = 0;
// 每个节点数据结构,包含KV,父节点,子左节点,子右节点
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> left;
Entry<K,V> right;
Entry<K,V> parent;
构造函数
public TreeMap() {
comparator = null;
}
// 传入自定义的比较器
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
// 可以使用传入的比较器 or 使用key 自带的比较
final int compare(Object k1, Object k2) {
return comparator==null ? ((Comparable<? super K>)k1).compareTo((K)k2)
: comparator.compare((K)k1, (K)k2);
}
put
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
if (t == null) {
// 空map 直接新建 entry 当 root 节点
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
// 利用 comparator 比较key 大小找到新增节点在那个parent下
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
// 找到相同key,直接覆盖 value 返回
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
else {
// 同上面一样,只是比较器用 key 自带
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
// 在 parent 下新建 Entry 添加
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
// 红黑树着色,平衡二叉树为了最坏的检索效率也是高效的,看参考资料三
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
TreeMap键值不能为null- Node 结构没有扩容概念
- put 返回的之前key 的value,若没有则为null
get
public V get(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
return (p==null ? null : p.value);
}
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
// Offload comparator-based version for sake of performance
if (comparator != null)
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
// key 不能为 null
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
// 二叉树查找
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
return null;
}
remove
public V remove(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
if (p == null)
return null;
// 删除 Entry
V oldValue = p.value;
deleteEntry(p);
return oldValue;
}
LinkedHashMap
HashMap 是无序的, TreeMap 是按 key 排序,而 LinkedHashMap 是使用迭代器时是按插入顺序。
// 继承 HashMap,可以简单理解是把 LinkedList中元素换成 HashMap.Node 就成了LinkedHashMap,但只可以单向访问
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V> extends HashMap<K,V>
// 头尾节点,
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head;
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail;
static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
}
// 访问控制,对于迭代器而言
// false 时,迭代器访问按插入顺序
// true 时,经常访问的key 放到末尾,看 afterNodeAccess
final boolean accessOrder;
put
// put 先调用父类 HashMap.put,但覆写 newNode 方法
Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
new LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
linkNodeLast(p);
return p;
}
// 新节点插在末尾,迭代时保证插入顺序
private void linkNodeLast(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last = tail;
tail = p;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
}
迭代器
final LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> nextNode() {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = next;
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
// 插入顺序访问
current = e;
next = e.after;
return e;
}
get
// 除了afterNodeAccess ,其他与 HashMap 相同
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)
return null;
if (accessOrder)
afterNodeAccess(e);
return e.value;
}
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { // move node to last
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last;
// accessOrder = false 直接退出
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {
// accessOrder = true,把当前访问的节点移动到最后 tail
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
p.after = null;
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a != null)
a.before = b;
else
last = b;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
tail = p;
++modCount;
}
}
LinkedHashMap 在 HashMap 基础上增加链表操作后新增访问控制(迭代器)
- 按插入顺序访问(后插入排在后面)
- 按使用次数访问(用的最多排在末尾)
参考资料
JDK8
面试官系统精讲Java 源码及大厂真题