Flink 1.12.1
Flink SQL 解析和执行流程如下,本节剖析 Operation -> Transformation 的具体流程。
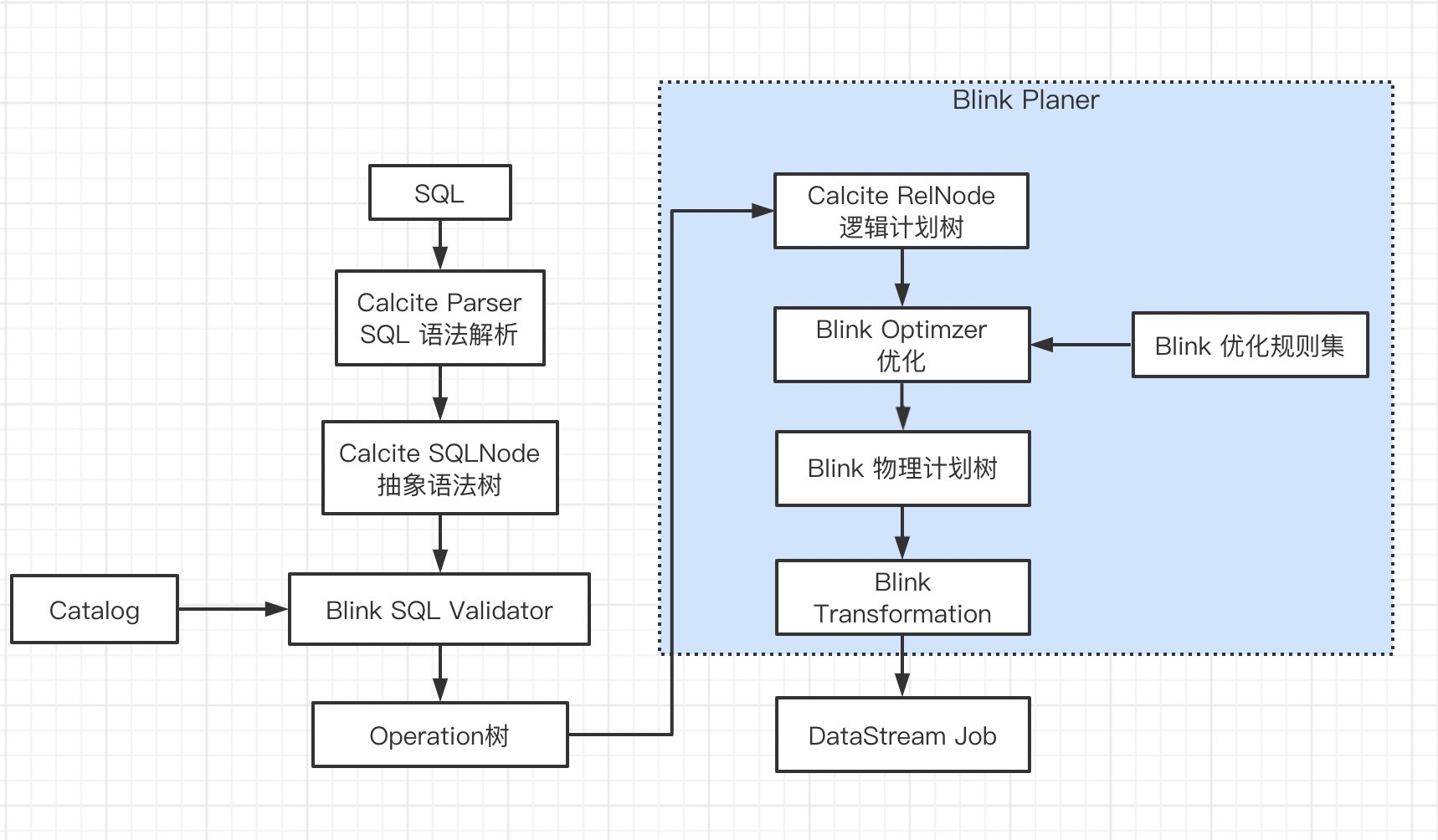
在上一节Flink SQL 执行流程(一) 将 SQL 解析成 Operation 树,本文关注逻辑计划树 -> 物理计划树 -> Transformation。
接着上一节返回 CatalogSinkModifyOperation(内部包含PlannerQueryOperation) 继续往下走。
//org.apache.flink.table.sqlexec.SqlToOperationConverter#convertSqlInsert
return new CatalogSinkModifyOperation(
identifier,
query,
insert.getStaticPartitionKVs(),
insert.isOverwrite(),
Collections.emptyMap());
// org.apache.flink.table.api.internal.TableEnvironmentImpl#executeSql
return executeOperation(operations.get(0));
// org.apache.flink.table.api.internal.TableEnvironmentImpl#executeOperation
private TableResult executeOperation(Operation operation) {
if (operation instanceof ModifyOperation) {
// insert 操作,还需要优化
return executeInternal(Collections.singletonList((ModifyOperation) operation));
public TableResult executeInternal(List<ModifyOperation> operations) {
// 重点:Operation -> Transformation
List<Transformation<?>> transformations = translate(operations);
// insert 表名
List<String> sinkIdentifierNames = extractSinkIdentifierNames(operations);
String jobName = getJobName("insert-into_" + String.join(",", sinkIdentifierNames));
// org.apache.flink.table.planner.delegation.StreamExecutor#createPipeline
Pipeline pipeline = execEnv.createPipeline(transformations, tableConfig, jobName);
try {
JobClient jobClient = execEnv.executeAsync(pipeline);
TableSchema.Builder builder = TableSchema.builder();
Object[] affectedRowCounts = new Long[operations.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < operations.size(); ++i) {
// use sink identifier name as field name
builder.field(sinkIdentifierNames.get(i), DataTypes.BIGINT());
affectedRowCounts[i] = -1L;
}
return TableResultImpl.builder()
.jobClient(jobClient)
.resultKind(ResultKind.SUCCESS_WITH_CONTENT)
.tableSchema(builder.build())
.data(
new InsertResultIterator(
jobClient, Row.of(affectedRowCounts), userClassLoader))
.build();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new TableException("Failed to execute sql", e);
}
}
- Operation -> Transformation
- sinkIdentifierNames:要插入数据的表全路径
- jobName:insert-into_表全路径
- Transformation -> StreamGraph
- executeAsync:异步提交任务,内部流程与 DataStream 流程相同先转换为 JobGraph、上传jar 和配置文件、启动 Yarn AppMaster
显然这就是 Flink 任务的提交流程,本文关注的是第一步(客户端提交流程之前的文章已介绍)。
// org.apache.flink.table.api.internal.TableEnvironmentImpl#translate
private List<Transformation<?>> translate(List<ModifyOperation> modifyOperations) {
return planner.translate(modifyOperations);
}
// org.apache.flink.table.planner.delegation.PlannerBase#translate
override def translate(
modifyOperations: util.List[ModifyOperation]): util.List[Transformation[_]] = {
if (modifyOperations.isEmpty) {
return List.empty[Transformation[_]]
}
// 在转化前先准备 env,transformation 要添加到 env
getExecEnv.configure(
getTableConfig.getConfiguration,
Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader)
overrideEnvParallelism()
// Operation -> Calcite RelNode 逻辑计划
val relNodes = modifyOperations.map(translateToRel)
// 优化 Calcite RelNode
val optimizedRelNodes = optimize(relNodes)
// 优化后的 RelNode -> execNodes
val execNodes = translateToExecNodePlan(optimizedRelNodes)
// execNodes 转化为 transformation
translateToPlan(execNodes)
}
Operation -> Calcite RelNode
// org.apache.flink.table.planner.delegation.PlannerBase#translateToRel
private[flink] def translateToRel(modifyOperation: ModifyOperation): RelNode = {
modifyOperation match {
...
case catalogSink: CatalogSinkModifyOperation =>
// 获取包含的 queryOperation
val input = getRelBuilder.queryOperation(modifyOperation.getChild).build()
val identifier = catalogSink.getTableIdentifier
val dynamicOptions = catalogSink.getDynamicOptions
// getTableSink 构建 Sink,返回(CatalogTable, TableSink实现类)
getTableSink(identifier, dynamicOptions).map {
case (table, sink: TableSink[_]) =>
// check the logical field type and physical field type are compatible
val queryLogicalType = FlinkTypeFactory.toLogicalRowType(input.getRowType)
// validate logical schema and physical schema are compatible
validateLogicalPhysicalTypesCompatible(table, sink, queryLogicalType)
// validate TableSink
validateTableSink(catalogSink, identifier, sink, table.getPartitionKeys)
// validate query schema and sink schema, and apply cast if possible
val query = validateSchemaAndApplyImplicitCast(
input,
TableSchemaUtils.getPhysicalSchema(table.getSchema),
catalogSink.getTableIdentifier,
getTypeFactory)
LogicalLegacySink.create(
query,
sink,
identifier.toString,
table,
catalogSink.getStaticPartitions.toMap)
case (table, sink: DynamicTableSink) =>
// 新版本 dynamic
DynamicSinkUtils.toRel(getRelBuilder, input, catalogSink, sink, table)
} match {
// 返回 RelNode
case Some(sinkRel) => sinkRel
case None =>
throw new TableException(s"Sink ${catalogSink.getTableIdentifier} does not exists")
}
QueryOperationConverter
// org.apache.flink.table.planner.calcite.FlinkRelBuilder
def queryOperation(queryOperation: QueryOperation): RelBuilder = {
val relNode = queryOperation.accept(toRelNodeConverter)
push(relNode)
this
}
private val toRelNodeConverter = {
new QueryOperationConverter(this)
}
QueryOperationConverter :将 Flink 中 QueryOperation 转换为 Calcite 中的关系表达 RelNode。
构建 Sink
// org.apache.flink.table.planner.delegation.PlannerBase#getTableSink
private def getTableSink(
objectIdentifier: ObjectIdentifier,
dynamicOptions: JMap[String, String])
: Option[(CatalogTable, Any)] = {
// 根据表全路径从 Catalog 获取到 CatalogTable
val lookupResult = JavaScalaConversionUtil.toScala(catalogManager.getTable(objectIdentifier))
lookupResult
.map(_.getTable) match {
case Some(table: ConnectorCatalogTable[_, _]) =>
JavaScalaConversionUtil.toScala(table.getTableSink) match {
case Some(sink) => Some(table, sink)
case None => None
}
// 二:获取 Catalog
// 三:获取 TableSink
case Some(table: CatalogTable) =>
val catalog = catalogManager.getCatalog(objectIdentifier.getCatalogName)
val tableToFind = if (dynamicOptions.nonEmpty) {
table.copy(FlinkHints.mergeTableOptions(dynamicOptions, table.getProperties))
} else {
table
}
val isTemporary = lookupResult.get.isTemporary
if (isLegacyConnectorOptions(objectIdentifier, table, isTemporary)) {
val tableSink = TableFactoryUtil.findAndCreateTableSink(
catalog.orElse(null),
objectIdentifier,
tableToFind,
getTableConfig.getConfiguration,
isStreamingMode,
isTemporary)
Option(table, tableSink)
} else {
val tableSink = FactoryUtil.createTableSink(
catalog.orElse(null),
objectIdentifier,
tableToFind,
getTableConfig.getConfiguration,
Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader,
isTemporary)
Option(table, tableSink)
}
case _ => None
}
}
获取 TableSink 时,先判断创建表的 connect 是老的还是新的写法,对应不同处理。新的写法是创建动态表
- connect 是否包含
connector.type,包含代表是老的 Sink - 若不包含,先尝试用老的方法 findAndCreateTableSink 获取下;没有异常表示还是老的创建方式(很严谨),有异常捕捉到下一步
- 新的,创建动态表
创建的过程先判断表所属的 Catalog 有没有表创建的工厂类,有则直接创建;没有再利用 Java SPI 去加载对应的表创建工厂类(Flink SQL 之 Create Table)。
DynamicSinkUtils
DynamicTableSink 转换为 RelNode
// org.apache.flink.table.planner.sinks.DynamicSinkUtils
public static RelNode toRel(
FlinkRelBuilder relBuilder,
RelNode input,
CatalogSinkModifyOperation sinkOperation,
DynamicTableSink sink,
CatalogTable table) {
final FlinkTypeFactory typeFactory = ShortcutUtils.unwrapTypeFactory(relBuilder);
final TableSchema schema = table.getSchema();
// 1. 校验 Sink 和 operation 的分区性/overwrite/元信息 特性是否一直
prepareDynamicSink(sinkOperation, sink, table);
// 2. 校验 operation 和 Sink schema 是否相同
final RelNode query =
validateSchemaAndApplyImplicitCast(
input, schema, sinkOperation.getTableIdentifier(), typeFactory);
relBuilder.push(query);
// 3. 获取表元数据列
final List<Integer> metadataColumns = extractPersistedMetadataColumns(schema);
if (!metadataColumns.isEmpty()) {
pushMetadataProjection(relBuilder, typeFactory, schema, sink);
}
final RelNode finalQuery = relBuilder.build();
return LogicalSink.create(
finalQuery,
sinkOperation.getTableIdentifier(),
table,
sink,
sinkOperation.getStaticPartitions());
}
RelNode 优化
一个 Optimization Engine 包含三个组成部分:
rules:也就是匹配规则,Calcite 内置上百种 Rules 来优化 relational expression,当然也支持自定义 rules;metadata providers:主要是向优化器提供信息,这些信息会有助于指导优化器向着目标(减少整体 cost)进行优化,信息可以包括行数、table 哪一列是唯一列等,也包括计算 RelNode 树中执行 subexpression cost 的函数;planner engines:它的主要目标是进行触发rules来达到指定目标,比如像cost-based optimizer(CBO)的目标是减少 cost(Cost 包括处理的数据行数、CPU cost、IO cost 等)。
优化器的作用是将解析器生成的关系代数表达式转换成执行计划,供执行引擎执行,在这个过程中,会应用一些规则优化,以帮助生成更高效的执行计划。优化器进行优化的地方如过滤条件的下压(push down),在进行 join 操作前,先进行 filter 操作,这样的话就不需要在 join 时进行全量 join,减少参与 join 的数据量等。
Calcite 中 RelOptPlanner 是 Calcite 中优化器的基类。Calcite 中关于优化器提供了两种实现:
HepPlanner:就是基于规则优化RBO的实现,它是一个启发式的优化器,按照规则进行匹配,直到达到次数限制(match 次数限制)或者遍历一遍后不再出现 rule match 的情况才算完成;VolcanoPlanner:就是基于成本优化CBO的实现,它会一直迭代rules,直到找到 cost 最小的 paln。
// org.apache.flink.table.planner.delegation.PlannerBase
val optimizedRelNodes = optimize(relNodes)
-> val optimizedRelNodes = getOptimizer.optimize(relNodes)
// org.apache.flink.table.planner.delegation.StreamPlanner#getOptimizer
override protected def getOptimizer: Optimizer = new StreamCommonSubGraphBasedOptimizer(this)
StreamCommonSubGraphBasedOptimizer
流上的基于子图的优化器,用来优化 Blink 流的 SQL 和 Table。
基于 DAG 的公共子图优化将原始的 RelNode DAG 优化为语义等价的 RelNode DAG。什么是公共子图?子图就是一个逻辑计划树的子树,公共子图也叫公共子树。公共子树就是多颗逻辑计划树相同的子树。Calcite Planner 不支持 DAG (包含了多个 Sink)的优化,所以 RelNode DAG 需要被分解为多颗子树(每颗子树一个根,即只有一个 Sink),每颗子树使用 org.apache.calcite.plan.RelOptPlanner 单独优化。
优化算法的过程如下:
- 首先将 RelNode DAG 分解为多颗子树(Flink 中对应的类为
RelNodeBlock),然后生成一个RelNodeBlock DAG。每个RelNodeBlock只有一个 Sink,代表一颗子树。 - 递归优化
RelNodeBlock,优化顺序是从叶子结点(Source)到根结点(Sink)。非根子树(RelNodeBlock)包装为一个IntermediateRelTable。 - 优化完成之后,将
IntermediateRelTable重新展开生成优化后的 RelNode DAG。
目前,选择这种优化策略主要基于以下考虑。
- 一般来说,使用多个 Sink 的用户倾向于使用 View,View 天然就是一个公共子图
- 经过优化之后,如 Project 下推、filter 下推,在最终的 DAG 中可能就没有公共子图了。
当前的策略可以改进的地方:
- 如何找到公共子图的切分点,如一些 Physical RelNode 可能是从多个 Logical RelNode 转换而来,所以一个合法的切分点一定不在这几个 Logical RelNode 之间
- 优化结果是局部最优(每个子图内最优),不是全局最优
逻辑优化使用的是 Calcite 的 Hep 优化器(基于规则),物理优化阶段使用了 Calcite 的 Hep 规则优化器和 Volcano 优化器(基于代价)。
Blink 为 StreamCommonSubGraphBasedOptimizer 添加很多规则(基本涵盖所有的操作)
// org.apache.flink.table.planner.plan.optimize.StreamCommonSubGraphBasedOptimizer#optimizeTree
val programs = calciteConfig.getStreamProgram
.getOrElse(FlinkStreamProgram.buildProgram(config.getConfiguration))
StreamCommonSubGraphBasedOptimizer 根据规则对每个操作生成对应的 PhysicalNode:以 join 为例,匹配到 StreamPhysicalJoinRule 就会生成 StreamPhysicalJoin PhysicalNode。
RelNode to ExecNode
在 RelNode -> ExecNode 之前,会先进行之前说的优化算法(公共子图)。
每个 FlinkPhysicalRelNode 都有 translateToExecNode 函数,会将 RelNode 转换为 ExecNode。以 StreamPhysicalJoin 为例,得到 StreamExecJoin。
// org.apache.flink.table.planner.plan.nodes.physical.stream.StreamPhysicalJoin#translateToExecNode
override def translateToExecNode(): ExecNode[_] = {
new StreamExecJoin(
joinSpec,
getUniqueKeys(left),
getUniqueKeys(right),
InputProperty.DEFAULT,
InputProperty.DEFAULT,
FlinkTypeFactory.toLogicalRowType(getRowType),
getRelDetailedDescription)
}
ExecNode to Transformation
// org.apache.flink.table.planner.delegation.StreamPlanner#translateToPlan
override protected def translateToPlan(execGraph: ExecNodeGraph): util.List[Transformation[_]] = {
val planner = createDummyPlanner()
// 遍历 execnode
execGraph.getRootNodes.map {
case node: StreamExecNode[_] => node.translateToPlan(planner)
case _ =>
throw new TableException("Cannot generate DataStream due to an invalid logical plan. " +
"This is a bug and should not happen. Please file an issue.")
}
}
// org.apache.flink.table.planner.plan.nodes.exec.ExecNodeBase#translateToPlan
public Transformation<T> translateToPlan(Planner planner) {
if (transformation == null) {
// 最终是调用 execnode.translateToPlanInternal
transformation = translateToPlanInternal((PlannerBase) planner);
if (this instanceof SingleTransformationTranslator) {
if (inputsContainSingleton()) {
transformation.setParallelism(1);
transformation.setMaxParallelism(1);
}
}
}
return transformation;
}
以 StreamExecJoin 为例,translateToPlan 函数返回 TwoInputTransformation,Transformation 中包含 StreamingJoinOperator/StreamingSemiAntiJoinOperator。到这里应该很熟悉了,是 DataStream 的套路,至此 SQL 语句最终生成一连串的 Transformation。
参考资料
Flink 内核原理与实现