demo
object JoinExplainSql {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
val settings = EnvironmentSettings.newInstance()
.useBlinkPlanner()
.inStreamingMode()
.build()
val tEnv = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env,settings)
tEnv.executeSql(
s"""
|CREATE TABLE table1 (
| name STRING,
| cnt int
|) WITH (
|'connector' = 'datagen'
|)
""".stripMargin)
tEnv.executeSql(
s"""
|CREATE TABLE table2 (
| name STRING,
| price int
|) WITH (
|'connector' = 'datagen'
|)
""".stripMargin)
tEnv.executeSql(
s"""
|CREATE TABLE sink_table (
| name STRING,
| money bigint
|) WITH (
|'connector' = 'print'
|)
""".stripMargin)
// a.cnt > b.price 会在 join operation 先判断 condition(a.cnt > b.price) 是否满足再join
println(tEnv.explainSql(
s"""
|insert into sink_table
|select a.name,
|a.cnt * b.price
|from table1 as a
|join table2 as b
|on a.name = b.name
|and a.cnt > b.price
""".stripMargin, ExplainDetail.JSON_EXECUTION_PLAN))
}
}
Demo 就是最简单的 join 操作,打印语法树
== Abstract Syntax Tree(relNode) == operation2relnode
LogicalSink(table=[default_catalog.default_database.sink_table], fields=[name, money])
+- LogicalProject(name=[$0], money=[CAST(*($1, $3)):BIGINT])
+- LogicalJoin(condition=[AND(=($0, $2), >($1, $3))], joinType=[inner])
:- LogicalTableScan(table=[[default_catalog, default_database, table1]])
+- LogicalTableScan(talbe=[[default_catalog, default_database, table2]])
== Optimized Physical Plan == relnode2Physicalnode 涉及 rule(StreamPhysicalJoinRule)
StreamPhysicalSink(table=[default_catalog.default_database.sink_table], fields=[name, money])
+- StreamPhysicalCalc(select=[name, CAST(*(cnt, price)) AS money])
+- StreamPhysicalJoin(joinType=[InnerJoin], where=[AND(=(name, name0), >(cnt, price))], select=[name, cnt, name0, price], leftInputSpec=[NoUniqueKey], rightInputSpec=[NoUniqueKey])
:- StreamPhysicalExchange(distribution=[hash[name]])
: +- StreamPhysicalTableSourceScan(table=[[default_catalog, default_database, table1]], fields=[name, cnt])
+- StreamPhysicalExchange(distribution=[hash[name]])
+- StreamPhysicalTableSourceScan(table=[[default_catalog, default_database, table2]], fields=[name, price])
== Optimized Execution Plan == Physicalnode2execnode
StreamExecSink(table=[default_catalog.default_database.sink_table], fields=[name, money])
+- StreamExecCalc(select=[name, CAST((cnt * price)) AS money])
+- StreamExecJoin(joinType=[InnerJoin], where=[((name = name0) AND (cnt > price))], select=[name, cnt, name0, price], leftInputSpec=[NoUniqueKey], rightInputSpec=[NoUniqueKey])
:- StreamExecExchange(distribution=[hash[name]])
: +- StreamExecTableSourceScan(table=[[default_catalog, default_database, table1]], fields=[name, cnt])
+- StreamExecExchange(distribution=[hash[name]])
+- StreamExecTableSourceScan(table=[[default_catalog, default_database, table2]], fields=[name, price])
结合之前的 Flink SQL 执行流程,本文分析下 Flink SQL 中 Streaming Join 的实现。
SQL翻译
根据上面输出的 PLAN 大致可以看出 SQL 经过三个流程
- Opeartion
- PhysicalNode:Opeartion 匹配到哪个 Rule,就被翻译成对应的 PhysicalNode
- ExecutionNode:PhysicalNode 调用 translateToExecNode 得到
- Transformation:ExecutionNode 调用 translateToPlanInternal,至此由 SQL 转化为 Transformation
StreamPhysicalJoinRule
Flink SQL 中有很多规则,对应不同的 SQL 类型。在翻译的过程中,SQL 类型与规则匹配,满足条件则会翻译成对应的 PhysicalNode。
// org.apache.flink.table.planner.plan.rules.physical.stream.StreamPhysicalJoinRule
override def matches(call: RelOptRuleCall): Boolean = {
val join: FlinkLogicalJoin = call.rel(0)
if (!join.getJoinType.projectsRight) {
// SEMI/ANTI join always converts to StreamExecJoin now
return true
}
val left: FlinkLogicalRel = call.rel(1).asInstanceOf[FlinkLogicalRel]
val right: FlinkLogicalRel = call.rel(2).asInstanceOf[FlinkLogicalRel]
val joinRowType = join.getRowType
// 不支持临时表 join
if (left.isInstanceOf[FlinkLogicalSnapshot]) {
throw new TableException(
"Temporal table join only support apply FOR SYSTEM_TIME AS OF on the right table.")
}
// this rule shouldn't match temporal table join
if (right.isInstanceOf[FlinkLogicalSnapshot] ||
TemporalJoinUtil.containsTemporalJoinCondition(join.getCondition)) {
return false
}
// 不支持 window join
val (windowBounds, remainingPreds) = extractWindowBounds(join)
if (windowBounds.isDefined) {
return false
}
if (containsWindowStartEqualityAndEndEquality(join)) {
return false
}
// remaining predicate must not access time attributes
val remainingPredsAccessTime = remainingPreds.isDefined &&
IntervalJoinUtil.accessesTimeAttribute(remainingPreds.get, joinRowType)
val rowTimeAttrInOutput = joinRowType.getFieldList
.exists(f => FlinkTypeFactory.isRowtimeIndicatorType(f.getType))
if (rowTimeAttrInOutput) {
throw new TableException(
"Rowtime attributes must not be in the input rows of a regular join. " +
"As a workaround you can cast the time attributes of input tables to TIMESTAMP before.")
}
// joins require an equality condition
// or a conjunctive predicate with at least one equality condition
// and disable outer joins with non-equality predicates(see FLINK-5520)
// And do not accept a FlinkLogicalTemporalTableSourceScan as right input
!remainingPredsAccessTime
}
StreamPhysicalJoinRule 是只适用常规 join,不带有其他特殊功能(临时表、窗口)
StreamPhysicalJoin
// org.apache.flink.table.planner.plan.nodes.physical.stream.StreamPhysicalJoin#translateToExecNode
override def translateToExecNode(): ExecNode[_] = {
new StreamExecJoin(
joinSpec,
getUniqueKeys(left),
getUniqueKeys(right),
InputProperty.DEFAULT,
InputProperty.DEFAULT,
FlinkTypeFactory.toLogicalRowType(getRowType),
getRelDetailedDescription)
}
StreamPhysicalNode -> ExecNod
StreamExecJoin
// org.apache.flink.table.planner.plan.nodes.exec.stream.StreamExecJoin#translateToPlanInternal
protected Transformation<RowData> translateToPlanInternal(PlannerBase planner) {
final ExecEdge leftInputEdge = getInputEdges().get(0);
final ExecEdge rightInputEdge = getInputEdges().get(1);
final Transformation<RowData> leftTransform =
(Transformation<RowData>) leftInputEdge.translateToPlan(planner);
final Transformation<RowData> rightTransform =
(Transformation<RowData>) rightInputEdge.translateToPlan(planner);
final RowType leftType = (RowType) leftInputEdge.getOutputType();
final RowType rightType = (RowType) rightInputEdge.getOutputType();
JoinUtil.validateJoinSpec(joinSpec, leftType, rightType, true);
final int[] leftJoinKey = joinSpec.getLeftKeys();
final int[] rightJoinKey = joinSpec.getRightKeys();
// 判断左右两侧的流,joinkey 和 uniquekey 关系
// 这决定后续 join 效率
final InternalTypeInfo<RowData> leftTypeInfo = InternalTypeInfo.of(leftType);
final JoinInputSideSpec leftInputSpec =
JoinUtil.analyzeJoinInput(leftTypeInfo, leftJoinKey, leftUniqueKeys);
final InternalTypeInfo<RowData> rightTypeInfo = InternalTypeInfo.of(rightType);
final JoinInputSideSpec rightInputSpec =
JoinUtil.analyzeJoinInput(rightTypeInfo, rightJoinKey, rightUniqueKeys);
final TableConfig tableConfig = planner.getTableConfig();
// 判断条件,join 时过滤:a.cnt > b.price
GeneratedJoinCondition generatedCondition =
JoinUtil.generateConditionFunction(tableConfig, joinSpec, leftType, rightType);
// state TTL
long minRetentionTime = tableConfig.getMinIdleStateRetentionTime();
// 根据 join 类型得到 Operator
AbstractStreamingJoinOperator operator;
FlinkJoinType joinType = joinSpec.getJoinType();
if (joinType == FlinkJoinType.ANTI || joinType == FlinkJoinType.SEMI) {
operator =
new StreamingSemiAntiJoinOperator(
joinType == FlinkJoinType.ANTI,
leftTypeInfo,
rightTypeInfo,
generatedCondition,
leftInputSpec,
rightInputSpec,
joinSpec.getFilterNulls(),
minRetentionTime);
} else {
boolean leftIsOuter = joinType == FlinkJoinType.LEFT || joinType == FlinkJoinType.FULL;
boolean rightIsOuter =
joinType == FlinkJoinType.RIGHT || joinType == FlinkJoinType.FULL;
operator =
new StreamingJoinOperator(
leftTypeInfo,
rightTypeInfo,
generatedCondition,
leftInputSpec,
rightInputSpec,
leftIsOuter,
rightIsOuter,
joinSpec.getFilterNulls(),
minRetentionTime);
}
// Operator 包装成 Transformation
final RowType returnType = (RowType) getOutputType();
final TwoInputTransformation<RowData, RowData, RowData> transform =
new TwoInputTransformation<>(
leftTransform,
rightTransform,
getDescription(),
operator,
InternalTypeInfo.of(returnType),
leftTransform.getParallelism());
// set KeyType and Selector for state
RowDataKeySelector leftSelect =
KeySelectorUtil.getRowDataSelector(leftJoinKey, leftTypeInfo);
RowDataKeySelector rightSelect =
KeySelectorUtil.getRowDataSelector(rightJoinKey, rightTypeInfo);
transform.setStateKeySelectors(leftSelect, rightSelect);
transform.setStateKeyType(leftSelect.getProducedType());
// 返回 Transformation
return transform;
}
ExecNode -> Transformation
- JoinInputSideSpec:joinkey 和 uniquekey 关系,决定后续 join 效率
- GeneratedJoinCondition:join 条件包含的不等于条件,后续需要根据该条件再过滤
- JoinOperator:真正执行的 Operator,本例选择 StreamingJoinOperator 来分析
StreamingJoinOperator
由 SQL 进入到 Transformation
先不看源码,我们思考下两条流如何 join
- 两条流的数据都先缓存(状态)
- 如何 hold 住大数据量的情况, RocksDB 后端
- 数据源源不断进来都缓存起来,如果不删减数据肯定会有问题
- join 条件对时间有要求的使用 Interval Join,不满足时间条件的数据直接删除
- 设置状态 TTL,自动清除不需要的数据(根据数据的生命周期来设置)
- 某一侧流来数据时,去另一侧流的缓存中筛选出匹配的数据,再输出到下游
- 每来一条数据都去另一侧遍历所有数据显然有严重的性能问题
- 对每侧数据都按 joinKey 先分组,这样只需要遍历另一侧中相同 joinKey 的数据,大大减少数据量
- 每来一条数据都去另一侧遍历所有数据显然有严重的性能问题
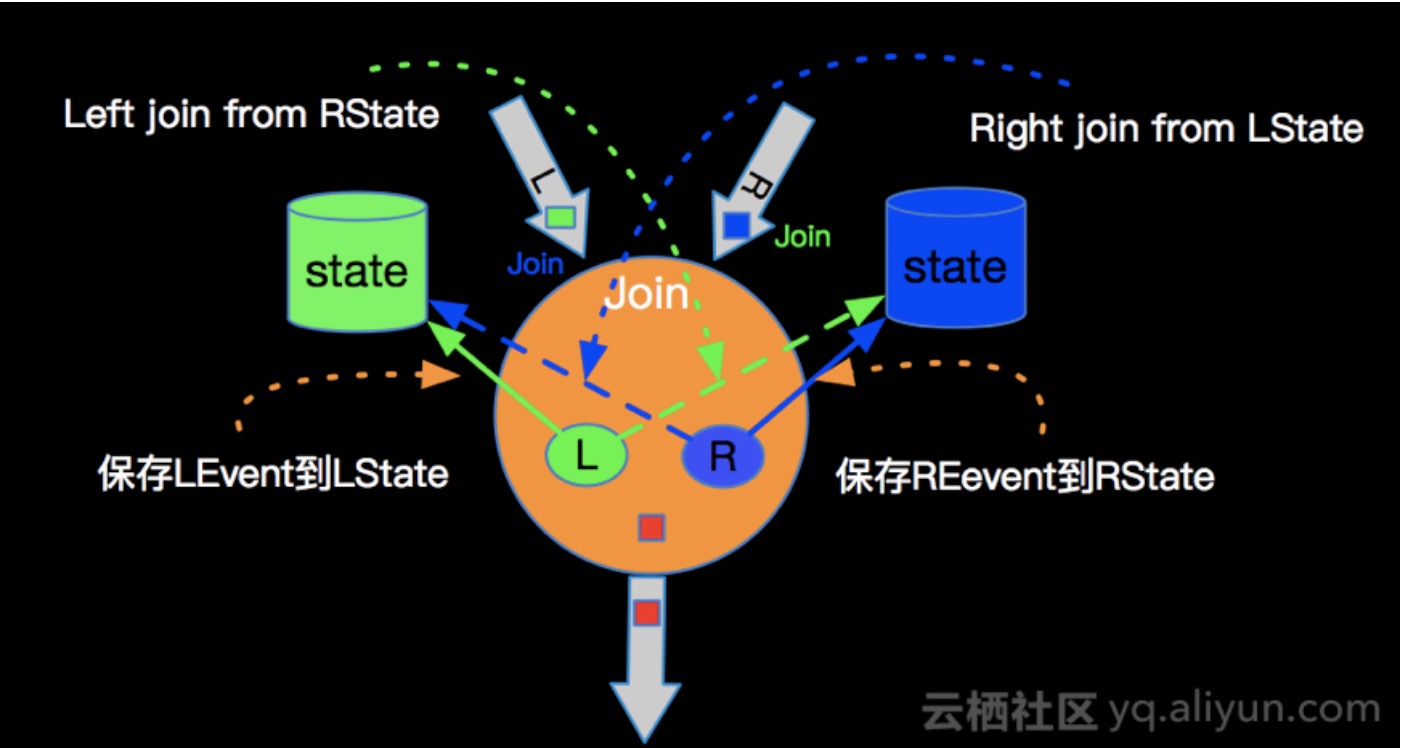
JoinRecordStateView
join 时两侧的数据都是缓存在状态,状态的数据结构是什么,影响关联时的效率
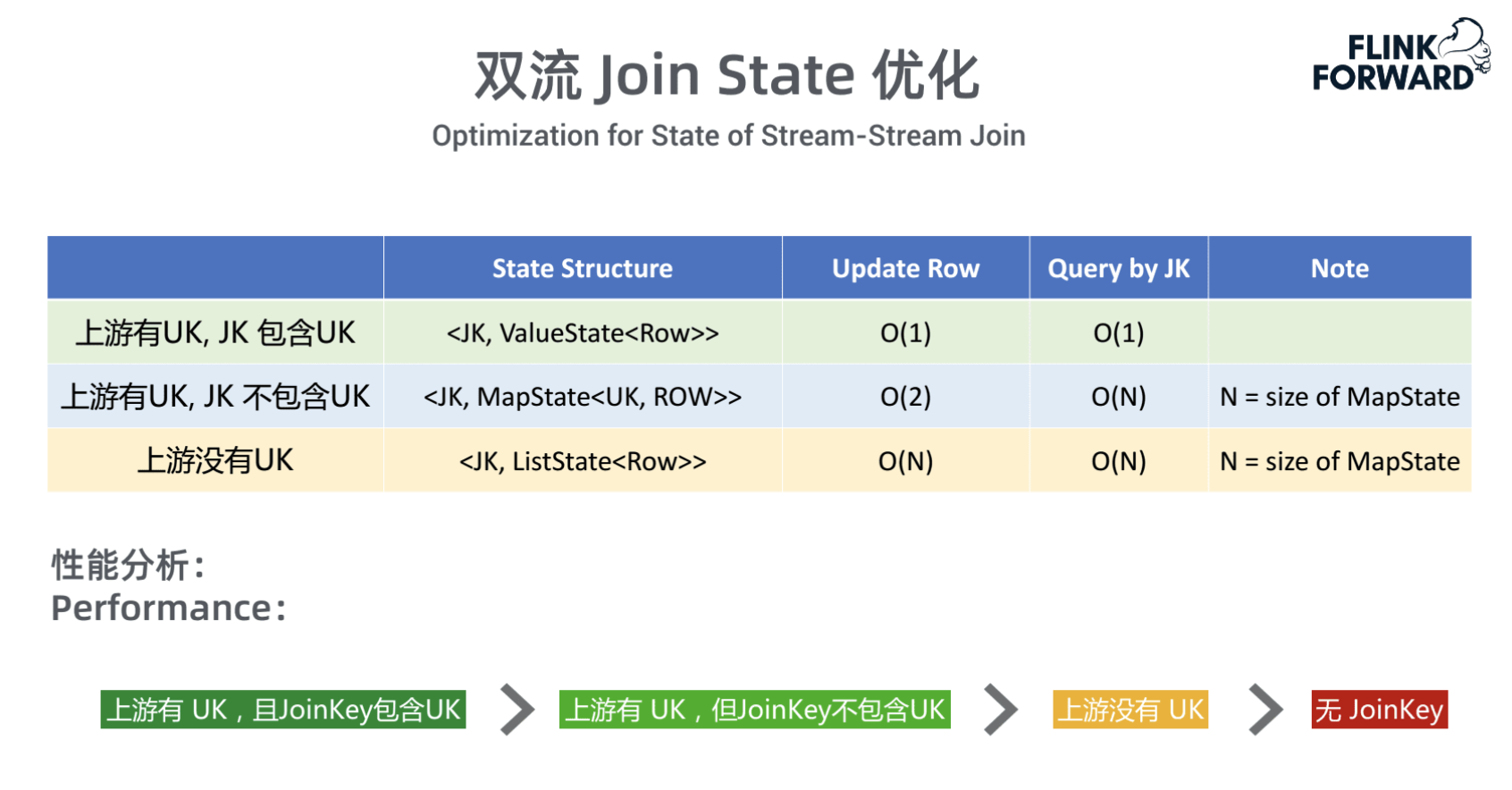
- 当 Join key 包含 Unique Key 时,一个 Join key 只会对应一条记录
- 存在 Unique Key 但 Join Key 不包含 Unique Key,一个 Join Key 可能会对应多条记录,但 Unique Key 能确定唯一数据
- 不存在 Unique Key,存在重复数据,需要记录重复记录的个数
若是存在外连接,在上述的结构中要加上计数器(另一侧中关联到的个数):当有回撤记录时,outer 需要计算另一侧之前关联的记录是否变为 0,若是则还需要向下游输出 outputNullPadding(outer) 记录表示 outer 没关联到数据。
inner state
- ValueState
- MapState<UK, RowData>
- MapState<RowData, Integer>
outer 要加计数器
- ValueState<Tuple2<RowData, Integer»
- MapState<UK, Tuple2<RowData, Integer»
- MapState<RowData, Tuple2<Integer, Integer»
流程
- 更新本侧状态(增/删)
- 根据 joinKey 查询另一侧状态,然后输出
a left join b 中,a 是outer ,b 是 inner;a 是每来一条数据都会输出,但 b 是要在 a 中关联到才输出
// event 是新增
//
if input record is accumulate
| if input side is outer // 本侧是 outer
// 另一侧没关联到数据,填充另一侧数据后输出,并更新状态,注意 matched rows = 0
| | if there is no matched rows on the other side, send +I[record+null], state.add(record, 0)
// 另一侧关联到数据
| | if there are matched rows on the other side
// 另一侧是 outer,那么另一侧也需要更新状态,
| | | if other side is outer
| | | | if the matched num in the matched rows == 0, send -D[null+other]
| | | | if the matched num in the matched rows > 0, skip
| | | | otherState.update(other, old + 1)
| | | endif
| | | send +I[record+other]s, state.add(record, other.size) // 输出关联到数据,并更新状态, matched rows = 关联到的另一侧数据个数
| | endif
| endif
| if input side not outer // 本侧是 inner
| | state.add(record) // 更新本侧状态
| | if there is no matched rows on the other side, skip // 另一侧关联不到数据,不输出,因为本侧是 inner
| | if there are matched rows on the other side
| | | if other side is outer
// 另一侧是 outer,除了输出关联到数据,还要更新另一侧的 matched rows + 1
| | | | if the matched num in the matched rows == 0, send -D[null+other]
| | | | if the matched num in the matched rows > 0, skip
| | | | otherState.update(other, old + 1)
| | | | send +I[record+other]s
| | | else
| | | | send +I/+U[record+other]s (using input RowKind) // 在另一侧是inner情况下关联到数据,直接输出即可
| | | endif
| | endif
| endif
endif
// event 是回撤
if input record is retract
// 删除本侧状态
| state.retract(record)
| if there is no matched rows on the other side
// 本侧是 outer,但另一侧找不到数据,直接填充另一侧数据为 null 输出
| | if input side is outer, send -D[record+null]
| endif
// 另一侧关联到数据了,本侧是 outer,直接输出关联好的的数据,符号 -D/-U
| if there are matched rows on the other side, send -D[record+other]s if outer, send -D/-U[record+other]s if inner.
// 本侧是 inner 但令一侧是 outer,还需要跟更新 outer 的 matched rows -1
// 假设被减之后的 matched rows=0,表示两侧由之前能关联到数据变为 无法关联到数据
// 还需要填充本侧数据为 null 后输出
| | if other side is outer
| | | if the matched num in the matched rows == 0, this should never happen!
| | | if the matched num in the matched rows == 1, send +I[null+other]
| | | if the matched num in the matched rows > 1, skip
| | | otherState.update(other, old - 1)
| | endif
| endif
endif
CodeGenerate
本案例中 a.cnt > b.price 就是代码自动生成 JoinCondition,两侧数据在做关联时还需要满足 JoinCondition (Join Key 是 a.name = b.name)。
// org.apache.flink.table.runtime.operators.join.stream.StreamingJoinOperator#processElement
AssociatedRecords associatedRecords =
AssociatedRecords.of(input, inputIsLeft, otherSideStateView, joinCondition);
// org.apache.flink.table.runtime.operators.join.stream.AbstractStreamingJoinOperator#open
// newInstance 将之前的代码 txt 编译成 class,后续调用 class.apply; 代码 txt 怎么生成继续往下看
JoinCondition condition =
generatedJoinCondition.newInstance(getRuntimeContext().getUserCodeClassLoader());
condition.setRuntimeContext(getRuntimeContext());
condition.open(new Configuration());
this.joinCondition = new JoinConditionWithNullFilters(condition);
// org.apache.flink.table.planner.plan.nodes.exec.stream.StreamExecJoin#translateToPlanInternal
GeneratedJoinCondition generatedCondition =
JoinUtil.generateConditionFunction(tableConfig, joinSpec, leftType, rightType);
// org.apache.flink.table.planner.plan.utils.JoinUtil#generateConditionFunction
def generateConditionFunction(
config: TableConfig,
joinSpec: JoinSpec,
leftType: LogicalType,
rightType: LogicalType): GeneratedJoinCondition = {
generateConditionFunction(
config,
joinSpec.getNonEquiCondition().orElse(null),
leftType,
rightType)
}
def generateConditionFunction(
config: TableConfig,
nonEquiCondition: RexNode,
leftType: LogicalType,
rightType: LogicalType): GeneratedJoinCondition = {
val ctx = CodeGeneratorContext(config)
// should consider null fields
val exprGenerator = new ExprCodeGenerator(ctx, false)
.bindInput(leftType)
.bindSecondInput(rightType)
val body = if (nonEquiCondition == null) {
// 没条件直接返回 true,即满足 join key 就可以
"return true;"
} else {
// 生成函数体代码
val condition = exprGenerator.generateExpression(nonEquiCondition)
s"""
|${condition.code}
|return ${condition.resultTerm};
|""".stripMargin
}
// 类代码
FunctionCodeGenerator.generateJoinCondition(
ctx,
"ConditionFunction",
body)
}
// org.apache.flink.table.planner.codegen.FunctionCodeGenerator#generateJoinCondition
def generateJoinCondition(
ctx: CodeGeneratorContext,
name: String,
bodyCode: String,
input1Term: String = CodeGenUtils.DEFAULT_INPUT1_TERM,
input2Term: String = CodeGenUtils.DEFAULT_INPUT2_TERM): GeneratedJoinCondition = {
val funcName = newName(name)
val funcCode =
j"""
public class $funcName extends ${className[AbstractRichFunction]}
implements ${className[JoinCondition]} {
${ctx.reuseMemberCode()}
public $funcName(Object[] references) throws Exception {
${ctx.reuseInitCode()}
}
${ctx.reuseConstructorCode(funcName)}
@Override
public void open(${className[Configuration]} parameters) throws Exception {
${ctx.reuseOpenCode()}
}
// appaly 是关联时调用的函数,具体代码就是之前生成的 condition.code
@Override
public boolean apply($ROW_DATA $input1Term, $ROW_DATA $input2Term) throws Exception {
${ctx.reusePerRecordCode()}
${ctx.reuseLocalVariableCode()}
${ctx.reuseInputUnboxingCode()}
$bodyCode // = condition.code
}
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
super.close();
${ctx.reuseCloseCode()}
}
}
""".stripMargin
new GeneratedJoinCondition(funcName, funcCode, ctx.references.toArray)
}
上面有大量的字符串替换,最终的 class 代码如下:
public class ConditionFunction$8 extends org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.AbstractRichFunction
implements org.apache.flink.table.runtime.generated.JoinCondition {
public ConditionFunction$8(Object[] references) throws Exception {
}
@Override
public void open(org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
}
// a.cnt > b.price
@Override
public boolean apply(org.apache.flink.table.data.RowData in1, org.apache.flink.table.data.RowData in2) throws Exception {
int field$4;
boolean isNull$4;
int field$5;
boolean isNull$5;
boolean isNull$6;
boolean result$7;
isNull$5 = in2.isNullAt(1);
field$5 = -1;
if (!isNull$5) {
field$5 = in2.getInt(1);
}
isNull$4 = in1.isNullAt(1);
field$4 = -1;
if (!isNull$4) {
field$4 = in1.getInt(1);
}
isNull$6 = isNull$4 || isNull$5;
result$7 = false;
if (!isNull$6) {
result$7 = field$4 > field$5;
}
return result$7;
}
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
super.close();
}
}
参考资料
Apache Flink 漫谈系列(09) - JOIN 算子
Flink 源码阅读笔记(19)- Flink SQL 中流表 Join 的实现