Flink 1.11
介绍
Complex Event Processing 复杂事件处理,Flink 提供CEP 库对其进行处理。Flink 在实现CEP时借鉴了 Efficient Pattern Matching over Event Streams 中NFA的模型,了解 NFA 的状态转移流程非常重要。
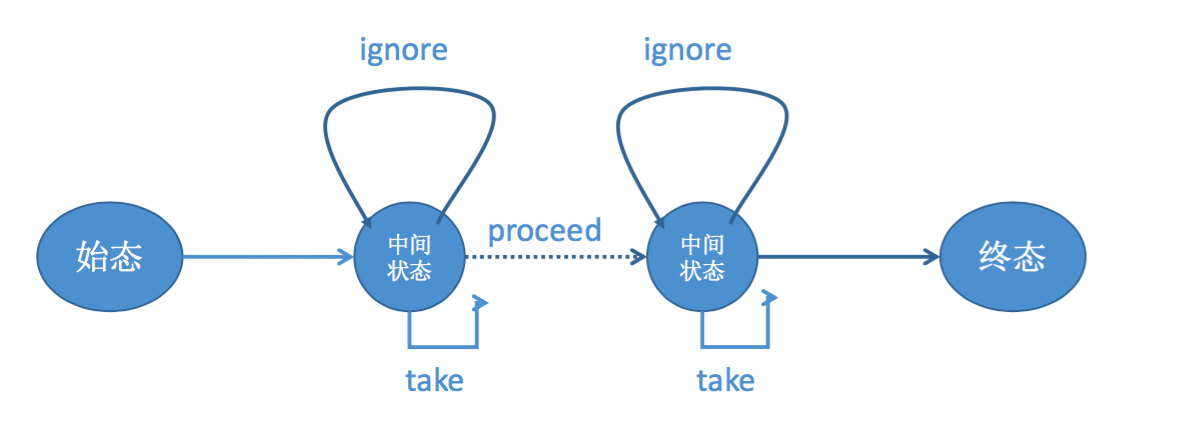
Flink CEP 内部是用 NFA(非确定有限自动机)来实现的,由点和边组成的一个状态图,以一个初始状态作为起点,经过一系列的中间状态,达到终态。点分为起始状态、中间状态、最终状态三种,边分为 take、ignore、proceed 三种
- take:必须存在一个条件判断,当到来的消息满足 take 边条件判断时,把这个消息放入结果集,将状态转移到下一状态。
- ignore:当消息到来时,可以忽略这个消息,将状态自旋在当前不变,是一个自己到自己的状态转移。
- proceed:又叫做状态的空转移,当前状态可以不依赖于消息到来而直接转移到下一状态。举个例子,当用户购买商品时,如果购买前有一个咨询客服的行为,需要把咨询客服行为和购买行为两个消息一起放到结果集中向下游输出;如果购买前没有咨询客服的行为,只需把购买行为放到结果集中向下游输出就可以了。 也就是说,如果有咨询客服的行为,就存在咨询客服状态的上的消息保存,如果没有咨询客服的行为,就不存在咨询客服状态的上的消息保存,咨询客服状态是由一条 proceed 边和下游的购买状态相连。
API 使用层面,如下图:
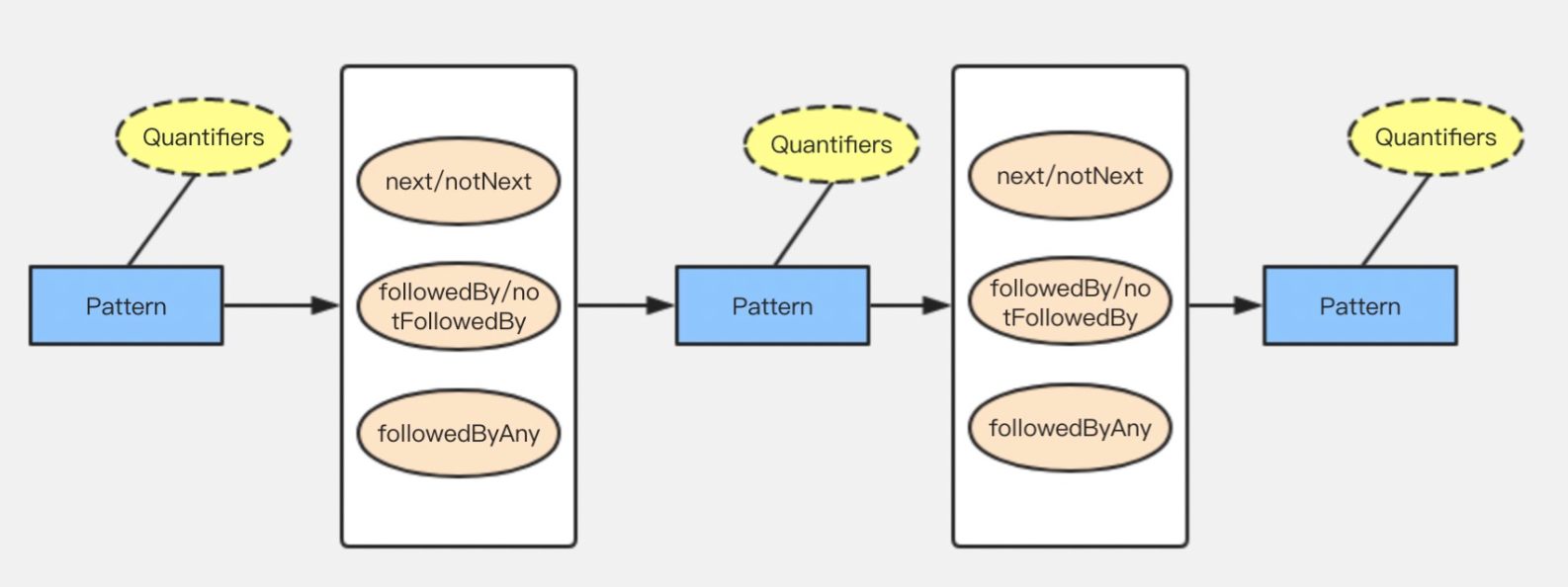
- 蓝色方框代表的是一个个单独的模式
- 浅黄色的椭圆代表的是这个模式上可以添加的属性
- 模式可以发生的循环次数;
times/oneOrMore/timesOrMore - 模式是贪婪的还是可选的;
greedy/optional
- 模式可以发生的循环次数;
- 橘色的椭圆代表的是模式间的关系,定义了多个模式之间是怎么样串联起来的
- 严格连续性:需要消息的顺序到达与模式完全一致;
next/notNext - 宽松连续性:允许忽略不匹配的事件;
followedBy/notFollowedBy - 非确定宽松连性:不仅可以忽略不匹配的事件,也可以忽略已经匹配的事件;
followedByAny
- 严格连续性:需要消息的顺序到达与模式完全一致;
- 事件匹配跳过策略
- NO_SKIP:不跳过,将发出所有可能的匹配事件
- SKIP_TO_FIRST:丢弃包含 PatternName 第一个之前匹配事件的每个部分匹配
- SKIP_TO_LAST:丢弃包含 PatternName 最后一个匹配事件之前的每个部分匹配
- SKIP_PAST_LAST_EVENT:丢弃包含匹配事件的每个部分匹配
- SKIP_TO_NEXT:丢弃以同一事件开始的所有部分匹配
demo
以超时输出的案例来讲解 CEP 的使用
object CEPDemo {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
// env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.IngestionTime)
env.setParallelism(1)
val source = env.socketTextStream("127.0.0.1", 1080)
val eventStream = source.filter(x => {
x.toString.contains(",")
}).map(x => {
val splits = x.toString.split(",")
Event(splits(0), splits(1).toInt)
}).keyBy(_.name)
// 定义模式:10s内 第一次消费大于 30,第二次消费大于 100
val pattern: Pattern[Event, Event] = Pattern
.begin[Event]("start").where(_.cost > 10)
// .next("middle").where(_.cost > 30)
.next("end").where(_.cost > 100).within(Time.seconds(10))
// 定义超时输出 Tag
val outputTag = new OutputTag[String]("timeout")
val patternStream = CEP.pattern(eventStream, pattern)
.flatSelect(outputTag,
new PatternFlatTimeoutFunction[Event, String]{
override def timeout(pattern: util.Map[String, util.List[Event]], timeoutTimestamp: Long, out: Collector[String]): Unit = {
// 超时
for (entry <- pattern) {
for (event <- entry._2) {
out.collect("timeout: " + entry._1 + " " + event.name + "," + event.cost + " ; " + timeoutTimestamp)
}
}
}
},new PatternFlatSelectFunction[Event, String] {
override def flatSelect(pattern: util.Map[String, util.List[Event]], out: Collector[String]): Unit = {
// 正常
for (entry <- pattern) {
for (event <- entry._2) {
out.collect(entry._1 + " " + event.name + "," + event.cost)
}
}
}
})
// 超时输出
patternStream.getSideOutput(outputTag).print()
// 符合条件输出
patternStream.print()
env.execute(this.getClass.getSimpleName)
}
case class Event(name:String, cost:Int)
}
输入
(base) vendannerdeMacBook-Pro:~ danner$ nc -lk 1080
a,100
a,200
b,100
# 延迟10s
a,10
输出
start a,100
end a,200
timeout: start a,200 ; 1605532649940
当前案例中 socketStream keyBy 分组后,pattern 分别对齐匹配
- a 输入两条数据,正常匹配后输出
- 过10s 后,a 再次输入,a 第二条数据显示超时;应该要在10 s 内再输入一条大于100的数据
- b 输入一条数据,后续在无任务输入,但却无任何超时输出
无论是使用事件时间还是处理时间,都需要后续 event 触发超时事件。如果是使用 TimeCharacteristic.IngestionTime 不需要后续 event 触发。
原理
下面来看看,在 Flink 中如何实现 CEP。
Pattern
在上面的例子中,我们使用 begin 和 next 构建一个 Pattern。
// org.apache.flink.cep.scala.pattern.Pattern.scala
/**
* Starts a new pattern sequence. The provided name is the one of the initial pattern
* of the new sequence. Furthermore, the base type of the event sequence is set.
*
* @param name The name of starting pattern of the new pattern sequence
* @tparam X Base type of the event pattern
* @return The first pattern of a pattern sequence
*/
def begin[X](name: String): Pattern[X, X] = Pattern(JPattern.begin(name))
def where(condition: F => Boolean): Pattern[T, F] = {
val condFun = new IterativeCondition[F] {
val cleanCond = cep.scala.cleanClosure(condition)
override def filter(value: F, ctx: JContext[F]): Boolean = cleanCond(value)
}
where(condFun)
}
def where(condition: IterativeCondition[F]): Pattern[T, F] = {
jPattern.where(condition)
this
}
def next(name: String): Pattern[T, T] = {
Pattern[T, T](jPattern.next(name))
}
def within(windowTime: Time): Pattern[T, F] = {
jPattern.within(windowTime)
this
}
// org.apache.flink.cep.pattern.Pattern.java
/** Name of the pattern. */
private final String name;
/** Previous pattern. */
private final Pattern<T, ? extends T> previous;
/** The condition an event has to satisfy to be considered a matched. */
private IterativeCondition<F> condition;
/** Window length in which the pattern match has to occur. */
private Time windowTime;
protected Pattern(
final String name,
final Pattern<T, ? extends T> previous,
final ConsumingStrategy consumingStrategy,
final AfterMatchSkipStrategy afterMatchSkipStrategy) {
this.name = name;
this.previous = previous;
this.quantifier = Quantifier.one(consumingStrategy);
this.afterMatchSkipStrategy = afterMatchSkipStrategy;
}
// previous 为 null
public static <X> Pattern<X, X> begin(final String name) {
return new Pattern<>(name, null, ConsumingStrategy.STRICT, AfterMatchSkipStrategy.noSkip());
}
// previous 为 当前 pattern
public Pattern<T, T> next(final String name) {
return new Pattern<>(name, this, ConsumingStrategy.STRICT, afterMatchSkipStrategy);
}
public Pattern<T, F> within(Time windowTime) {
if (windowTime != null) {
this.windowTime = windowTime;
}
return this;
}
public Pattern<T, F> where(IterativeCondition<F> condition) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(condition, "The condition cannot be null.");
ClosureCleaner.clean(condition, ExecutionConfig.ClosureCleanerLevel.RECURSIVE, true);
if (this.condition == null) {
this.condition = condition;
} else {
this.condition = new RichAndCondition<>(this.condition, condition);
}
return this;
}
jPattern 是 Java 版本的 Pattern。
- begin:新建一个
Pattern - where:给当前
Pattern增加condition - next:新建一个
Pattern,并将当前Pattern赋予 previous - within:当前
Pattern的 windowTime 属性赋值
构建完成应该是一条 Pattern 的单向链,返回的是最后一个 Pattern。
PatternStream
得到一条 Pattern 链后,与 Stream 合成 PatternStream。
// org.apache.flink.cep.scala.CEP.scala
def pattern[T](input: DataStream[T], pattern: Pattern[T, _ <: T]): PatternStream[T] = {
wrapPatternStream(JCEP.pattern(input.javaStream, pattern.wrappedPattern))
}
// org.apache.flink.cep.CEP.java
public static <T> PatternStream<T> pattern(DataStream<T> input, Pattern<T, ?> pattern) {
return new PatternStream<>(input, pattern);
}
// org.apache.flink.cep.PatternStream
// PatternStream 其实不是 DataStream 类,只是对创建 parttern stream 封装了
// 本例中 PatternStream 创建一个 SingleOutputStreamOperator
private final PatternStreamBuilder<T> builder;
private PatternStream(final PatternStreamBuilder<T> builder) {
this.builder = checkNotNull(builder);
}
PatternStream(final DataStream<T> inputStream, final Pattern<T, ?> pattern) {
this(PatternStreamBuilder.forStreamAndPattern(inputStream, pattern));
}
// org.apache.flink.cep.PatternStreamBuilder
static <IN> PatternStreamBuilder<IN> forStreamAndPattern(final DataStream<IN> inputStream, final Pattern<IN, ?> pattern) {
return new PatternStreamBuilder<>(inputStream, pattern, null, null);
}
private PatternStreamBuilder(
final DataStream<IN> inputStream,
final Pattern<IN, ?> pattern,
@Nullable final EventComparator<IN> comparator,
@Nullable final OutputTag<IN> lateDataOutputTag) {
this.inputStream = checkNotNull(inputStream);
this.pattern = checkNotNull(pattern);
this.comparator = comparator;
this.lateDataOutputTag = lateDataOutputTag;
}
以上得到 PatternStreamBuilder,这里是想创建什么呢?
// org.apache.flink.cep.scala.PatternStream
def flatSelect[L: TypeInformation, R: TypeInformation](
outputTag: OutputTag[L],
patternFlatTimeoutFunction: PatternFlatTimeoutFunction[T, L],
patternFlatSelectFunction: PatternFlatSelectFunction[T, R])
: DataStream[R] = {
...
asScalaStream(
jPatternStream.flatSelect(
outputTag,
cleanedTimeout,
implicitly[TypeInformation[R]],
cleanedSelect))
}
// org.apache.flink.cep.PatternStream
public <L, R> SingleOutputStreamOperator<R> flatSelect(
final OutputTag<L> timedOutPartialMatchesTag,
final PatternFlatTimeoutFunction<T, L> patternFlatTimeoutFunction,
final TypeInformation<R> outTypeInfo,
final PatternFlatSelectFunction<T, R> patternFlatSelectFunction) {
//
final PatternProcessFunction<T, R> processFunction =
fromFlatSelect(builder.clean(patternFlatSelectFunction))
.withTimeoutHandler(timedOutPartialMatchesTag, builder.clean(patternFlatTimeoutFunction))
.build();
// 创建 SingleOutputStreamOperator DataStream
return process(processFunction, outTypeInfo);
}
public <R> SingleOutputStreamOperator<R> process(
final PatternProcessFunction<T, R> patternProcessFunction,
final TypeInformation<R> outTypeInfo) {
// build SingleOutputStreamOperator
return builder.build(
outTypeInfo,
builder.clean(patternProcessFunction));
}
// org.apache.flink.cep.PatternProcessFunctionBuilder
static <IN, OUT> FlatSelectBuilder<IN, OUT> fromFlatSelect(final PatternFlatSelectFunction<IN, OUT> function) {
return new FlatSelectBuilder<>(function);
}
static class FlatSelectBuilder<IN, OUT> {
private final PatternFlatSelectFunction<IN, OUT> flatSelectFunction;
FlatSelectBuilder(PatternFlatSelectFunction<IN, OUT> function) {
this.flatSelectFunction = checkNotNull(function);
}
<TIMED_OUT> FlatTimeoutSelectBuilder<IN, OUT, TIMED_OUT> withTimeoutHandler(
final OutputTag<TIMED_OUT> outputTag,
final PatternFlatTimeoutFunction<IN, TIMED_OUT> timeoutHandler) {
return new FlatTimeoutSelectBuilder<>(flatSelectFunction, timeoutHandler, outputTag);
}
PatternProcessFunction<IN, OUT> build() {
return new PatternFlatSelectAdapter<>(flatSelectFunction);
}
}
// org.apache.flink.cep.PatternProcessFunctionBuilder
static class FlatTimeoutSelectBuilder<IN, OUT, TIMED_OUT> {
private final PatternFlatSelectFunction<IN, OUT> flatSelectFunction;
private final PatternFlatTimeoutFunction<IN, TIMED_OUT> timeoutHandler;
private final OutputTag<TIMED_OUT> outputTag;
FlatTimeoutSelectBuilder(
final PatternFlatSelectFunction<IN, OUT> flatSelectFunction,
final PatternFlatTimeoutFunction<IN, TIMED_OUT> timeoutHandler,
final OutputTag<TIMED_OUT> outputTag) {
this.flatSelectFunction = checkNotNull(flatSelectFunction);
this.timeoutHandler = checkNotNull(timeoutHandler);
this.outputTag = checkNotNull(outputTag);
}
PatternProcessFunction<IN, OUT> build() {
return new PatternTimeoutFlatSelectAdapter<>(flatSelectFunction, timeoutHandler, outputTag);
}
}
// org.apache.flink.cep.functions.adaptors.PatternTimeoutFlatSelectAdapter
public class PatternTimeoutFlatSelectAdapter<IN, OUT, T>
extends PatternFlatSelectAdapter<IN, OUT>
implements TimedOutPartialMatchHandler<IN> {
private final PatternFlatTimeoutFunction<IN, T> flatTimeoutFunction;
private final OutputTag<T> timedOutPartialMatchesTag;
private transient SideCollector<T> sideCollector;
public PatternTimeoutFlatSelectAdapter(
PatternFlatSelectFunction<IN, OUT> flatSelectFunction,
PatternFlatTimeoutFunction<IN, T> flatTimeoutFunction,
OutputTag<T> timedOutPartialMatchesTag) {
super(flatSelectFunction);
this.flatTimeoutFunction = checkNotNull(flatTimeoutFunction);
this.timedOutPartialMatchesTag = checkNotNull(timedOutPartialMatchesTag);
}
上面的代码转了好几层,但 processFunction 最终实现是 PatternTimeoutFlatSelectAdapter,包含处理和超时函数以及超时 Tag。build 函数返回的是 SingleOutputStreamOperator
// org.apache.flink.cep.PatternStreamBuilder
<OUT, K> SingleOutputStreamOperator<OUT> build(
final TypeInformation<OUT> outTypeInfo,
final PatternProcessFunction<IN, OUT> processFunction) {
checkNotNull(outTypeInfo);
checkNotNull(processFunction);
final TypeSerializer<IN> inputSerializer = inputStream.getType().createSerializer(inputStream.getExecutionConfig());
// 时间属性
final boolean isProcessingTime = inputStream.getExecutionEnvironment().getStreamTimeCharacteristic() == TimeCharacteristic.ProcessingTime;
// 超时标识
final boolean timeoutHandling = processFunction instanceof TimedOutPartialMatchHandler;
// NFACompiler:根据 pattern 创建
// NFACompiler 将 pattern 转化为 List<State<T>>
final NFACompiler.NFAFactory<IN> nfaFactory = NFACompiler.compileFactory(pattern, timeoutHandling);
//
final CepOperator<IN, K, OUT> operator = new CepOperator<>(
inputSerializer,
isProcessingTime,
nfaFactory,
comparator,
pattern.getAfterMatchSkipStrategy(),
processFunction,
lateDataOutputTag);
final SingleOutputStreamOperator<OUT> patternStream;
if (inputStream instanceof KeyedStream) {
// 本例是 KeyedStream
KeyedStream<IN, K> keyedStream = (KeyedStream<IN, K>) inputStream;
// 将 CepOperator 转化成 transform 并加到 env 中,后期生成 streamGraph
// 返回 SingleOutputStreamOperator
patternStream = keyedStream.transform(
"CepOperator",
outTypeInfo,
operator);
} else {
// 注意:如果 inputStream 不是 KeyedStream,会先 keyby 将所有数据到同一个 key
// 为什么这么操作?CepOperator 是对 KeyedStream,所以必须要有这一步
KeySelector<IN, Byte> keySelector = new NullByteKeySelector<>();
patternStream = inputStream.keyBy(keySelector).transform(
"GlobalCepOperator",
outTypeInfo,
operator
).forceNonParallel();
}
return patternStream;
}
本小节主要是利用 pattern 生成 CepOperator,此 Operator 和 InputStream 生成一个新的 DataStream(正常算子操作)。你可以把 pattern 理解为一个算子中的操作,当你要实现一个复杂的逻辑时需要在 processFunction 写很多代码而使用 CEP 只需定义 pattern 即可。
NFA
本节介绍 CepOperator 内容和处理机制。
// org.apache.flink.cep.operator.CepOperator
/**
* CEP pattern operator 只对 KeyedStream 操作。
* 每个 key 都会创建 NFA 以及优先级队列取缓存乱序数据
* NFA 和 队列都会使用 state 保存
*/
@Internal
public class CepOperator<IN, KEY, OUT>
extends AbstractUdfStreamOperator<OUT, PatternProcessFunction<IN, OUT>>
implements OneInputStreamOperator<IN, OUT>, Triggerable<KEY, VoidNamespace> {
// 初始化
public void open() throws Exception {
super.open();
timerService = getInternalTimerService(
"watermark-callbacks",
VoidNamespaceSerializer.INSTANCE,
this);
// 创建 nfa
nfa = nfaFactory.createNFA();
nfa.open(cepRuntimeContext, new Configuration());
context = new ContextFunctionImpl();
collector = new TimestampedCollector<>(output);
cepTimerService = new TimerServiceImpl();
// metrics
this.numLateRecordsDropped = metrics.counter(LATE_ELEMENTS_DROPPED_METRIC_NAME);
}
// 每来一条 event 数据,调用一次
public void processElement(StreamRecord<IN> element) throws Exception {
if (isProcessingTime) {
if (comparator == null) {
// 本案例 comparator = null
// 获取 state NFAState
NFAState nfaState = getNFAState();
long timestamp = getProcessingTimeService().getCurrentProcessingTime();
// 更新 timestamp,并找出超时的 event
// 结果回调 PatternFlatTimeoutFunction 函数
advanceTime(nfaState, timestamp);
// 处理 event
// 结果回调 PatternFlatSelectFunction
processEvent(nfaState, element.getValue(), timestamp);
// 更新 nfaState
updateNFA(nfaState);
} else {
long currentTime = timerService.currentProcessingTime();
// 以时间戳为 key,event 为 value 缓存到 优先级队列
bufferEvent(element.getValue(), currentTime);
// register a timer for the next millisecond to sort and emit buffered data
timerService.registerProcessingTimeTimer(VoidNamespace.INSTANCE, currentTime + 1);
}
} else {
long timestamp = element.getTimestamp();
IN value = element.getValue();
if (timestamp > lastWatermark) {
// 正常时间到来的数据,buff event 并开始处理
saveRegisterWatermarkTimer();
bufferEvent(value, timestamp);
} else if (lateDataOutputTag != null) {
// 延迟数据,侧流输出
output.collect(lateDataOutputTag, element);
} else {
numLateRecordsDropped.inc();
}
}
}
// 标记时间戳
private void advanceTime(NFAState nfaState, long timestamp) throws Exception {
try (SharedBufferAccessor<IN> sharedBufferAccessor = partialMatches.getAccessor()) {
// advanceTime 下面再分析
Collection<Tuple2<Map<String, List<IN>>, Long>> timedOut =
nfa.advanceTime(sharedBufferAccessor, nfaState, timestamp);
// 有超时 event ,交给自定义的 timeout 函数处理
// 只有新的 event 来才会触发
if (!timedOut.isEmpty()) {
processTimedOutSequences(timedOut);
}
}
}
// nfa 处理新的 event
private void processEvent(NFAState nfaState, IN event, long timestamp) throws Exception {
try (SharedBufferAccessor<IN> sharedBufferAccessor = partialMatches.getAccessor()) {
Collection<Map<String, List<IN>>> patterns =
nfa.process(sharedBufferAccessor, nfaState, event, timestamp, afterMatchSkipStrategy, cepTimerService);
// pattern 匹配到新的 event ,交给自定义的 flatSelect 函数处理
processMatchedSequences(patterns, timestamp);
}
}
// 上面涉及到乱序数据,什么时候处理呢?
// Triggerable eventTime,processTime
public void onEventTime(InternalTimer<KEY, VoidNamespace> timer) throws Exception {
// STEP 1 获取未处理的 event 的 key
PriorityQueue<Long> sortedTimestamps = getSortedTimestamps();
NFAState nfaState = getNFAState();
// STEP 2 处理 process
while (!sortedTimestamps.isEmpty() && sortedTimestamps.peek() <= timerService.currentWatermark()) {
long timestamp = sortedTimestamps.poll();
advanceTime(nfaState, timestamp);
try (Stream<IN> elements = sort(elementQueueState.get(timestamp))) {
elements.forEachOrdered(
event -> {
try {
processEvent(nfaState, event, timestamp);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
);
}
elementQueueState.remove(timestamp);
}
// STEP 3 更新时间戳和处理超时 event
advanceTime(nfaState, timerService.currentWatermark());
// STEP 4 nfaState
updateNFA(nfaState);
if (!sortedTimestamps.isEmpty() || !partialMatches.isEmpty()) {
saveRegisterWatermarkTimer();
}
// STEP 5 更新 watermark
updateLastSeenWatermark(timerService.currentWatermark());
}
public void onProcessingTime(InternalTimer<KEY, VoidNamespace> timer) throws Exception {
// STEP 1 获取未处理的 event 的 key
PriorityQueue<Long> sortedTimestamps = getSortedTimestamps();
NFAState nfa = getNFAState();
// STEP 2 处理 event
while (!sortedTimestamps.isEmpty()) {
long timestamp = sortedTimestamps.poll();
advanceTime(nfa, timestamp);
try (Stream<IN> elements = sort(elementQueueState.get(timestamp))) {
elements.forEachOrdered(
event -> {
try {
processEvent(nfa, event, timestamp);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
);
}
elementQueueState.remove(timestamp);
}
// STEP 3 更新 nfaState
updateNFA(nfa);
}
在介绍 NAF 是如何根据 pattern 处理 event,先介绍几个数据结构:
// org.apache.flink.cep.nfa.NFAState
/**
* State kept for a {@link NFA}. 保留了现有的匹配情况
* managed state
*/
// 每次接收到新的事件,都会遍历 partialMatches 来尝试匹配,
// 看是否能够让 partialMatch 转化为 completedMatch。
// 正在进行的匹配
private Queue<ComputationState> partialMatches;
// 完成的匹配
private Queue<ComputationState> completedMatches;
// org.apache.flink.cep.nfa.sharedbuffer.SharedBuffer
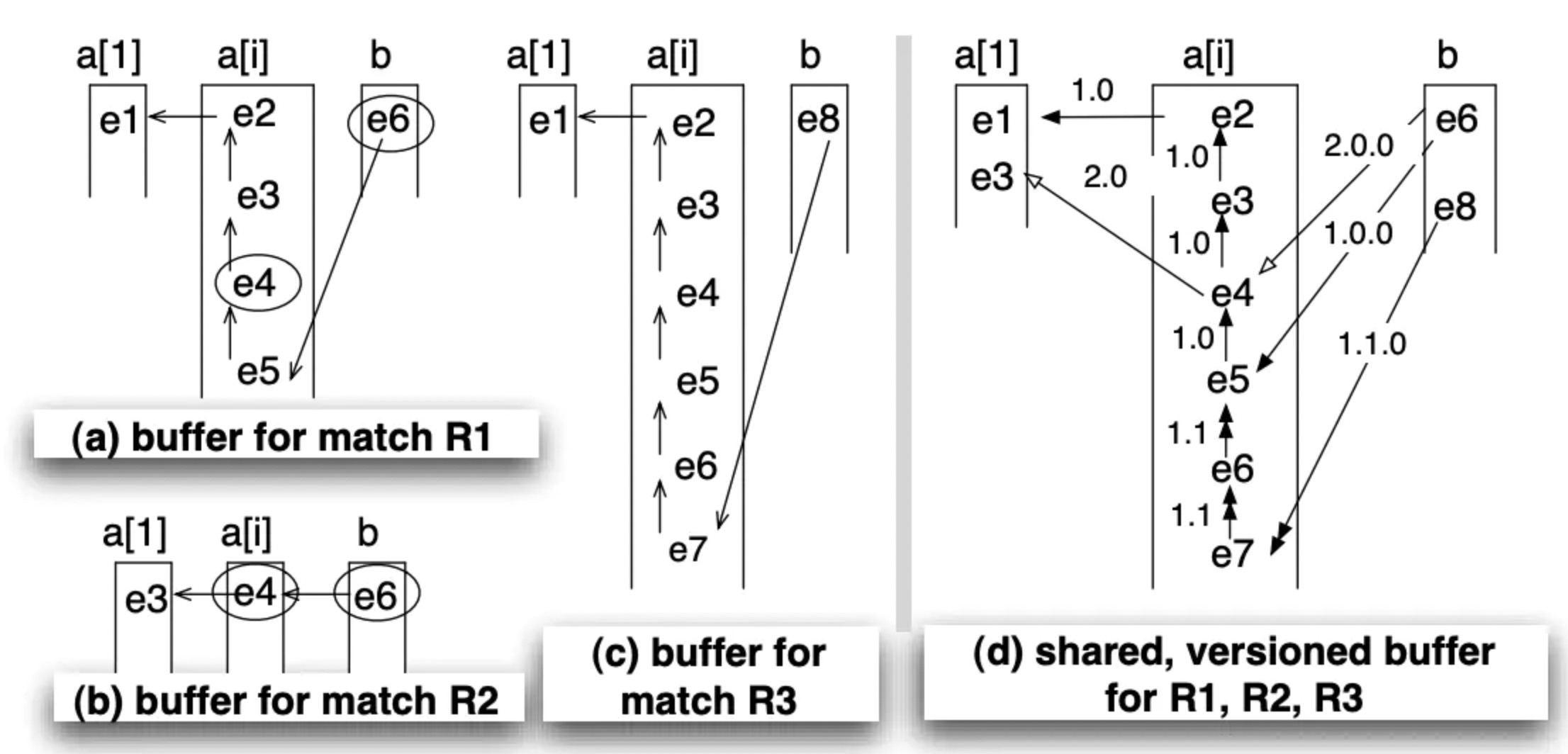
// pattern 是在整个数据流匹配的,只要 pattern 超过两个节点,必然会得到几条匹配序列
// 如果每条匹配列都单独存储,必然是有重复的 event 被保存的,SharedBuffer 实现匹配序列共享缓存
// 如下图:三条匹配序列,分别保存的结果是图 a, b, c;那么 event3,4,6 这三个 event 保存了三次
// 图 d 实现 SharedBuffer,没有重复保存,每个event 保留对上个 event 的引用
// org.apache.flink.cep.nfa.NFA
private Collection<Map<String, List<T>>> doProcess(
final SharedBufferAccessor<T> sharedBufferAccessor,
final NFAState nfaState,
final EventWrapper event,
final AfterMatchSkipStrategy afterMatchSkipStrategy,
final TimerService timerService) throws Exception {
final PriorityQueue<ComputationState> newPartialMatches = new PriorityQueue<>(NFAState.COMPUTATION_STATE_COMPARATOR);
final PriorityQueue<ComputationState> potentialMatches = new PriorityQueue<>(NFAState.COMPUTATION_STATE_COMPARATOR);
// 遍历 partialMatches
for (ComputationState computationState : nfaState.getPartialMatches()) {
// event 根据 pattern,生成 Collection<ComputationState>
// 一个 event 可能会触发 pattern 链的多个节点,生成多个 ComputationState
final Collection<ComputationState> newComputationStates = computeNextStates(
sharedBufferAccessor,
computationState,
event,
timerService);
// ComputationState 有变化,设置可更新状态
if (newComputationStates.size() != 1) {
nfaState.setStateChanged();
} else if (!newComputationStates.iterator().next().equals(computationState)) {
nfaState.setStateChanged();
}
//delay adding new computation states in case a stop state is reached and we discard the path.
final Collection<ComputationState> statesToRetain = new ArrayList<>();
//if stop state reached in this path
boolean shouldDiscardPath = false;
for (final ComputationState newComputationState : newComputationStates) {
if (isFinalState(newComputationState)) {
potentialMatches.add(newComputationState);
} else if (isStopState(newComputationState)) {
// stop 释放当前匹配序列的 event
shouldDiscardPath = true;
sharedBufferAccessor.releaseNode(newComputationState.getPreviousBufferEntry());
} else {
// add new computation state; it will be processed once the next event arrives
statesToRetain.add(newComputationState);
}
}
if (shouldDiscardPath) {
for (final ComputationState state : statesToRetain) {
sharedBufferAccessor.releaseNode(state.getPreviousBufferEntry());
}
} else {
newPartialMatches.addAll(statesToRetain);
}
}
if (!potentialMatches.isEmpty()) {
nfaState.setStateChanged();
}
List<Map<String, List<T>>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (afterMatchSkipStrategy.isSkipStrategy()) {
processMatchesAccordingToSkipStrategy(sharedBufferAccessor,
nfaState,
afterMatchSkipStrategy,
potentialMatches,
newPartialMatches,
result);
} else {
for (ComputationState match : potentialMatches) {
Map<String, List<T>> materializedMatch =
sharedBufferAccessor.materializeMatch(
sharedBufferAccessor.extractPatterns(
match.getPreviousBufferEntry(),
match.getVersion()).get(0)
);
result.add(materializedMatch);
sharedBufferAccessor.releaseNode(match.getPreviousBufferEntry());
}
}
nfaState.setNewPartialMatches(newPartialMatches);
return result;
}
注意以下几点:
- processTime:需要后续 event 触发才能判断之前的 event 是否超时
- eventTime:缓存乱序的 event ,实际应用中需要注意 event 数量
- 每个 key 都会创建 NFA ,这是不容小觑的开销