Flink 1.11
Flink 任务在运行之前会经历以下几个阶段:
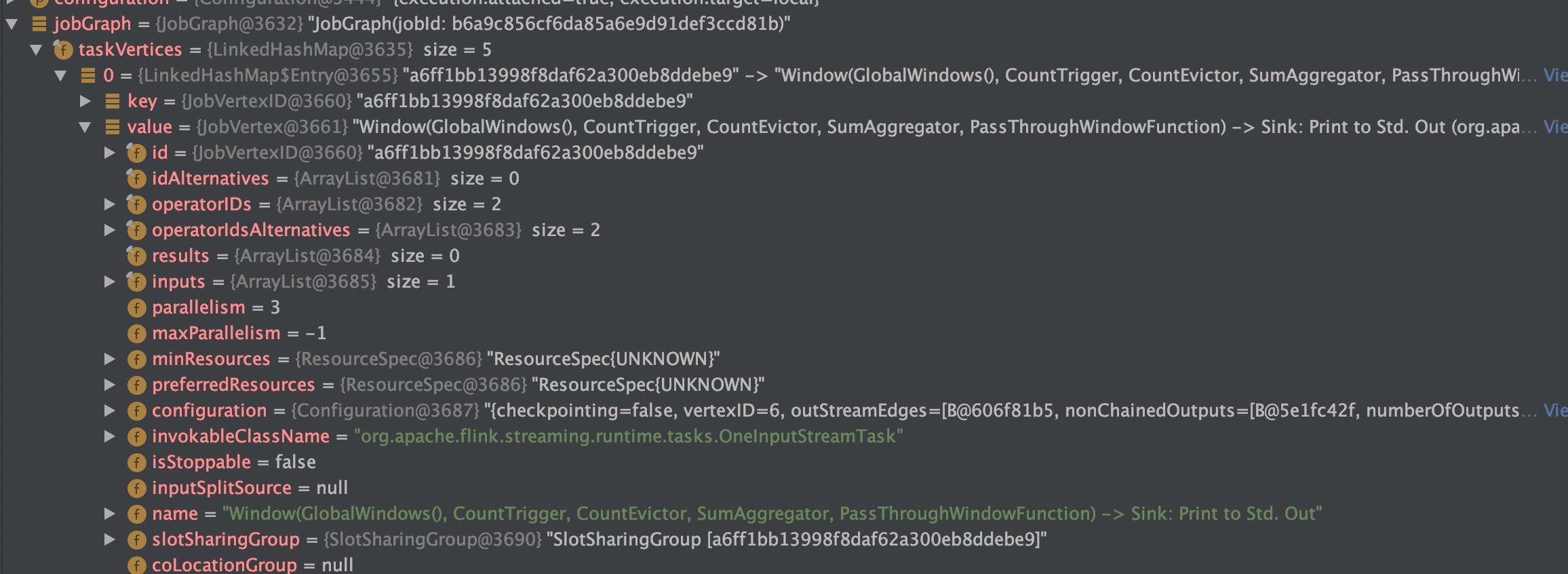
Program -> StreamGraph -> JobGraph -> ExecutionGraph -> 物理执行计划
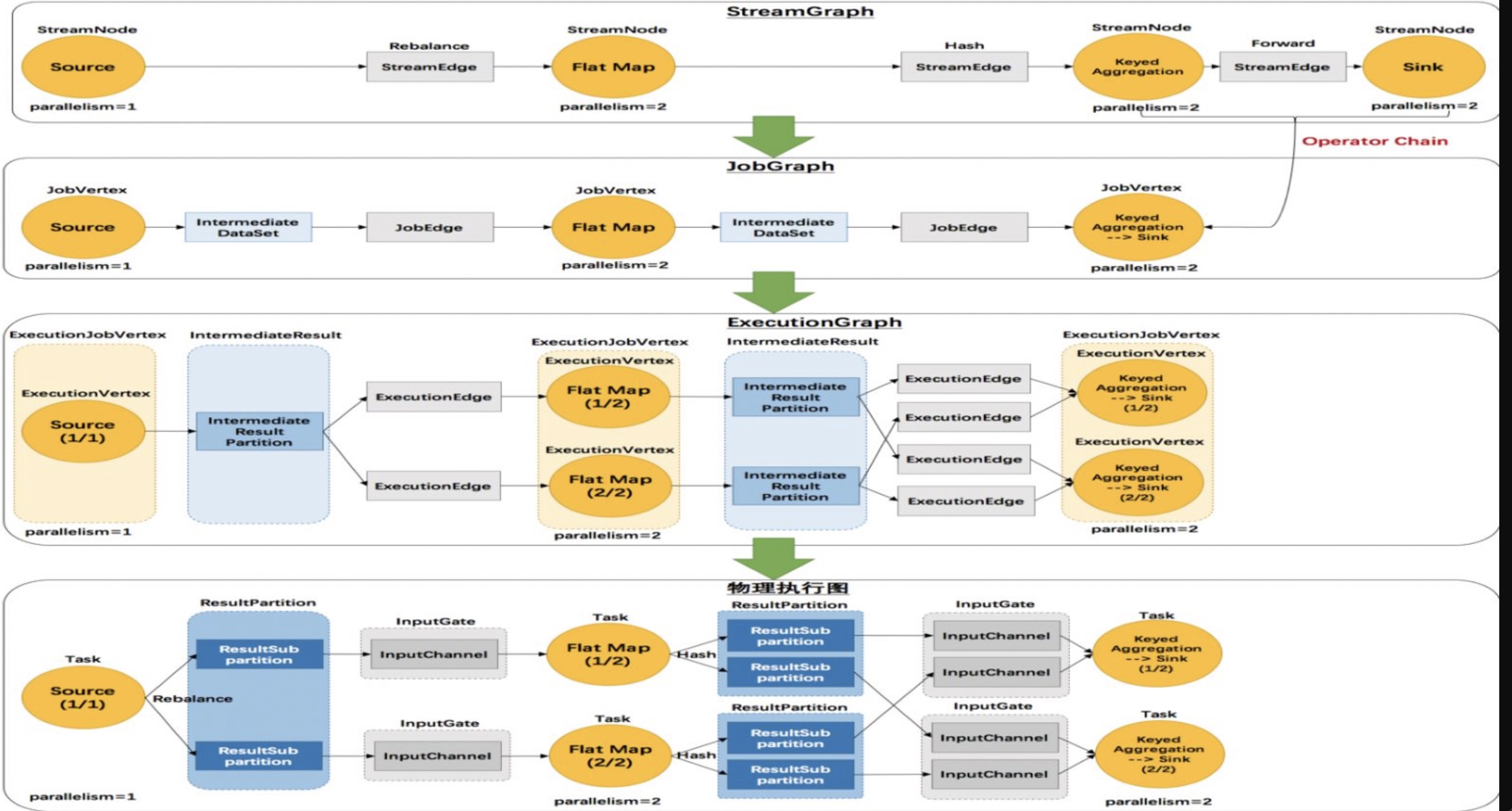
StreamGraph 之后会生成 JobGraph
从 Source 节点开始,然后去遍历寻找能够嵌到一起的 operator,如果能够嵌到一起则嵌到一起,不能嵌到一起的单独生成
jobVertex,通过 JobEdge 链接上下游 JobVertex,最终形成JobVertex层面的 DAG。将多个符合条件的节点串联(Chain) 在一起形成一个节点,从而减少数据在不同节点之间流动所产生的序列化、反序列化、网络传输的开销。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val parameterTool = ParameterTool.fromArgs(args)
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
val text = env.readTextFile(parameterTool.get("input")).setParallelism(1)
env.getConfig.setGlobalJobParameters(parameterTool)
val windowSize = parameterTool.getInt("window", 10)
val slideSize = parameterTool.getInt("slide", 5)
val counts = text.flatMap(_.split(",")).map((_, 1)).setParallelism(4)
.slotSharingGroup("flatmap_sg")
.keyBy(0)
.countWindow(windowSize, slideSize)
.sum(1).setParallelism(3).slotSharingGroup("sum_sg")
counts.print().setParallelism(3)
env.execute("test")
}
JobGraph 生成入口
// org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment.java
/**
* Triggers the program execution. The environment will execute all parts of
* the program that have resulted in a "sink" operation. Sink operations are
* for example printing results or forwarding them to a message queue.
*
* <p>The program execution will be logged and displayed with the provided name
*
* @param jobName
* Desired name of the job
* @return The result of the job execution, containing elapsed time and accumulators.
* @throws Exception which occurs during job execution.
*/
public JobExecutionResult execute(String jobName) throws Exception {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(jobName, "Streaming Job name should not be null.");
// 生成 StreamGraph
return execute(getStreamGraph(jobName));
}
// org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment.java
/**
* executeAsync(streamGraph)
* -> YarnJobClusterExecutor.execute(streamGraph, configuration)
* -> AbstractJobClusterExecutor.execute; //AbstractJobClusterExecutor 本地提交 job 流程
* -> PipelineExecutorUtils.getJobGraph(pipeline, configuration)
*/
// org.apache.flink.client.deployment.executors.PipelineExecutorUtils
public static JobGraph getJobGraph(@Nonnull final Pipeline pipeline, @Nonnull final Configuration configuration) throws MalformedURLException {
...
final ExecutionConfigAccessor executionConfigAccessor = ExecutionConfigAccessor.fromConfiguration(configuration);
final JobGraph jobGraph = FlinkPipelineTranslationUtil
.getJobGraph(pipeline, configuration, executionConfigAccessor.getParallelism());
configuration
.getOptional(PipelineOptionsInternal.PIPELINE_FIXED_JOB_ID)
.ifPresent(strJobID -> jobGraph.setJobID(JobID.fromHexString(strJobID)));
// 设置 jars
jobGraph.addJars(executionConfigAccessor.getJars());
jobGraph.setClasspaths(executionConfigAccessor.getClasspaths());
jobGraph.setSavepointRestoreSettings(executionConfigAccessor.getSavepointRestoreSettings());
return jobGraph;
}
// org.apache.flink.client.FlinkPipelineTranslationUtil
public static JobGraph getJobGraph(
Pipeline pipeline,
Configuration optimizerConfiguration,
int defaultParallelism) {
FlinkPipelineTranslator pipelineTranslator = getPipelineTranslator(pipeline);
return pipelineTranslator.translateToJobGraph(pipeline,
optimizerConfiguration,
defaultParallelism);
}
// 创建 PipelineTranslator (流批不同)
private static FlinkPipelineTranslator getPipelineTranslator(Pipeline pipeline) {
// 批处理
PlanTranslator planTranslator = new PlanTranslator();
if (planTranslator.canTranslate(pipeline)) {
return planTranslator;
}
// 流处理
StreamGraphTranslator streamGraphTranslator = new StreamGraphTranslator();
if (streamGraphTranslator.canTranslate(pipeline)) {
return streamGraphTranslator;
}
throw new RuntimeException("Translator " + streamGraphTranslator + " cannot translate "
+ "the given pipeline " + pipeline + ".");
}
// org.apache.flink.client.StreamGraphTranslator
public JobGraph translateToJobGraph(
Pipeline pipeline,
Configuration optimizerConfiguration,
int defaultParallelism) {
checkArgument(pipeline instanceof StreamGraph,
"Given pipeline is not a DataStream StreamGraph.");
StreamGraph streamGraph = (StreamGraph) pipeline;
// 调用 StreamGraph.getJobGraph 生成 JobGraph
return streamGraph.getJobGraph(null);
}
// org.apache.flink.streaming.api.graph.StreamGraph
public JobGraph getJobGraph() {
return getJobGraph(null);
}
public JobGraph getJobGraph(@Nullable JobID jobID) {
// 与 streamGraph 相同,有对应的 StreamingJobGraphGenerator 来产生 JobGraph
return StreamingJobGraphGenerator.createJobGraph(this, jobID);
}
构建 JobGraph
// org.apache.flink.streaming.api.graph.StreamingJobGraphGenerator
public static JobGraph createJobGraph(StreamGraph streamGraph, @Nullable JobID jobID) {
return new StreamingJobGraphGenerator(streamGraph, jobID).createJobGraph();
}
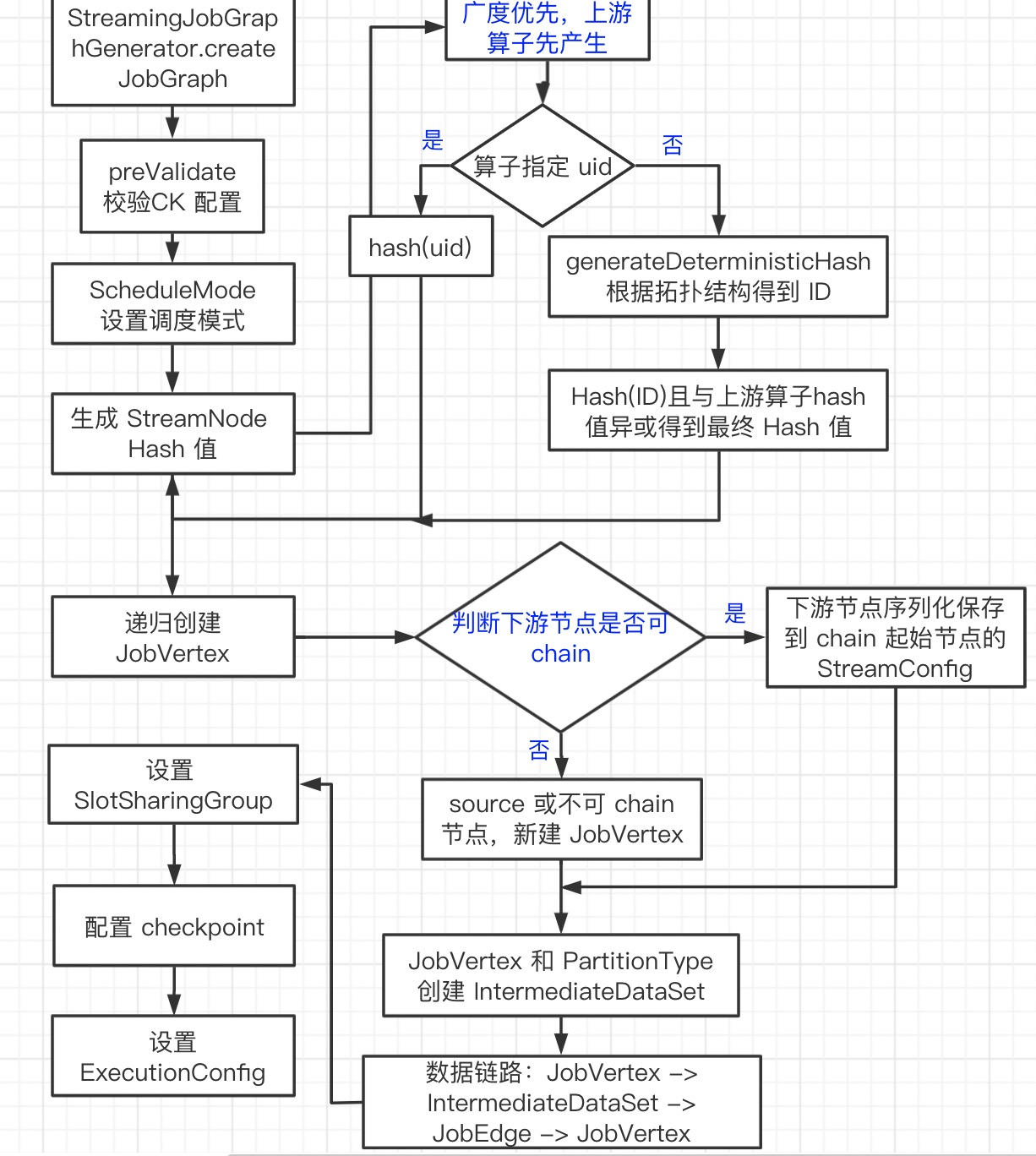
private JobGraph createJobGraph() {
// 校验 checkpoint 配置
preValidate();
// DEFAULT_SCHEDULE_MODE ,在初始化 StreamGraphGenerator 时设置,
// 设置调度模式,采⽤用的 EAGER 模式,既所有节点都是立即启动的
jobGraph.setScheduleMode(streamGraph.getScheduleMode());
// ⼴度优先遍历 StreamGraph,并且为每个 SteamNode 生成散列值, 这里的散列值产生算法
// 可以保证如果提交的拓扑没有改变,则每次⽣成的散列值都是一样的。一个 StreamNode 对应一个散列值。
Map<Integer, byte[]> hashes = defaultStreamGraphHasher.traverseStreamGraphAndGenerateHashes(streamGraph);
// 为向后兼容性生成遗留版本散列,用户为算子指定 hash 值
List<Map<Integer, byte[]>> legacyHashes = new ArrayList<>(legacyStreamGraphHashers.size());
for (StreamGraphHasher hasher : legacyStreamGraphHashers) {
legacyHashes.add(hasher.traverseStreamGraphAndGenerateHashes(streamGraph));
}
// 重点:⽣成 JobVertex,JobEdge 等,并尽可能地将多个节点 chain 在⼀一起
setChaining(hashes, legacyHashes);
// 将每个 JobVertex 的入边集合也序列化到该 JobVertex 的 StreamConfig 中
// 出边集合已经在 setChaining 的时候写⼊了
setPhysicalEdges();
// 为每个 JobVertex 指定所属的 SlotSharingGroup 以及针对 Iteration 的头尾设置 CoLocationGroup
setSlotSharingAndCoLocation();
setManagedMemoryFraction(
Collections.unmodifiableMap(jobVertices),
Collections.unmodifiableMap(vertexConfigs),
Collections.unmodifiableMap(chainedConfigs),
id -> streamGraph.getStreamNode(id).getMinResources(),
id -> streamGraph.getStreamNode(id).getManagedMemoryWeight());
// 配置 checkpoint
configureCheckpointing();
jobGraph.setSavepointRestoreSettings(streamGraph.getSavepointRestoreSettings());
// 分布式缓存文件注册 cacheFile
JobGraphUtils.addUserArtifactEntries(streamGraph.getUserArtifacts(), jobGraph);
// 设置 ExecutionConfig
try {
jobGraph.setExecutionConfig(streamGraph.getExecutionConfig());
}
...
return jobGraph;
}
Hash
为每个 StreamNode 产生一个 hash,这个 hash 用来生成 JobGraph 中对应的 JobVertex 的 ID。在 Flink 中,当需要状态恢复时,根据 StreamNode 的 hash 从 CK/SP 中找到相对应的状态。StreamNode 的 hash 可以由用户直接指定或者根据算子拓扑结构生成。在 Flink 中,最好为每个都指定算子ID ( uid(“xxx”) ),当程序升级改变原先拓扑结构后也还能使用之前的状态。
// org.apache.flink.streaming.api.graph.StreamGraphHasherV2
public Map<Integer, byte[]> traverseStreamGraphAndGenerateHashes(StreamGraph streamGraph) {
// hash 算法 Murmur3_128HashFunction
final HashFunction hashFunction = Hashing.murmur3_128(0);
final Map<Integer, byte[]> hashes = new HashMap<>();
Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet<>();
Queue<StreamNode> remaining = new ArrayDeque<>();
List<Integer> sources = new ArrayList<>();
for (Integer sourceNodeId : streamGraph.getSourceIDs()) {
sources.add(sourceNodeId);
}
// 确保每次 source 的顺序都相同,才能保证每次生成哈希生成相同
Collections.sort(sources);
// 以广度优先的方式遍历图形,从 source 开始
for (Integer sourceNodeId : sources) {
remaining.add(streamGraph.getStreamNode(sourceNodeId));
visited.add(sourceNodeId);
}
StreamNode currentNode;
while ((currentNode = remaining.poll()) != null) {
// 生成 hash
if (generateNodeHash(currentNode, hashFunction, hashes, streamGraph.isChainingEnabled(), streamGraph)) {
// 子节点
for (StreamEdge outEdge : currentNode.getOutEdges()) {
StreamNode child = streamGraph.getTargetVertex(outEdge);
if (!visited.contains(child.getId())) {
remaining.add(child);
visited.add(child.getId());
}
}
} else {
// We will revisit this later.
visited.remove(currentNode.getId());
}
}
return hashes;
}
// hash 生成过程
private boolean generateNodeHash(
StreamNode node,
HashFunction hashFunction,
Map<Integer, byte[]> hashes,
boolean isChainingEnabled,
StreamGraph streamGraph) {
// 获取用户为算子指定的 uid
String userSpecifiedHash = node.getTransformationUID();
if (userSpecifiedHash == null) {
// 用户无指定 uid
for (StreamEdge inEdge : node.getInEdges()) {
// 必须保证上游算子先生成 hash
if (!hashes.containsKey(inEdge.getSourceId())) {
return false;
}
}
Hasher hasher = hashFunction.newHasher();
byte[] hash = generateDeterministicHash(node, hasher, hashes, isChainingEnabled, streamGraph);
if (hashes.put(node.getId(), hash) != null) {
// Sanity check
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected state. Tried to add node hash " +
"twice. This is probably a bug in the JobGraph generator.");
}
return true;
} else {
// 若用户指定 uid,直接 hash(uid)
Hasher hasher = hashFunction.newHasher();
byte[] hash = generateUserSpecifiedHash(node, hasher);
// 保证 hash 值无重复
for (byte[] previousHash : hashes.values()) {
if (Arrays.equals(previousHash, hash)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Hash collision on user-specified ID " +
"\"" + userSpecifiedHash + "\". " +
"Most likely cause is a non-unique ID. Please check that all IDs " +
"specified via `uid(String)` are unique.");
}
}
if (hashes.put(node.getId(), hash) != null) {
// Sanity check
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected state. Tried to add node hash " +
"twice. This is probably a bug in the JobGraph generator.");
}
return true;
}
}
// 用户无指定 uid 时 hash 过程
private byte[] generateDeterministicHash(
StreamNode node,
Hasher hasher,
Map<Integer, byte[]> hashes,
boolean isChainingEnabled,
StreamGraph streamGraph) {
// 第一步
// 当前 StreamNode 之前已经处理过的节点的个数,作为当前 StreamNode id,添加到 hasher
// 没有使用 StreamNode id,因为此 id 生成取决于算子添加顺序
generateNodeLocalHash(hasher, hashes.size());
// 第二步
// 若下游算子可以 chain,则再次将处理过的节点的个数加入 hash
for (StreamEdge outEdge : node.getOutEdges()) {
if (isChainable(outEdge, isChainingEnabled, streamGraph)) {
generateNodeLocalHash(hasher, hashes.size());
}
}
byte[] hash = hasher.hash().asBytes();
// 验证上游算子是否已全部得到 hash 值
for (StreamEdge inEdge : node.getInEdges()) {
byte[] otherHash = hashes.get(inEdge.getSourceId());
...
// 第三步
// 与所有上游算子 hash 值进行位操作
for (int j = 0; j < hash.length; j++) {
hash[j] = (byte) (hash[j] * 37 ^ otherHash[j]);
}
}
...
return hash;
}
- 算子指定 uid,直接 hash uid 得到 StreamNode 的 hash 值
- 无指定 uid,需要以下三部分共同参与计算
- 当前 StreamNode 之前已经处理过的节点的个数,作为当前 StreamNode 的 id,添加到 hasher 中
- 遍历当前 StreamNode 输出的每个 StreamEdge,并判断当前 StreamNode 与这个 StreamEdge 的目标 StreamNode 是否可以进行链接,如果可以,则将当前 StreamNode 的 id 继续放入 hasher 中
- 上述步骤后产生的字节数据,与当前 StreamNode 的所有输入 StreamNode 对应的字节数据,进行相应的位操作,最终得到的字节数据,就是当前 StreamNode 对应的长度为 16 的字节数组。
Chaining
// org.apache.flink.streaming.api.graph.StreamingJobGraphGenerator
/**
* 从数据源递归创建 JobVertex
*/
private void setChaining(Map<Integer, byte[]> hashes, List<Map<Integer, byte[]>> legacyHashes) {
for (Integer sourceNodeId : streamGraph.getSourceIDs()) {
createChain(
sourceNodeId,
0,
new OperatorChainInfo(sourceNodeId, hashes, legacyHashes, streamGraph));
}
}
private List<StreamEdge> createChain(Integer currentNodeId, int chainIndex, OperatorChainInfo chainInfo) {
Integer startNodeId = chainInfo.getStartNodeId();
// 每个 startNodeId 只一次
if (!builtVertices.contains(startNodeId)) {
// 当前链的输出 Edges (不可 chain 节点)
List<StreamEdge> transitiveOutEdges = new ArrayList<StreamEdge>();
// 可以与当前节点 chain 的 StreamEdge
List<StreamEdge> chainableOutputs = new ArrayList<StreamEdge>();
// 不可以与当前节点 chain 的 StreamEdge
List<StreamEdge> nonChainableOutputs = new ArrayList<StreamEdge>();
StreamNode currentNode = streamGraph.getStreamNode(currentNodeId);
for (StreamEdge outEdge : currentNode.getOutEdges()) {
// 判断是否可以 chain
if (isChainable(outEdge, streamGraph)) {
chainableOutputs.add(outEdge);
} else {
nonChainableOutputs.add(outEdge);
}
}
for (StreamEdge chainable : chainableOutputs) {
// 可 chain 递归调用,chainIndex + 1
transitiveOutEdges.addAll(
createChain(chainable.getTargetId(), chainIndex + 1, chainInfo));
}
// 不可 chain,直接加入 transitiveOutEdges,然后递归调用,注意 chainIndex = 0
for (StreamEdge nonChainable : nonChainableOutputs) {
transitiveOutEdges.add(nonChainable);
createChain(nonChainable.getTargetId(), 0, chainInfo.newChain(nonChainable.getTargetId()));
}
// ⽣成当前节点的显示名:operatorName + 可 chain 节点的 operatorName (每个算子有固定的 operatorName)
chainedNames.put(currentNodeId, createChainedName(currentNodeId, chainableOutputs));
chainedMinResources.put(currentNodeId, createChainedMinResources(currentNodeId, chainableOutputs));
chainedPreferredResources.put(currentNodeId, createChainedPreferredResources(currentNodeId, chainableOutputs));
OperatorID currentOperatorId = chainInfo.addNodeToChain(currentNodeId, chainedNames.get(currentNodeId));
if (currentNode.getInputFormat() != null) {
getOrCreateFormatContainer(startNodeId).addInputFormat(currentOperatorId, currentNode.getInputFormat());
}
if (currentNode.getOutputFormat() != null) {
getOrCreateFormatContainer(startNodeId).addOutputFormat(currentOperatorId, currentNode.getOutputFormat());
}
// 如果当前节点是起始节点, 则直接创建 JobVertex 并返回 StreamConfig
// 否则先创建⼀个空的 StreamConfig
StreamConfig config = currentNodeId.equals(startNodeId)
? createJobVertex(startNodeId, chainInfo)
: new StreamConfig(new Configuration());
// 设置 JobVertex 的 StreamConfig, 基本上是序列化 StreamNode 中的配置到 StreamConfig 中
// 其中包括 序列化器, StreamOperator, Checkpoint 等相关配置;
setVertexConfig(currentNodeId, config, chainableOutputs, nonChainableOutputs);
if (currentNodeId.equals(startNodeId)) {
// chain 的起始节点标记成
config.setChainStart();
config.setChainIndex(0);
config.setOperatorName(streamGraph.getStreamNode(currentNodeId).getOperatorName());
// 物理出边写入配置, 部署时会⽤到
config.setOutEdgesInOrder(transitiveOutEdges);
config.setOutEdges(streamGraph.getStreamNode(currentNodeId).getOutEdges());
// 将当前节点 (headOfChain) 与所有出边(不可 chain)相连
for (StreamEdge edge : transitiveOutEdges) {
// 通过 StreamEdge 构建出 JobEdge,创建 IntermediateDataSet,⽤来将 JobVertex 和 JobEdge 相连
connect(startNodeId, edge);
}
// 将 chain 中所有子节点的 StreamConfig 写入到 headOfChain 节点的 CHAINED_TASK_CONFIG 配置中
// 部署时,取出 CHAINED_TASK_CONFIG 并生成对应的 ChainOperators (算子)
config.setTransitiveChainedTaskConfigs(chainedConfigs.get(startNodeId));
} else {
// 如果是 chain 中的子节点
chainedConfigs.computeIfAbsent(startNodeId, k -> new HashMap<Integer, StreamConfig>());
config.setChainIndex(chainIndex);
StreamNode node = streamGraph.getStreamNode(currentNodeId);
config.setOperatorName(node.getOperatorName());
// 将当前节点的 StreamConfig 添加到该 chain 的 config 集合中
chainedConfigs.get(startNodeId).put(currentNodeId, config);
}
config.setOperatorID(currentOperatorId);
// 如果节点的输出 StreamEdge 已经为空,则说明是链的结尾
if (chainableOutputs.isEmpty()) {
config.setChainEnd();
}
return transitiveOutEdges;
} else {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
}
public static boolean isChainable(StreamEdge edge, StreamGraph streamGraph) {
// 获取 StreamEdge 的上游和下游 StreamNode
StreamNode upStreamVertex = streamGraph.getSourceVertex(edge);
StreamNode downStreamVertex = streamGraph.getTargetVertex(edge);
/** 判断是否可以 chain
* 一:下游节点只有一个输入
* 二:上下游节点共享槽是同一个
* 三:上下游算子都不为空,
* 上游算子连接策略不为 never 且下游算子连接策略为 always
(连接策略在创建 StreamOperator 时已确定,每个 Operator 有特定的连接策略)
* 四:edge 分区函数是 ForwardPartitioner
* 五:shuffle 模式不是 Batch(生成者全部生成后才开始消费)
* 六:上下游并行度相同
* 七:chain enable
*/
return downStreamVertex.getInEdges().size() == 1
&& upStreamVertex.isSameSlotSharingGroup(downStreamVertex)
&& areOperatorsChainable(upStreamVertex, downStreamVertex, streamGraph)
&& (edge.getPartitioner() instanceof ForwardPartitioner)
&& edge.getShuffleMode() != ShuffleMode.BATCH
&& upStreamVertex.getParallelism() == downStreamVertex.getParallelism()
&& streamGraph.isChainingEnabled();
}
- startNodeId 已经被构建完成,则直接返回一个空集合
- startNodeId 没有构建,则开始新的构建
- 递归构建链的下游节点(递归寻找嵌到一起的 operator,不能嵌到一起的节点单独生成 jobVertex),在下游节点都递归构建完成后,再构建当前节点
- 如果当前节点是一个链的起始节点,则新建
JobVertex,并将相关配置都通过StreamConfig提供的接口,配置到JobVertex的 configuration 属性中 - 如果是链的中间节点,则相关配置(差不多是整个 StreamNode)添加到其对应的
StreamConfig对象( 以 CHAINED_TASK_CONFIG 为 key)中;在部署时反序列化出算子
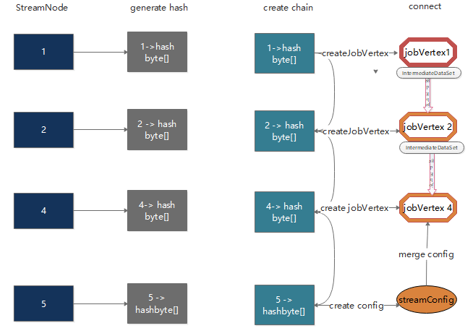
JobVertex
// org.apache.flink.streaming.api.graph.StreamingJobGraphGenerator
private StreamConfig createJobVertex(
Integer streamNodeId,
OperatorChainInfo chainInfo) {
JobVertex jobVertex;
StreamNode streamNode = streamGraph.getStreamNode(streamNodeId);
byte[] hash = chainInfo.getHash(streamNodeId);
...
// 以 streaNode hash 创建 JobVertexID
JobVertexID jobVertexId = new JobVertexID(hash);
List<Tuple2<byte[], byte[]>> chainedOperators = chainInfo.getChainedOperatorHashes(streamNodeId);
List<OperatorIDPair> operatorIDPairs = new ArrayList<>();
if (chainedOperators != null) {
for (Tuple2<byte[], byte[]> chainedOperator : chainedOperators) {
OperatorID userDefinedOperatorID = chainedOperator.f1 == null ? null : new OperatorID(chainedOperator.f1);
operatorIDPairs.add(OperatorIDPair.of(new OperatorID(chainedOperator.f0), userDefinedOperatorID));
}
}
if (chainedInputOutputFormats.containsKey(streamNodeId)) {
jobVertex = new InputOutputFormatVertex(
chainedNames.get(streamNodeId),
jobVertexId,
operatorIDPairs);
chainedInputOutputFormats
.get(streamNodeId)
.write(new TaskConfig(jobVertex.getConfiguration()));
} else {
jobVertex = new JobVertex(
chainedNames.get(streamNodeId),
jobVertexId,
operatorIDPairs);
}
for (OperatorCoordinator.Provider coordinatorProvider : chainInfo.getCoordinatorProviders()) {
try {
jobVertex.addOperatorCoordinator(new SerializedValue<>(coordinatorProvider));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new FlinkRuntimeException(String.format(
"Coordinator Provider for node %s is not serializable.", chainedNames.get(streamNodeId)));
}
}
jobVertex.setResources(chainedMinResources.get(streamNodeId), chainedPreferredResources.get(streamNodeId));
jobVertex.setInvokableClass(streamNode.getJobVertexClass());
int parallelism = streamNode.getParallelism();
if (parallelism > 0) {
jobVertex.setParallelism(parallelism);
} else {
parallelism = jobVertex.getParallelism();
}
jobVertex.setMaxParallelism(streamNode.getMaxParallelism());
...
// TODO: inherit InputDependencyConstraint from the head operator
jobVertex.setInputDependencyConstraint(streamGraph.getExecutionConfig().getDefaultInputDependencyConstraint());
jobVertices.put(streamNodeId, jobVertex);
builtVertices.add(streamNodeId);
jobGraph.addVertex(jobVertex);
return new StreamConfig(jobVertex.getConfiguration());
}
private void connect(Integer headOfChain, StreamEdge edge) {
physicalEdgesInOrder.add(edge);
Integer downStreamVertexID = edge.getTargetId();
// 上下游节点
JobVertex headVertex = jobVertices.get(headOfChain);
JobVertex downStreamVertex = jobVertices.get(downStreamVertexID);
// 下游节点增加一个输入
StreamConfig downStreamConfig = new StreamConfig(downStreamVertex.getConfiguration());
downStreamConfig.setNumberOfInputs(downStreamConfig.getNumberOfInputs() + 1);
StreamPartitioner<?> partitioner = edge.getPartitioner();
ResultPartitionType resultPartitionType;
switch (edge.getShuffleMode()) {
case PIPELINED:
resultPartitionType = ResultPartitionType.PIPELINED_BOUNDED;
break;
case BATCH:
resultPartitionType = ResultPartitionType.BLOCKING;
break;
case UNDEFINED:
resultPartitionType = determineResultPartitionType(partitioner);
break;
default:
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Data exchange mode " +
edge.getShuffleMode() + " is not supported yet.");
}
// 创建 JobEdge 和 IntermediateDataSet
// 根据 StreamPartitioner 类型决定在上游节点(生产者)的子任务和下游节点(消费者)之间的连接模式
JobEdge jobEdge;
if (isPointwisePartitioner(partitioner)) {
jobEdge = downStreamVertex.connectNewDataSetAsInput(
headVertex,
DistributionPattern.POINTWISE,
resultPartitionType);
} else {
jobEdge = downStreamVertex.connectNewDataSetAsInput(
headVertex,
DistributionPattern.ALL_TO_ALL,
resultPartitionType);
}
// 设置数据传输策略,以便在web上显示
jobEdge.setShipStrategyName(partitioner.toString());
...
}
// org.apache.flink.runtime.jobgraph.JobVertex
public JobEdge connectNewDataSetAsInput(
JobVertex input,
DistributionPattern distPattern,
ResultPartitionType partitionType) {
// 创建 IntermediateDataSet 实例,作为上游 JobVertex 的结果输出
// JobVertex 产生的数据被抽象为 IntermediateDataSet
IntermediateDataSet dataSet = input.createAndAddResultDataSet(partitionType);
// IntermediateDataSet 作为 JobEdge 的输入
JobEdge edge = new JobEdge(dataSet, this, distPattern);
// JobVertex 保存输入 JobEdge 信息
this.inputs.add(edge);
// JobEdge 是 IntermediateDataSet 消费者
dataSet.addConsumer(edge);
return edge;
}
整体链路:JobVertex -> IntermediateDataSet -> JobEdge -> JobVertex;
- ⼀个 IntermediateDataSet 有一个消息 producer,可以有多个消费者 JobEdge;
- 一个 JobEdge 则有一个数据源 IntermediateDataSet ,一个目标 JobVertex;
- ⼀个 JobVertex 可以产⽣多个输出 IntermediateDataSet ,也可以接受来自多个 JobEdge 的数据。
JobGraph 的关键在于将多个 StreamNode 优化为一个 JobVertex, 对应的 StreamEdge 则转化为 JobEdge, 并且 JobVertex 和 JobEdge 之间通过 IntermediateDataSet 形成一个生产者和消费者的连接关系。
实例
打断点展示 JobGraph
- IDEA 中 org.apache.flink.client.deployment.executors.LocalExecutor
- Standalone 里 org.apache.flink.client.deployment.executors.AbstractSessionClusterExecutor
- Yarn 上 org.apache.flink.client.deployment.executors.AbstractJobClusterExecutor