在Flip-27 提出了类似于基于MailBox 单线程的执行模型,取代现有的多线程模型(1.10之前的版本)。所有的并发操作都通过队列(mailbox)进行排队,单线程依次处理,这样避免了并发操作。
StreamTask 是上面提及的单线程执行体。线程中会调用 MailboxProcessor 一直处理 mail(其他要执行task、event)。
// org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.tasks.mailbox.MailboxProcessor#runMailboxLoop
public void runMailboxLoop() throws Exception {
suspended = !mailboxLoopRunning;
final TaskMailbox localMailbox = mailbox;
checkState(
localMailbox.isMailboxThread(),
"Method must be executed by declared mailbox thread!");
assert localMailbox.getState() == TaskMailbox.State.OPEN : "Mailbox must be opened!";
final MailboxController defaultActionContext = new MailboxController(this);
while (isNextLoopPossible()) { // !suspended
// The blocking `processMail` call will not return until default action is available.
processMail(localMailbox, false); //检查Mailbox是否有mail,并处理
if (isNextLoopPossible()) {
// event 处理 -> StreamTask.processInput
mailboxDefaultAction.runDefaultAction(
defaultActionContext); // lock is acquired inside default action as needed
}
}
}
整体流程变得非常简单,主线程不断获取mail处理即可。在checkpoint章节,会具体分析如何将消息传入 mailbox。
既然是单线程,那么 event的处理也都是在此线程中处理。以event的流转来分析整个处理流程。
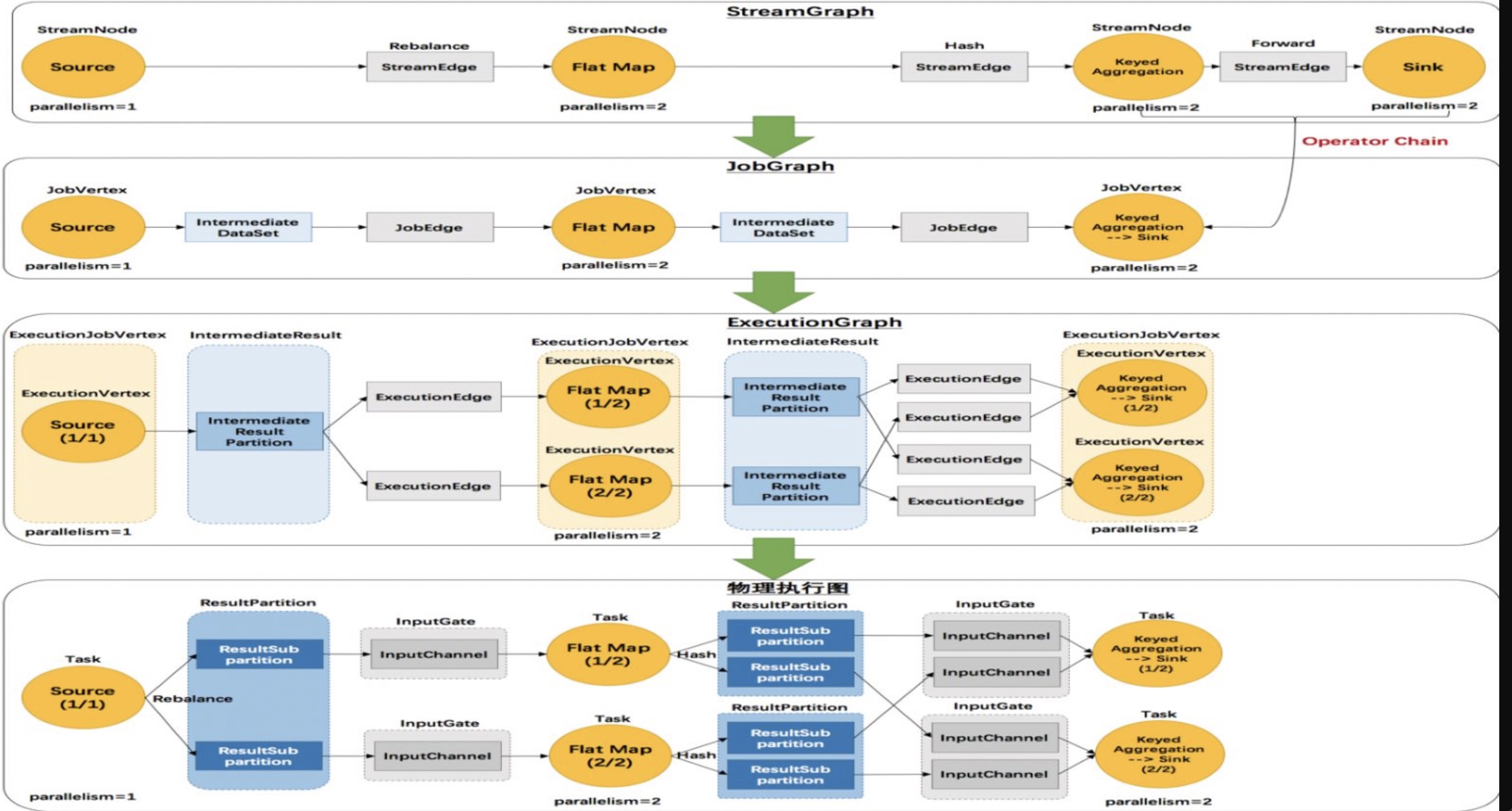
在进入分析之前,先熟悉下几个术语
- InputGate:输入网关,与Edge一一对应,包含一/多个 InputChannel
- InputChannel:对应当前subTask 并行度,有两种实现
- LocalInputChannel:上下游在同个TaskManager
- RemoteInputChannel:上下游不在同个TaskManager,需要跨网络
- InputChannel:对应当前subTask 并行度,有两种实现
- ResultPartition:结果分区,与InputGate 一一对应,包含一/多个ResultSubPartition
- ResultSubPartition:结果子分区,对应下游subTask 并行度,有两种实现
- PipelinedSubpartition:流模式,纯内存,一次性,默认100ms/满足大小后往下游发送
- BoundedBlockingSubpartition:批处理,内存/文件,需要等待上游所有的数据处理完毕
- ResultSubPartition:结果子分区,对应下游subTask 并行度,有两种实现
event 输入、处理、输出,这三个流程分析
输入
// org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.tasks.StreamTask#processInput
protected void processInput(MailboxDefaultAction.Controller controller) throws Exception {
// 处理 event
InputStatus status = inputProcessor.processInput();
if (status == InputStatus.MORE_AVAILABLE && recordWriter.isAvailable()) {
// MORE_AVAILABLE(表示还有可用的数据等待处理)并且 recordWriter 可用(之前的异步操作已经处理完成)
return;
}
if (status == InputStatus.END_OF_INPUT) {
// END_OF_INPUT,它表示数据处理完成,这里就会告诉 MailBox 数据已经处理完成了
controller.allActionsCompleted();
return;
}
TaskIOMetricGroup ioMetrics = getEnvironment().getMetricGroup().getIOMetricGroup();
TimerGauge timer;
CompletableFuture<?> resumeFuture;
if (!recordWriter.isAvailable()) {
// 反压时间,写出buffer 满了,导致recordWriter 无法继续写入,阻塞
// 等是否buffer 后,唤醒
timer = ioMetrics.getBackPressuredTimePerSecond();
resumeFuture = recordWriter.getAvailableFuture();
} else {
// 等待时间,等到有数据进 inputGate(inputChannelsWithData)
timer = ioMetrics.getIdleTimeMsPerSecond();
resumeFuture = inputProcessor.getAvailableFuture();
}
// 阻塞,直到有可用的数据到/recordWriter 可用
// resumeFuture完成后,异步操作
assertNoException(
resumeFuture.thenRun(
new ResumeWrapper(controller.suspendDefaultAction(timer), timer)));
}
阻塞,直到有可用的数据到/有可用buffer
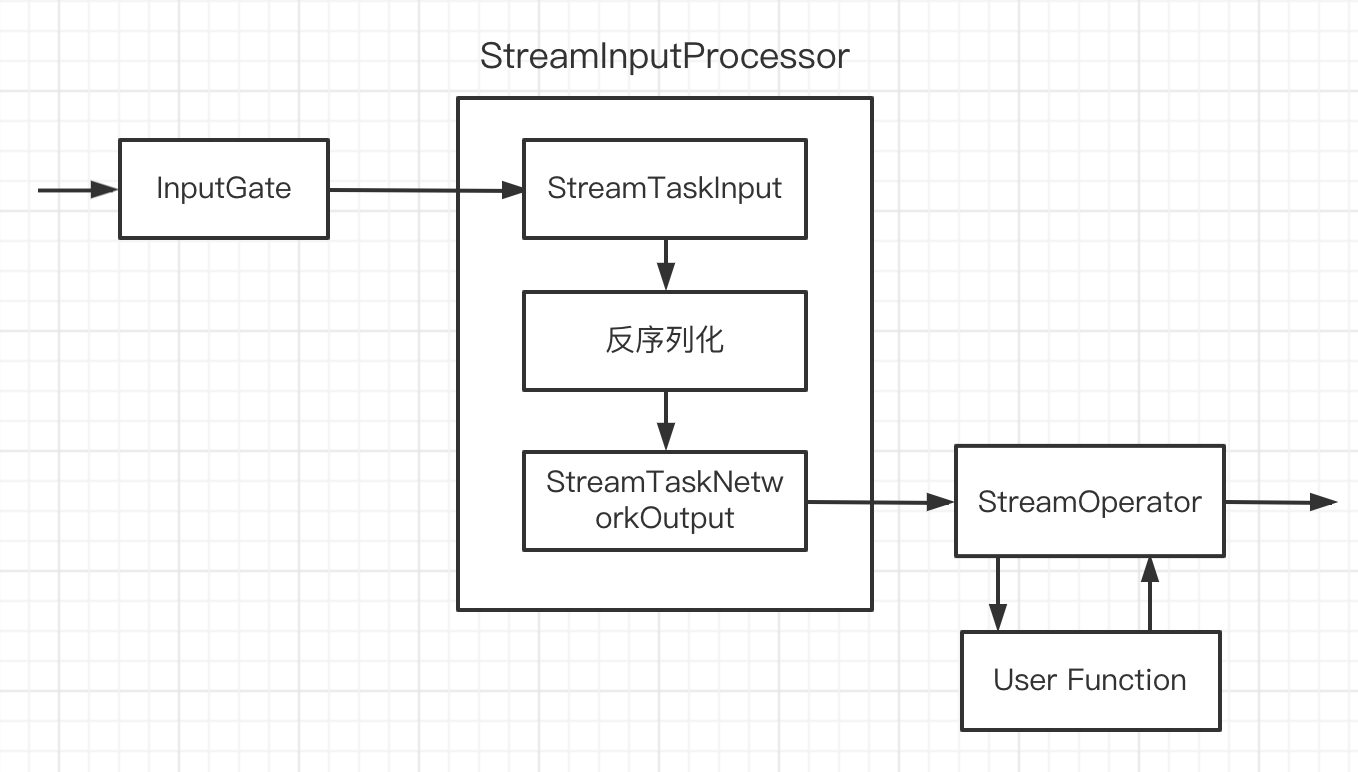
StreamInputProcessor
基本实现类 StreamOneInputProcessor/StreamTwoInputProcessor
// org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.io.StreamOneInputProcessor#processInput
public InputStatus processInput() throws Exception {
InputStatus status = input.emitNext(output); // StreamTaskInput 处理
if (status == InputStatus.END_OF_INPUT) {
endOfInputAware.endInput(input.getInputIndex() + 1);
} else if (status == InputStatus.END_OF_RECOVERY) {
if (input instanceof RecoverableStreamTaskInput) {
input = ((RecoverableStreamTaskInput<IN>) input).finishRecovery();
}
return InputStatus.MORE_AVAILABLE;
}
return status;
}
看上图,StreamInputProcessor 只是做了封装,逻辑在StreamTaskInput和StreamTaskNetworkOutput中。
InputGate
inputProcessor.getAvailableFuture()
-> org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.io.StreamOneInputProcessor#getAvailableFuture
-> org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.io.AbstractStreamTaskNetworkInput#getAvailableFuture
-> org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.io.checkpointing.CheckpointedInputGate#getAvailableFuture
-> org.apache.flink.runtime.io.network.partition.consumer.InputGate#getAvailableFuture
// org.apache.flink.runtime.io.AvailabilityProvider.AvailabilityHelper#getAvailableFuture
public CompletableFuture<?> getAvailableFuture() {
return availableFuture;
}
获取输入event时,会一直阻塞在InputGate,直到 Future.complete。
那什么时候会完成呢?任意一个 InputChannel 有数据(在输出小节会分析)
StreamTaskInput
数据输入的抽象,根据数据从哪里读取,分为两类:
StreamTaskNetworkInput:从上游task获取数据(没有chain),InputGateStreamTaskSourceInput:外部数据源获取数据,SourceFunction
// org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.io.AbstractStreamTaskNetworkInput#emitNext
public InputStatus emitNext(DataOutput<T> output) throws Exception {
while (true) {
// get the stream element from the deserializer
if (currentRecordDeserializer != null) {
RecordDeserializer.DeserializationResult result;
try {
// 反序列化,得到element,有好几种类型
result = currentRecordDeserializer.getNextRecord(deserializationDelegate);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new IOException(
String.format("Can't get next record for channel %s", lastChannel), e);
}
if (result.isBufferConsumed()) {
currentRecordDeserializer = null;
}
if (result.isFullRecord()) {
// 真正去处理数据
processElement(deserializationDelegate.getInstance(), output);
return InputStatus.MORE_AVAILABLE;
}
}
// 继续获取下一个buffer,底层是从InputChannel获取
Optional<BufferOrEvent> bufferOrEvent = checkpointedInputGate.pollNext();
if (bufferOrEvent.isPresent()) {
// return to the mailbox after receiving a checkpoint barrier to avoid processing of
// data after the barrier before checkpoint is performed for unaligned checkpoint
// mode
if (bufferOrEvent.get().isBuffer()) {
processBuffer(bufferOrEvent.get());
} else {
return processEvent(bufferOrEvent.get());
}
} else {
if (checkpointedInputGate.isFinished()) {
checkState(
checkpointedInputGate.getAvailableFuture().isDone(),
"Finished BarrierHandler should be available");
return InputStatus.END_OF_INPUT;
}
return InputStatus.NOTHING_AVAILABLE;
}
}
}
// org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.io.AbstractStreamTaskNetworkInput#processElement
private void processElement(StreamElement recordOrMark, DataOutput<T> output) throws Exception {
// 处理四类数据
if (recordOrMark.isRecord()) {
// event,本文分析这里
output.emitRecord(recordOrMark.asRecord());
} else if (recordOrMark.isWatermark()) {
// watermark
statusWatermarkValve.inputWatermark(
recordOrMark.asWatermark(), flattenedChannelIndices.get(lastChannel), output);
} else if (recordOrMark.isLatencyMarker()) {
// Latency
output.emitLatencyMarker(recordOrMark.asLatencyMarker());
} else if (recordOrMark.isStreamStatus()) {
// StreamStatus
statusWatermarkValve.inputStreamStatus(
recordOrMark.asStreamStatus(),
flattenedChannelIndices.get(lastChannel),
output);
} else {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Unknown type of StreamElement");
}
}
反序列化
从buffer 获取到的是二进制,需要反序列化成对象。
result = currentRecordDeserializer.getNextRecord(deserializationDelegate);
// deserializationDelegate.getInstance() 得到反序列化后的对象
processElement(deserializationDelegate.getInstance(), output);
// org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.io.AbstractStreamTaskNetworkInput
deserializationDelegate =
new NonReusingDeserializationDelegate<>(
new StreamElementSerializer<>(inputSerializer));
// org.apache.flink.runtime.plugable.NonReusingDeserializationDelegate
// 对象不重用
public void read(DataInputView in) throws IOException {
this.instance = this.serializer.deserialize(in);
}
// org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.streamrecord.StreamElementSerializer
public StreamElement deserialize(DataInputView source) throws IOException {
int tag = source.readByte();
if (tag == TAG_REC_WITH_TIMESTAMP) {
long timestamp = source.readLong();
return new StreamRecord<T>(typeSerializer.deserialize(source), timestamp);
} else if (tag == TAG_REC_WITHOUT_TIMESTAMP) {
return new StreamRecord<T>(typeSerializer.deserialize(source));
} else if (tag == TAG_WATERMARK) {
return new Watermark(source.readLong());
} else if (tag == TAG_STREAM_STATUS) {
return new StreamStatus(source.readInt());
} else if (tag == TAG_LATENCY_MARKER) {
return new LatencyMarker(
source.readLong(),
new OperatorID(source.readLong(), source.readLong()),
source.readInt());
} else {
throw new IOException("Corrupt stream, found tag: " + tag);
}
}
StreamElementSerializer 序列化成四种数据
-
StreamRecord: event -
Watermark:水印 -
StreamStatus:stream 状态,分为空闲(IDLE)和忙碌(Active),空闲时不参与 Watermark计算 -
LatencyMarker:延迟指标,后续会分析
StreamTaskNetworkOutput
序列化后的对象要进行处理,本节只针对 event
output.emitRecord(recordOrMark.asRecord());
StreamTaskNetworkOutput 名字里有output,但不是往下游输出的意思,是将event 交给Operator 处理。
// org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.tasks.OneInputStreamTask.StreamTaskNetworkOutput#emitRecord
public void emitRecord(StreamRecord<IN> record) throws Exception {
numRecordsIn.inc();
operator.setKeyContextElement1(record);
operator.processElement(record);
}
处理
event 处理是 UserFunction 定义的,这里处理很简单只是将event 交给 UserFunction。
// org.apache.flink.streaming.api.operators.KeyedProcessOperator#processElement
public void processElement(StreamRecord<IN> element) throws Exception {
collector.setTimestamp(element);
context.element = element;
// 调用用户写的函数,collector=Out
userFunction.processElement(element.getValue(), context, collector);
context.element = null;
}
做过Flink 开发应该了解,处理后的数据输出是调用 Out.collect
输出
UserFunction 输出要往下游发送,下游与本task的关系分为三种情况
-
OperatorChain:task chain一起了,
collect方法直接调用下游算子 processElement;因为在同一个线程内无序列化、无网络开销、无线程切换。 -
下游task是同个TM,
collect方法通过本地内存(同个TM下,共享BufferPool)数据传递,有序列化、有线程切换、无网络开销 -
下游task不在同个TM,
collect方法通过网络通信传递数据,有序列化、有线程切换、有网络开销
Output
常用的实现有两类:
-
RecordWriterOutput:线程间、网络间(task没有chain)实现数据序列化和写入。包装了RecordWrite,使用RecordWrite把数据交给数据交换层。 -
ChainingOutput:chain task,直接调用下游算子 processElement -
BroadcastingOutput:包装一组 Output,向下游所有task广播数据
ChainingOutput
// org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.tasks.ChainingOutput#collect(org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.streamrecord.StreamRecord<T>)
public void collect(StreamRecord<T> record) {
if (this.outputTag != null) {
// we are not responsible for emitting to the main output.
return;
}
pushToOperator(record);
}
protected <X> void pushToOperator(StreamRecord<X> record) {
try {
// we know that the given outputTag matches our OutputTag so the record
// must be of the type that our operator expects.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
StreamRecord<T> castRecord = (StreamRecord<T>) record;
numRecordsIn.inc();
input.setKeyContextElement(castRecord);
// 调用下游 Operator.processElement
input.processElement(castRecord);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ExceptionInChainedOperatorException(e);
}
}
RecordWriterOutput
// org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.io.RecordWriterOutput#collect(org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.streamrecord.StreamRecord<OUT>)
public void collect(StreamRecord<OUT> record) {
if (this.outputTag != null) {
// we are not responsible for emitting to the main output.
return;
}
pushToRecordWriter(record);
}
// org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.io.RecordWriterOutput#pushToRecordWriter
private <X> void pushToRecordWriter(StreamRecord<X> record) {
serializationDelegate.setInstance(record);
try {
// 写出过程中调用 serializationDelegate.write 序列化
recordWriter.emit(serializationDelegate);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
-
序列化
-
写出
序列化
// org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.io.RecordWriterOutput
TypeSerializer<StreamElement> outRecordSerializer =
new StreamElementSerializer<>(outSerializer);
if (outSerializer != null) {
serializationDelegate = new SerializationDelegate<StreamElement>(outRecordSerializer);
}
// org.apache.flink.runtime.plugable.SerializationDelegate#write
public void write(DataOutputView out) throws IOException {
this.serializer.serialize(this.instance, out);
}
StreamElementSerializer
// org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.streamrecord.StreamElementSerializer#serialize
public void serialize(StreamElement value, DataOutputView target) throws IOException {
if (value.isRecord()) {
StreamRecord<T> record = value.asRecord();
if (record.hasTimestamp()) {
target.write(TAG_REC_WITH_TIMESTAMP);
target.writeLong(record.getTimestamp());
} else {
target.write(TAG_REC_WITHOUT_TIMESTAMP);
}
typeSerializer.serialize(record.getValue(), target);
} else if (value.isWatermark()) {
target.write(TAG_WATERMARK);
target.writeLong(value.asWatermark().getTimestamp());
} else if (value.isStreamStatus()) {
target.write(TAG_STREAM_STATUS);
target.writeInt(value.asStreamStatus().getStatus());
} else if (value.isLatencyMarker()) {
target.write(TAG_LATENCY_MARKER);
target.writeLong(value.asLatencyMarker().getMarkedTime());
target.writeLong(value.asLatencyMarker().getOperatorId().getLowerPart());
target.writeLong(value.asLatencyMarker().getOperatorId().getUpperPart());
target.writeInt(value.asLatencyMarker().getSubtaskIndex());
} else {
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
RecordWriter
recordWriter.emit(serializationDelegate);
// org.apache.flink.runtime.io.network.api.writer.ChannelSelectorRecordWriter#emit
public void emit(T record) throws IOException {
emit(record, channelSelector.selectChannel(record));
}
protected void emit(T record, int targetSubpartition) throws IOException {
checkErroneous();
// 调用 StreamElementSerializer
targetPartition.emitRecord(serializeRecord(serializer, record), targetSubpartition);
if (flushAlways) {
// 每来一个数据都直接发送,这样吞吐是很慢的,默认是100ms 往下游发
targetPartition.flush(targetSubpartition);
}
}
输出有多个下游(并行度),要选择是输出到哪个下游
ChannelSelector
KeyGroupStreamPartitioner 为例,event 的key hash后分发给下游的某个task
// org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.partitioner.KeyGroupStreamPartitioner#selectChannel
public int selectChannel(SerializationDelegate<StreamRecord<T>> record) {
K key;
try {
//
key = keySelector.getKey(record.getInstance().getValue());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Could not extract key from " + record.getInstance().getValue(), e);
}
return KeyGroupRangeAssignment.assignKeyToParallelOperator(
key, maxParallelism, numberOfChannels);
}
-
抽取 key
-
根据key、最大并行度、可写出的下游数得到task index,就是数据分发策略(细节看参考资料三)
// org.apache.flink.runtime.state.KeyGroupRangeAssignment
public static int assignKeyToParallelOperator(Object key, int maxParallelism, int parallelism) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(key, "Assigned key must not be null!");
return computeOperatorIndexForKeyGroup(
maxParallelism, parallelism, assignToKeyGroup(key, maxParallelism));
}
public static int assignToKeyGroup(Object key, int maxParallelism) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(key, "Assigned key must not be null!");
return computeKeyGroupForKeyHash(key.hashCode(), maxParallelism);
}
public static int computeKeyGroupForKeyHash(int keyHash, int maxParallelism) {
return MathUtils.murmurHash(keyHash) % maxParallelism;
}
public static int computeOperatorIndexForKeyGroup(
int maxParallelism, int parallelism, int keyGroupId) {
return keyGroupId * parallelism / maxParallelism;
}
-
key hashcode
-
murmurHash对最大并行度取模
-
模数*下游数/最大并行度
ResultSubPartition
知道数据往哪个下游发送后,写出数据
// org.apache.flink.runtime.io.network.partition.BufferWritingResultPartition#emitRecord
public void emitRecord(ByteBuffer record, int targetSubpartition) throws IOException {
BufferBuilder buffer = appendUnicastDataForNewRecord(record, targetSubpartition);
while (record.hasRemaining()) {
// full buffer, partial record
finishUnicastBufferBuilder(targetSubpartition);
// 此时会引发 ResultSubpartition flush,因为 不止一个 ResultSubpartition
buffer = appendUnicastDataForRecordContinuation(record, targetSubpartition);
}
if (buffer.isFull()) {
// full buffer, full record
finishUnicastBufferBuilder(targetSubpartition);
}
// partial buffer, full record
}
-
数据写入对应分区有空闲的
BufferBuilder-
当前Subpartition 是否有BufferBuilder,若没有需要申请
-
申请 BufferBuilder,涉及到
BufferPool;每个创建好的 BufferBuilder都会加入到对应的 ResultSubpartition
-
-
若数据没写完(当前申请的buffer已用完),当前
BufferBuilder里数据标记 flush,再将数据剩下的一部分继续写 -
若BufferBuilder 满,当前
BufferBuilder标记 flush
那 ResultSubpartition 什么时候flush呢?
-
设置 flushAlways,每来一条数据就flush
-
ResultSubpartition buffers 中添加BufferBuilder时,判断不止一个BufferBuilder/添加的BufferBuilder标记为 flush;ResultSubpartition 已积累了一个BufferBuilder数据
-
间隔
DEFAULT_NETWORK_BUFFER_TIMEOUTms,RecordWriter 就会强制所有 ResultSubpartition flush
// org.apache.flink.runtime.io.network.partition.PipelinedSubpartition#flush
public void flush() {
final boolean notifyDataAvailable;
synchronized (buffers) {
if (buffers.isEmpty() || flushRequested) {
return;
}
// if there is more then 1 buffer, we already notified the reader
// (at the latest when adding the second buffer)
boolean isDataAvailableInUnfinishedBuffer =
buffers.size() == 1 && buffers.peek().getBufferConsumer().isDataAvailable();
notifyDataAvailable = !isBlocked && isDataAvailableInUnfinishedBuffer;
flushRequested = buffers.size() > 1 || isDataAvailableInUnfinishedBuffer;
}
if (notifyDataAvailable) {
// 满足条件,去通知
notifyDataAvailable();
}
}
public PipelinedSubpartitionView createReadView(
BufferAvailabilityListener availabilityListener) {
....
readView = new PipelinedSubpartitionView(this, availabilityListener);
return readView;
}
private void notifyDataAvailable() {
final PipelinedSubpartitionView readView = this.readView;
if (readView != null) {
readView.notifyDataAvailable();
}
}
// org.apache.flink.runtime.io.network.partition.PipelinedSubpartitionView#notifyDataAvailable
public void notifyDataAvailable() {
availabilityListener.notifyDataAvailable();
}
PipelinedSubpartitionView 接到数据flush 通知后,会将消息继续传递给 availabilityListener,那availabilityListener 是什么呢?
LocalInputChannel
上下游任务同个TM
//org.apache.flink.runtime.io.network.partition.consumer.LocalInputChannel#requestSubpartition
ResultSubpartitionView subpartitionView =
partitionManager.createSubpartitionView(
partitionId, subpartitionIndex, this);
// org.apache.flink.runtime.io.network.partition.ResultPartitionManager#createSubpartitionView
subpartitionView =
partition.createSubpartitionView(subpartitionIndex, availabilityListener);
// org.apache.flink.runtime.io.network.partition.BufferWritingResultPartition#createSubpartitionView
public ResultSubpartitionView createSubpartitionView(
int subpartitionIndex, BufferAvailabilityListener availabilityListener)
throws IOException {
checkElementIndex(subpartitionIndex, numSubpartitions, "Subpartition not found.");
checkState(!isReleased(), "Partition released.");
ResultSubpartition subpartition = subpartitions[subpartitionIndex];
// PipelinedSubpartition.createReadView
ResultSubpartitionView readView = subpartition.createReadView(availabilityListener);
LOG.debug("Created {}", readView);
return readView;
}
由此可见,availabilityListener => LocalInputChannel
PipelinedSubpartition 有数据输出,LocalInputChannel 回调函数立刻被调用,开始消费。
// org.apache.flink.runtime.io.network.partition.consumer.LocalInputChannel#notifyDataAvailable
public void notifyDataAvailable() {
notifyChannelNonEmpty();
}
// org.apache.flink.runtime.io.network.partition.consumer.InputChannel#notifyChanelNonEmpty
protected void notifyChannelNonEmpty() {
inputGate.notifyChannelNonEmpty(this);
}
// org.apache.flink.runtime.io.network.partition.consumer.SingleInputGate#notifyChannelNonEmpty
void notifyChannelNonEmpty(InputChannel channel) {
queueChannel(checkNotNull(channel), null, false);
}
private void queueChannel(
InputChannel channel, @Nullable Integer prioritySequenceNumber, boolean forcePriority) {
try (GateNotificationHelper notification =
new GateNotificationHelper(this, inputChannelsWithData)) {
synchronized (inputChannelsWithData) {
boolean priority = prioritySequenceNumber != null || forcePriority;
if (!forcePriority
&& priority
&& isOutdated(
prioritySequenceNumber,
lastPrioritySequenceNumber[channel.getChannelIndex()])) {
// priority event at the given offset already polled (notification is not atomic
// in respect to
// buffer enqueuing), so just ignore the notification
return;
}
if (!queueChannelUnsafe(channel, priority)) {
return;
}
if (priority && inputChannelsWithData.getNumPriorityElements() == 1) {
notification.notifyPriority();
}
if (inputChannelsWithData.size() == 1) {
// 唤醒阻塞在 inputChannelsWithData 线程
notification.notifyDataAvailable();
}
}
}
}
// org.apache.flink.runtime.io.network.partition.consumer.GateNotificationHelper
public GateNotificationHelper(InputGate inputGate, Object availabilityMonitor) {
this.inputGate = inputGate;
this.availabilityMonitor = availabilityMonitor;
}
public void close() {
if (toNotifyPriority != null) {
toNotifyPriority.complete(null);
}
if (toNotify != null) {
toNotify.complete(null);
}
}
public void notifyDataAvailable() {
availabilityMonitor.notifyAll();
toNotify = inputGate.availabilityHelper.getUnavailableToResetAvailable();
}
GateNotificationHelper 在close 回调时,调用 toNotify.complete => InputGate.availabilityHelper.availableFuture.complete
对应到输入时 阻塞在InputGate