Flink 1.11
之前已经提到 1.10 版本中 SQL 创建表的流程,1.11 相比来说有一些变化
connector:- 1.10 每个属性都需要加 “connector” 字符串,这很冗余;
- 1.11 已不需要,但老的
with写法也还兼容,根据是否包含 “connector.type” 属性来区分
table:- 1.10 创建的是
org.apache.flink.table.factories.TableFactory,sink 时调用的是 DataStream 方法 - 1.11 创建的是
org.apache.flink.table.factories.Factory,sink 时调用的是 Operator 方法
- 1.10 创建的是
DynamicTable:- 1.10:没有这个概念;存在 append、 upsert、toRetract 三种类型的 sink
- 1.11:只有 DynamicTable,至于之前存在的三种类型,由
getChangelogMode函数决定
CDC:- 1.10:不支持
- 1.11:支持 CDC, kafka table source 接入时,会根据抽取 binlog 组件反序列化成相应的
RowData;maxwell 也是抽取 binlog 的组件,但 1.11 并不支持,我们需要定制。
Table
从 table 创建开始
CREATE TABLE topic_products (
id BIGINT,
name STRING,
description STRING,
weight DECIMAL(10, 2)
) WITH (
'connector' = 'kafka',
'topic' = 'maxwell',
'properties.bootstrap.servers' = 'localhost:9092',
'properties.group.id' = 'testGroup',
'format' = 'canal-json')
// org.apache.flink.table.planner.plan.schema.CatalogSourceTable
private def buildTableScan(
cluster: RelOptCluster,
hints: JList[RelHint],
conf: ReadableConfig,
typeFactory: FlinkTypeFactory): LogicalTableScan = {
...
//
val tableSource = FactoryUtil.createTableSource(
schemaTable.getCatalog,
schemaTable.getTableIdentifier,
newCatalogTable,
conf,
Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader)
validateTableSource(tableSource)
val tableSourceTable = new TableSourceTable(
relOptSchema,
schemaTable.getTableIdentifier,
sourceRowType,
statistic,
tableSource,
schemaTable.isStreamingMode,
catalogTable,
hintedOptions)
LogicalTableScan.create(cluster, tableSourceTable, hints)
}
// org.apache.flink.table.factories.FactoryUtil
public static DynamicTableSource createTableSource(
@Nullable Catalog catalog,
ObjectIdentifier objectIdentifier,
CatalogTable catalogTable,
ReadableConfig configuration,
ClassLoader classLoader) {
final DefaultDynamicTableContext context = new DefaultDynamicTableContext(
objectIdentifier,
catalogTable,
configuration,
classLoader);
try {
// DynamicTable 1.11 新出的概念,查阅 FLIP-95
final DynamicTableSourceFactory factory = getDynamicTableFactory(
DynamicTableSourceFactory.class,
catalog,
context);
// 根据 with 属性找到对应工厂类,创建 table
return factory.createDynamicTableSource(context);
}
...
}
private static <T extends DynamicTableFactory> T getDynamicTableFactory(
Class<T> factoryClass,
@Nullable Catalog catalog,
DefaultDynamicTableContext context) {
// catalog 是否已存在
if (catalog != null) {
final Factory factory = catalog.getFactory()
.filter(f -> factoryClass.isAssignableFrom(f.getClass()))
.orElse(null);
if (factory != null) {
return (T) factory;
}
}
// 直接用 options 利用 SPI 去加载,与1.10 类似,不在赘述
final String connectorOption = context.getCatalogTable()
.getOptions()
.get(CONNECTOR.key());
if (connectorOption == null) {
throw new ValidationException(
String.format(
"Table options do not contain an option key '%s' for discovering a connector.",
CONNECTOR.key()));
}
try {
return discoverFactory(context.getClassLoader(), factoryClass, connectorOption);
}
...
}
上面是创建表的过程,与1.10 大同小异。接下来 kafka table source 为例,介绍 1.11 是如何支持 CDC 。
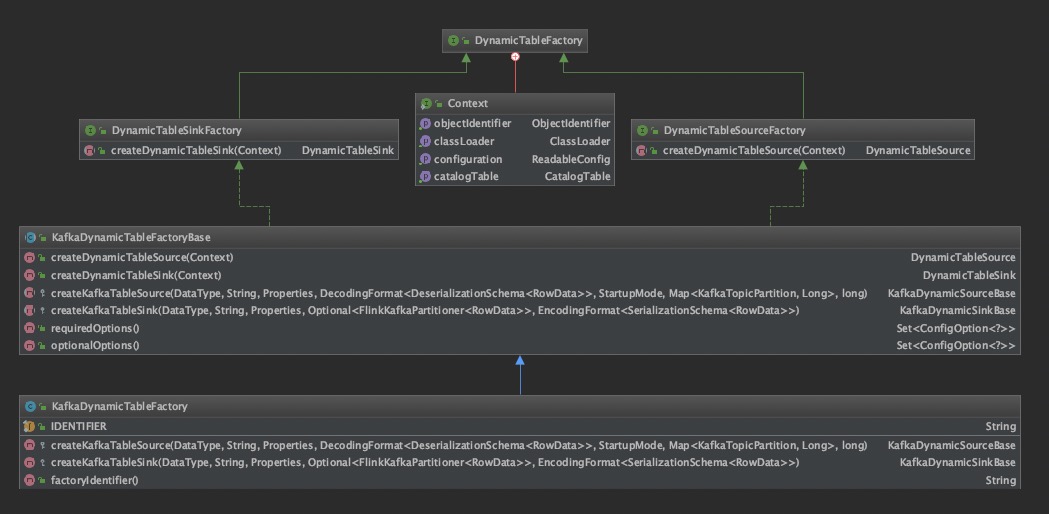
// return factory.createDynamicTableSource(context);
// org.apache.flink.streaming.connectors.kafka.table.KafkaDynamicTableFactoryBase
public DynamicTableSource createDynamicTableSource(Context context) {
FactoryUtil.TableFactoryHelper helper = FactoryUtil.createTableFactoryHelper(this, context);
ReadableConfig tableOptions = helper.getOptions();
String topic = tableOptions.get(TOPIC);
// 查找序列化 format 属性对应的序列化工厂类,下面重点分析
DecodingFormat<DeserializationSchema<RowData>> decodingFormat = helper.discoverDecodingFormat(
DeserializationFormatFactory.class,
FactoryUtil.FORMAT);
// Validate the option data type.
helper.validateExcept(KafkaOptions.PROPERTIES_PREFIX);
// Validate the option values.
validateTableOptions(tableOptions);
// DataType 表的数据结构
DataType producedDataType = context.getCatalogTable().getSchema().toPhysicalRowDataType();
final KafkaOptions.StartupOptions startupOptions = getStartupOptions(tableOptions, topic);
return createKafkaTableSource(
producedDataType,
topic,
getKafkaProperties(context.getCatalogTable().getOptions()),
decodingFormat,
startupOptions.startupMode,
startupOptions.specificOffsets,
startupOptions.startupTimestampMillis);
}
// org.apache.flink.streaming.connectors.kafka.table.KafkaDynamicTableFactory
protected KafkaDynamicSourceBase createKafkaTableSource(
DataType producedDataType,
String topic,
Properties properties,
DecodingFormat<DeserializationSchema<RowData>> decodingFormat,
StartupMode startupMode,
Map<KafkaTopicPartition, Long> specificStartupOffsets,
long startupTimestampMillis) {
return new KafkaDynamicSource(
producedDataType,
topic,
properties,
decodingFormat,
startupMode,
specificStartupOffsets,
startupTimestampMillis);
}
工厂类介绍完毕,下面看 table
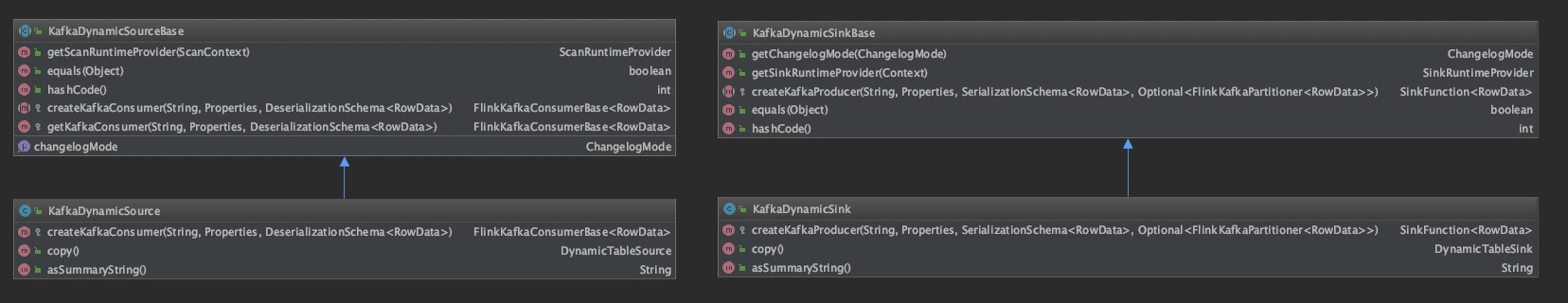
// org.apache.flink.streaming.connectors.kafka.table.KafkaDynamicSource
public KafkaDynamicSource(
DataType outputDataType,
String topic,
Properties properties,
DecodingFormat<DeserializationSchema<RowData>> decodingFormat,
StartupMode startupMode,
Map<KafkaTopicPartition, Long> specificStartupOffsets,
long startupTimestampMillis) {
super(
outputDataType,
topic,
properties,
decodingFormat,
startupMode,
specificStartupOffsets,
startupTimestampMillis);
}
// org.apache.flink.streaming.connectors.kafka.table.KafkaDynamicSourceBase
protected KafkaDynamicSourceBase(
DataType outputDataType,
String topic,
Properties properties,
DecodingFormat<DeserializationSchema<RowData>> decodingFormat,
StartupMode startupMode,
Map<KafkaTopicPartition, Long> specificStartupOffsets,
long startupTimestampMillis) {
this.outputDataType = Preconditions.checkNotNull(
outputDataType, "Produced data type must not be null.");
this.topic = Preconditions.checkNotNull(topic, "Topic must not be null.");
this.properties = Preconditions.checkNotNull(properties, "Properties must not be null.");
this.decodingFormat = Preconditions.checkNotNull(
decodingFormat, "Decoding format must not be null.");
this.startupMode = Preconditions.checkNotNull(startupMode, "Startup mode must not be null.");
this.specificStartupOffsets = Preconditions.checkNotNull(
specificStartupOffsets, "Specific offsets must not be null.");
this.startupTimestampMillis = startupTimestampMillis;
}
至此表的创建流程已完毕,下面介绍序列化和 CDC
序列化
在创建表时,指定序列化类型;同理我们需要根据 Option 加载对应序列化的工厂类
// org.apache.flink.formats.json.canal.CanalJsonFormatFactory
// 创建表时 format 数据的标示符
public static final String IDENTIFIER = "canal-json";
public String factoryIdentifier() {
return IDENTIFIER;
}
public DecodingFormat<DeserializationSchema<RowData>> createDecodingFormat(
DynamicTableFactory.Context context,
ReadableConfig formatOptions) {
FactoryUtil.validateFactoryOptions(this, formatOptions);
final boolean ignoreParseErrors = formatOptions.get(IGNORE_PARSE_ERRORS);
TimestampFormat timestampFormatOption = JsonOptions.getTimestampFormat(formatOptions);
return new DecodingFormat<DeserializationSchema<RowData>>() {
@Override
public DeserializationSchema<RowData> createRuntimeDecoder(
DynamicTableSource.Context context, DataType producedDataType) {
final RowType rowType = (RowType) producedDataType.getLogicalType();
final TypeInformation<RowData> rowDataTypeInfo =
(TypeInformation<RowData>) context.createTypeInformation(producedDataType);
// 传入表结构 rowType,表信息 rowDataTypeInfo ,创建 canal-json 反序列化
return new CanalJsonDeserializationSchema(
rowType,
rowDataTypeInfo,
ignoreParseErrors,
timestampFormatOption);
}
@Override
public ChangelogMode getChangelogMode() {
return ChangelogMode.newBuilder()
.addContainedKind(RowKind.INSERT)
.addContainedKind(RowKind.UPDATE_BEFORE)
.addContainedKind(RowKind.UPDATE_AFTER)
.addContainedKind(RowKind.DELETE)
.build();
}
};
}
// 注意 CanalJsonFormatFactory 不支持创建序列化类,看参考资料一
public EncodingFormat<SerializationSchema<RowData>> createEncodingFormat(
DynamicTableFactory.Context context,
ReadableConfig formatOptions) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Canal format doesn't support as a sink format yet.");
}
// org.apache.flink.formats.json.canal.CanalJsonDeserializationSchema
public CanalJsonDeserializationSchema(
RowType rowType,
TypeInformation<RowData> resultTypeInfo,
boolean ignoreParseErrors,
TimestampFormat timestampFormatOption) {
this.resultTypeInfo = resultTypeInfo;
this.ignoreParseErrors = ignoreParseErrors;
this.fieldCount = rowType.getFieldCount();
// JsonRowDataDeserializationSchema 才是真正去反序列化的类
// createJsonRowType 传入表结构和需要的 json 字段
// CanalJsonDeserializationSchema 是根据 JsonRowDataDeserializationSchema 返回的结果再包装成 RowData
this.jsonDeserializer = new JsonRowDataDeserializationSchema(
createJsonRowType(fromLogicalToDataType(rowType)),
// the result type is never used, so it's fine to pass in Canal's result type
resultTypeInfo,
false, // ignoreParseErrors already contains the functionality of failOnMissingField
ignoreParseErrors,
timestampFormatOption);
}
private static RowType createJsonRowType(DataType databaseSchema) {
// canal 抽取 binlog 输出 json,flink 中只获取 data,old,type 三个字段
return (RowType) DataTypes.ROW(
DataTypes.FIELD("data", DataTypes.ARRAY(databaseSchema)),
DataTypes.FIELD("old", DataTypes.ARRAY(databaseSchema)),
DataTypes.FIELD("type", DataTypes.STRING())).getLogicalType();
}
@Override
public void deserialize(byte[] message, Collector<RowData> out) throws IOException {
try {
// JsonRowDataDeserializationSchema 得到结果就是 createJsonRowType 定义的类型
// 0 = data,1 = oldData, 2 = type(insert,update,delete)
RowData row = jsonDeserializer.deserialize(message);
String type = row.getString(2).toString(); // "type" field
if (OP_INSERT.equals(type)) {
// "data" field is an array of row, contains inserted rows
ArrayData data = row.getArray(0);
for (int i = 0; i < data.size(); i++) {
RowData insert = data.getRow(i, fieldCount);
insert.setRowKind(RowKind.INSERT);
out.collect(insert);
}
} else if (OP_UPDATE.equals(type)) {
// update 数据分解成 2 个数据:UPDATE_BEFORE,UPDATE_AFTER
ArrayData data = row.getArray(0);
ArrayData old = row.getArray(1);
for (int i = 0; i < data.size(); i++) {
GenericRowData after = (GenericRowData) data.getRow(i, fieldCount);
GenericRowData before = (GenericRowData) old.getRow(i, fieldCount);
for (int f = 0; f < fieldCount; f++) {
if (before.isNullAt(f)) {
// not null fields in "old" (before) means the fields are changed
// null/empty fields in "old" (before) means the fields are not changed
// so we just copy the not changed fields into before
before.setField(f, after.getField(f));
}
}
before.setRowKind(RowKind.UPDATE_BEFORE);
after.setRowKind(RowKind.UPDATE_AFTER);
out.collect(before);
out.collect(after);
}
} else if (OP_DELETE.equals(type)) {
// delete 类型数据
ArrayData data = row.getArray(0);
for (int i = 0; i < data.size(); i++) {
RowData insert = data.getRow(i, fieldCount);
insert.setRowKind(RowKind.DELETE);
out.collect(insert);
}
} else {
if (!ignoreParseErrors) {
throw new IOException(format(
"Unknown \"type\" value \"%s\". The Canal JSON message is '%s'", type, new String(message)));
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// a big try catch to protect the processing.
if (!ignoreParseErrors) {
throw new IOException(format(
"Corrupt Canal JSON message '%s'.", new String(message)), t);
}
}
}
RowData 是 Table 内部的数据结构,里面可以设置 RowKind,使用 Flink SQL 会直接应用上 RowData。用户想直接用 RowData 也是可以的,1.11 的新版 connector API 就是将 RowData 暴露给了 connector 开发者。
JsonRowDataDeserializationSchema 根据表结构反序列化得到 RowData;CanalJsonDeserializationSchema 根据 canal 组件的 binglog-json 格式对 RowData 设置 RowKind 去契合流计算中的 CDC 数据格式。
定制
1.11 只支持 Canal 和 Debezium 组件的 binlog-json 格式,如果使用 Maxwell 组件需要自己添加。
Source
kafka 作为 Source 时,需要反序列化 binlog 数据。其实 Maxwell 和 Canal 抽取 binlog 后得到的 json 非常类似,也包含(data,old,type),不过 type 是小写的 insert,update,delete(使用 maxwell bootstrap 时,type = bootstrap-insert)。
- 复制 Canal 代码
- IDENTIFIER 改为 maxwell-json
- maxwell 中每个 json 只包含一条数据的变化,可以去掉 Canal 原有的 循环
- 可以
createJsonRowType函数添加ts和position字段,供后续 sql 逻辑处理时 last_value 使用
Sink
Sink 需要将原有的 RowData 序列化成 maxwell-json 格式。思路类似:maxwell 调用 createJsonRowType 函数确定需要序列化的字段,JsonRowDataDeserializationSchema.serialize(RowData) 得到序列化的结果。