优化器的核心部分,但如果对标题中的Memo 概念不熟悉,建议多看几遍参考资料(理论知识看参考资料,这里只有流程解读)。
源码目录:com.starrocks.sql.optimizer.OptimizerTaskTest#testTwoJoin
RuleRewrite 后
LOGICAL_JOIN {INNER JOIN, onPredicate = null , Predicate = null} 4
-> LOGICAL_JOIN {INNER JOIN, onPredicate = null , Predicate = null} 2
-> LogicalOlapScanOperator {table=0, selectedPartitionId=[], outputColumns=[1: t1], predicate=null, limit=-1} 0
-> LogicalOlapScanOperator {table=1, selectedPartitionId=[], outputColumns=[1: t1], predicate=null, limit=-1} 1
-> LogicalOlapScanOperator {table=2, selectedPartitionId=[], outputColumns=[1: t1], predicate=null, limit=-1} 3
数据结构
Memo
// com.starrocks.sql.optimizer.Memo
public class Memo {
private final List<Group> groups;
private Group rootGroup;
private final Map<GroupExpression, GroupExpression> groupExpressions;
用于记录优化器搜索过程中产生的各种备选的 Plan
rootGroup:根节点group,查询顶点groups:存储所有 groupgroupExpressions:Map结构,记录所有GroupExpression,有去重功能防止重复生成GroupExpression
Group
// com.starrocks.sql.optimizer.Group
public class Group {
private final List<GroupExpression> logicalExpressions;
private final List<GroupExpression> physicalExpressions;
private boolean isExplored;
private Statistics statistics;
private final Map<PhysicalPropertySet, Pair<Double, GroupExpression>> lowestCostExpressions;
逻辑等价类:一系列逻辑相等(输出数据都是相同)的逻辑/物理节点集合,
-
logicalExpressions/physicalExpressions:逻辑/物理表达式,同个Group 下的表达式逻辑都相同 isExplored:是否已探索(尝试去应用规则来转换生成新的GroupExpression),只应用一次ExploreGroupTask会修改
lowestCostExpressions:- 代表每一个 Group 中,满足 Required Property 下的最佳 Expression,并记录相应的
Cost - 生成最优物理计划时使用
- 代表每一个 Group 中,满足 Required Property 下的最佳 Expression,并记录相应的
GroupExpression
// com.starrocks.sql.optimizer.GroupExpression
public class GroupExpression {
private final BitSet ruleMasks = new BitSet(RuleType.NUM_RULES.ordinal() + 1);
private boolean statsDerived = false;
private final Map<PhysicalPropertySet, Pair<Double, List<PhysicalPropertySet>>> lowestCostTable;
可以简单理解与OptExpression 相等
ruleMasks:记录当前Expression 已应用的rule,每个rule 在每个GroupExpression 只能应用一次;OptimizeExpressionTask收集rule 时, 会剔除已作用过的 ruleApplyRuleTask会修改值
statsDerived:Statistics是否已生成,只会生成一次;DeriveStatsTask会设置
lowestCostTable:- 代表每一个 GroupExpression 中,满足了 Required Property 条件的节点,它的子节点需要满足的 Required Properties
OptimizeExpressionTask
// com.starrocks.sql.optimizer.task.OptimizeExpressionTask
public class OptimizeExpressionTask extends OptimizerTask {
private final boolean isExplore;
优化表达式任务,负责Exploration 和 Implementation 过程
isExplore: 是否在探索(GroupExpression 关系代数变换);=false 表示想计算cost 可以添加 Implementation Rule(to Physical)OptimizeGroupTask: 调用 OptimizeExpressionTask 时,=falseExploreGroupTask: 调用 OptimizeExpressionTask 时,=true
ExploreGroupTask
// com.starrocks.sql.optimizer.task.ExploreGroupTask
public class ExploreGroupTask extends OptimizerTask {
public void execute() {
if (group.isExplored()) {
return;
}
for (GroupExpression logical : group.getLogicalExpressions()) {
pushTask(new OptimizeExpressionTask(context, logical, true));
}
group.setExplored();
}
Explore group logical transform => 调用 OptimizeExpressionTask,注意isExplore = true
DeriveStatsTask
// com.starrocks.sql.optimizer.task.DeriveStatsTask
public class DeriveStatsTask extends OptimizerTask {
获取 GroupExpression 的统计信息(Cost 计算需要)
OptimizeGroupTask
// com.starrocks.sql.optimizer.task.OptimizeGroupTask
// Optimize a group within a given context.
public class OptimizeGroupTask extends OptimizerTask {
public void execute() {
// 1 Group Cost LB > Context Cost UB
// => 如果group最优cost > 当前已有cost,提前退出表示没有继续优化的意义
// 2 Group has optimized given the context
// => group 内已有满足RequiredProperty 的groupExpression,无需优化
if (group.getCostLowerBound() >= context.getUpperBoundCost() ||
group.hasBestExpression(context.getRequiredProperty())) {
return;
}
for (int i = group.getLogicalExpressions().size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
pushTask(new OptimizeExpressionTask(context, group.getLogicalExpressions().get(i)));
}
for (int i = group.getPhysicalExpressions().size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
pushTask((new EnforceAndCostTask(context, group.getPhysicalExpressions().get(i))));
}
}
优化Group,会递归调用(每次UpperBoundCost 都会变化),是优化任务的起点
ApplyRuleTask
// com.starrocks.sql.optimizer.task.ApplyRuleTask
public class ApplyRuleTask extends OptimizerTask {
private final GroupExpression groupExpression;
将 Rule 应用到 Logical Plan 中,实现 Logical->Logical、Logical->Physical 的转换,
通过等价变换拓展每个 Group 的搜索空间(生成新的logical/physical)。
EnforceAndCostTask
// com.starrocks.sql.optimizer.task.EnforceAndCostTask
public class EnforceAndCostTask extends OptimizerTask implements Cloneable {
// localCost + sum of all InputCost entries.
private double curTotalCost;
// the local cost of the group expression
private double localCost;
// Current stage of enumeration through child groups
// 当前要计算的child group index
private int curChildIndex = -1;
// Indicator of last child group that we waited for optimization
// task压栈前要计算的childGroup index
private int prevChildIndex = -1;
计算 Physical Plan Cost 的过程,如果某个 Expression 不满足Property,会 Enforce 出其他 Operator,例如 Broadcast、Shuffle、Sort 等算子
SeriallyTaskScheduler
// com.starrocks.sql.optimizer.task.SeriallyTaskScheduler#executeTasks
private final Stack<OptimizerTask> tasks;
public void executeTasks(TaskContext context) {
long timeout = context.getOptimizerContext().getSessionVariable().getOptimizerExecuteTimeout();
Stopwatch watch = context.getOptimizerContext().getTraceInfo().getStopwatch();
while (!tasks.empty()) {
if (timeout > 0 && watch.elapsed(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) > timeout) {
// Should have at least one valid plan
// group will be null when in rewrite phase
Group group = context.getOptimizerContext().getMemo().getRootGroup();
if (group == null || !group.hasBestExpression(context.getRequiredProperty())) {
throw new StarRocksPlannerException("StarRocks planner use long time " + timeout +
" ms in " + (group == null ? "logical" : "memo") + " phase, This probably because " +
"1. FE Full GC, " +
"2. Hive external table fetch metadata took a long time, " +
"3. The SQL is very complex. " +
"You could " +
"1. adjust FE JVM config, " +
"2. try query again, " +
"3. enlarge new_planner_optimize_timeout session variable",
ErrorType.INTERNAL_ERROR);
}
break;
}
OptimizerTask task = tasks.pop();
context.getOptimizerContext().setTaskContext(context);
// 任务开始执行
task.execute();
}
}
Stack 结构先进后出,利用此特性可以Top-Down 遍历,看图感受下(数字表示group id)
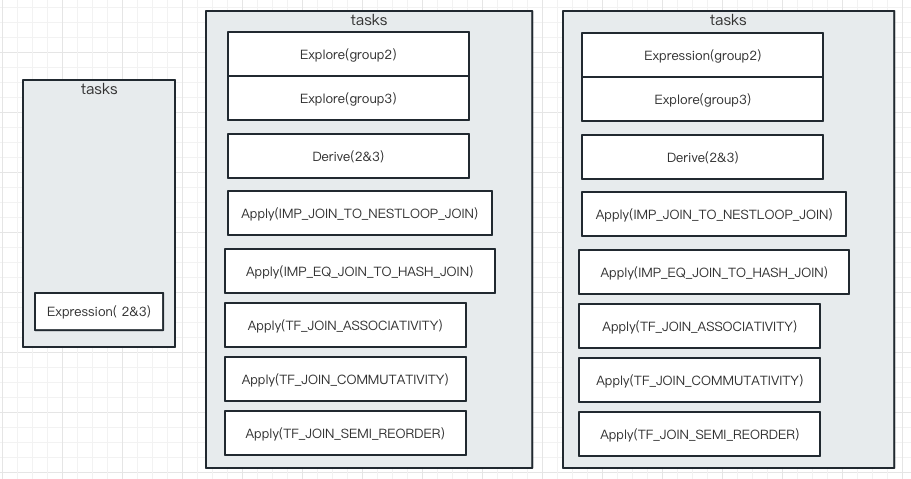
- 左边是第一次执行
OptimizeGroupTask后,压入OptimizeExpressionTask(2&3)任务 - 中间是弹出
OptimizeExpressionTask(2&3)并执行,生成5个ApplyRuleTask、1个DeriveStatsTask、2个ExploreGroupTask - 右边是弹出最后压栈的
Explore(group2)并执行,生成OptimizeExpressionTask(group2)压栈 - 继续执行的话,执行
OptimizeExpressionTask(group2)并压入ApplyRuleTask、DeriveStatsTask、ExploreGroupTask
优化流程
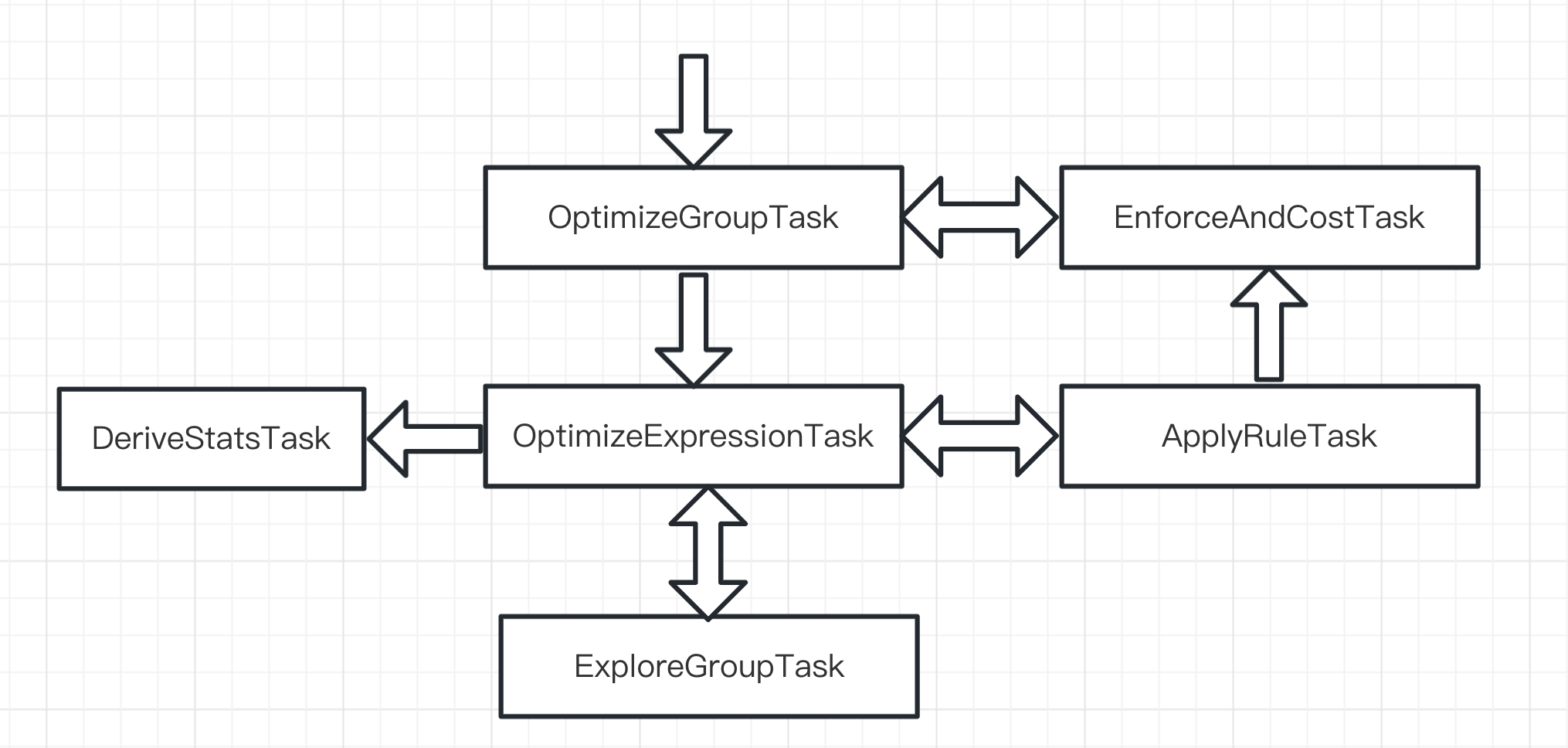
tasks
OptimizeGroupTask-> rootGroup 起始OptimizeExpressionTask优化Group 内的所有Logical ExpressionEnforceAndCostTask计算Group 内所有Physical Expression Cost
OptimizeExpressionTaskApplyRuleTask将Rule 应用到 GroupExpression 进行Expression 变换(logical->logicalorlogical->physical)DeriveStatsTask收集统计信息ExploreGroupTask探索当前GroupExpression 的input Group- ExploreGroupTask 和DeriveStatsTask 顺序 执行有讲究的,这样保证执行DeriveStatsTask 时,子group 都已执行DeriveStatsTask
DeriveStatsTask收集统计信息(保证子group 已执行该task),这个task 逻辑最简单ExploreGroupTask会调用 OptimizeExpressionTask 来优化,isExplore=trueApplyRuleTask将Rule 应用到 GroupExpression,可能会生成新的Expression- 生成logical Expression:调用 OptimizeExpressionTask 继续优化新生成的Expression
- 生成physical Expression:调用EnforceAndCostTask 计算Expression Cost
EnforceAndCostTask:计算当前ExpressionCost = localCost + inputCost- 深度优先input cost
- 如何计算input cost? 调用OptimizeGroupTask
整个流程简化为
深度优先的递归进行logical 变换,并获取所有groupExpression Stats
Root 物理节点开始计算cost,深度优先递归child cost
memo
结合Memo 变化从另一个角度来理解下
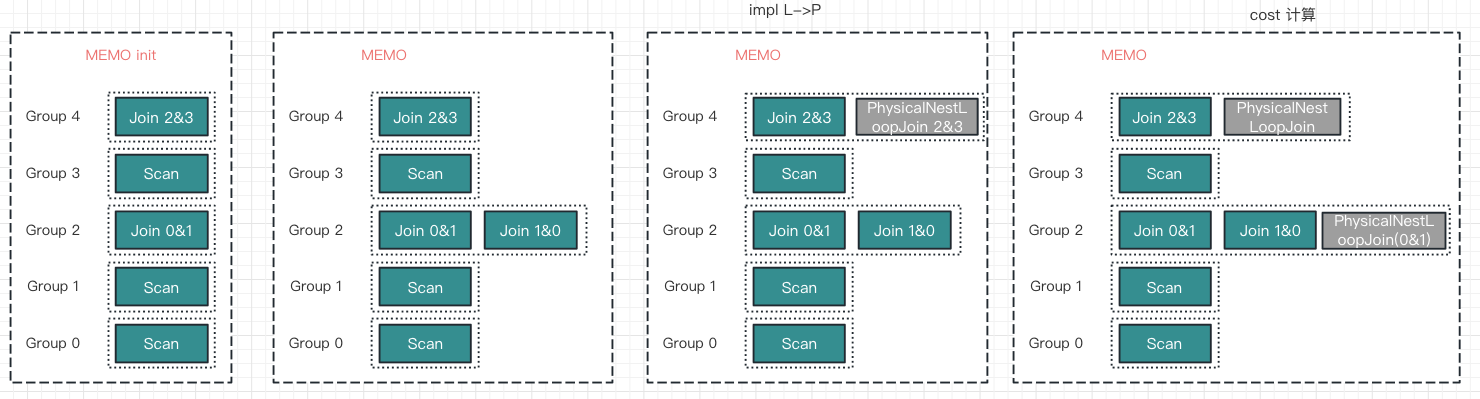
- 第一幅是memo.init 调用后,将OptExpression 拷贝到memo
- 第二幅是group2
ApplyRuleTask生成新的LogicalExpression(交换律) - 执行到第三幅之前,“深度优先的递归将logical变换,并获取所有groupExpression Stats” 已全部执行
- 第三幅是执行
Apply(IMP_JOIN_TO_NESTLOOP_JOIN)生成新的“PhysicalNestLoopJoin 2&3”,并开始调用EnforceAndCostTask - 第四幅是执行
EnforceAndCostTask时,计算input cost- OptimizeGroupTask -> OptimizeExpressionTask -> ApplyRuleTask -> 生成新的PyhsicalExpression
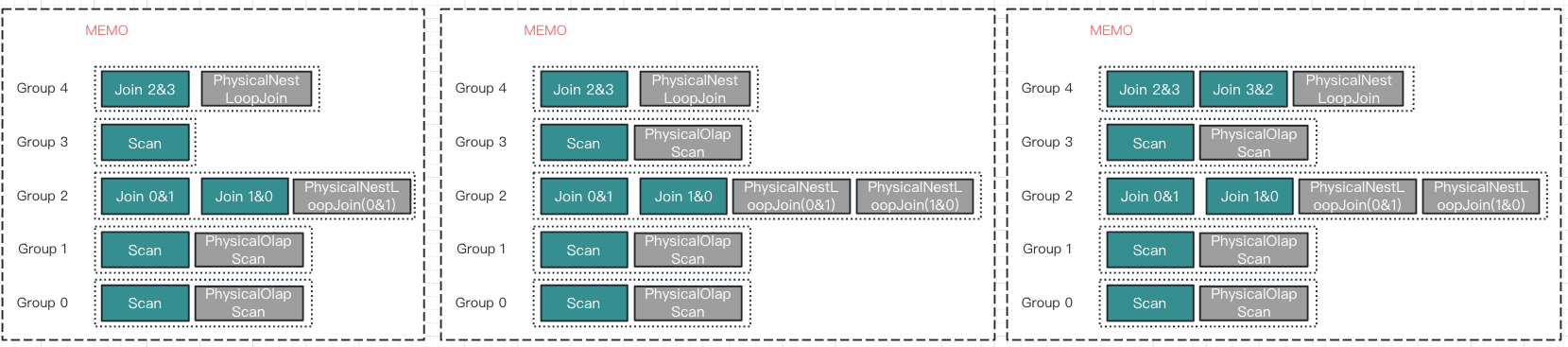
- 左图:上面第四幅生成新的PyhsicalExpression,紧接着要
EnforceAndCostTask;同理会计算 input cost,就又会生成新的PhysicalExpression - 中间图:
- 左图”PhysicalNestLoopJoin(0&1)” input cost 计算结束后,会继续
Apply(IMP_JOIN_TO_NESTLOOP_JOIN)生成”PhysicalNestLoopJoin(1&0)” (为啥input cost 都结束了这里才计算,因为Stack 特性) - 同理计算完”PhysicalNestLoopJoin(1&0)”后,会继续上面第四幅计算input cost => 之前所有都是在计算 input1,现在计算input2(join操作有两个input);生成新的PyhsicalExpression
- 左图”PhysicalNestLoopJoin(0&1)” input cost 计算结束后,会继续
- 右图:
- 到这里之前,上图第四幅计算input cost 全部结束,”PhysicalNestLoopJoin 2&3” 的Cost 值生成(从Top-Down)
- Group4
Apply(TF_JOIN_COMMUTATIVITY生成新的LogicalExpression
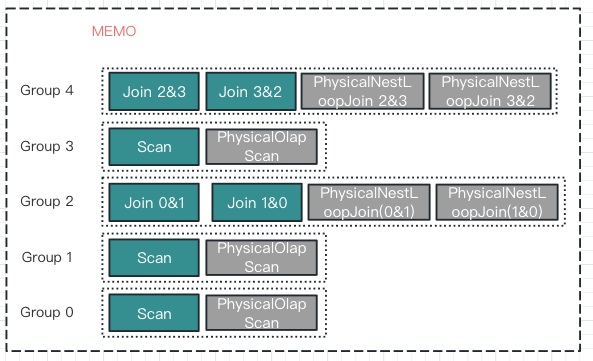
上面右图生成新的LogicalExpression 后,
OptimizeExpressionTask -> ApplyRuleTask -> 新的PhysicalExpression(PhysicalNestLoopJoin 3&2)
然后开始新一轮的EnforceAndCostTask,与之前不同的是,input cost 都已经计算过了,无需再递归计算。
- 在初始时只有basic groups,每个group中一个initial logical m-expr,和AST中的expr 一一对应
- 开始对root group执行OptimizeGroupTask,其中会对唯一的m-expr调用OptimizeExpressionTask,生成logical/physical m-exprs
- 新生成的logical m-expr 会继续优化导致一系列m-expr 的生成,从而在已有group 中扩展新的m-expr 或在memo 中加入新的group
- 新生成的physical m-expr生成EnforceAndCostTask,递归下去得到完成的physical plan,并用其cost更新search context中的cost upper bound,帮助后续pruning。
- 优化过程中会不断有physical m-expr 的生成,然后就递归到下层去生成对应的plan/subplan,并得到各个层次上的局部最优解记入lowestCostExpressions/lowestCostTable 中,并返回到上层做汇总,最终回到top group 得到完整physical plan
- 最终root group 不再有新的logical / physical m-expr生成时,优化结束
Cost
其他几个task 逻辑都不复杂,重点看看EnforceAndCostTask 是如何计算Cost,加深理解。
// com.starrocks.sql.optimizer.task.EnforceAndCostTask
public class EnforceAndCostTask extends OptimizerTask implements Cloneable {
// localCost + sum of all InputCost entries.
private double curTotalCost;
// the local cost of the group expression
private double localCost;
// Current stage of enumeration through child groups
// 当前要计算的child group index
private int curChildIndex = -1;
// Indicator of last child group that we waited for optimization
// task压栈前要计算的childGroup index
private int prevChildIndex = -1;
public void execute() {
...
// Init costs and get required properties for children
initRequiredProperties();
// 开始计算cost
for (; curPropertyPairIndex < childrenRequiredPropertiesList.size(); curPropertyPairIndex++) {
List<PhysicalPropertySet> childrenRequiredProperties =
childrenRequiredPropertiesList.get(curPropertyPairIndex);
// Calculate local cost and update total cost
if (curChildIndex == 0 && prevChildIndex == -1) {
localCost = CostModel.calculateCost(groupExpression);
curTotalCost += localCost;
}
for (; curChildIndex < groupExpression.getInputs().size(); curChildIndex++) {
PhysicalPropertySet childRequiredProperty = childrenRequiredProperties.get(curChildIndex);
Group childGroup = groupExpression.getInputs().get(curChildIndex);
// Check whether the child group is already optimized for the property
// 获取下游Group 中满足property并且cost最小的 groupExpression(如果group 中存在)
GroupExpression childBestExpr = childGroup.getBestExpression(childRequiredProperty);
if (childBestExpr == null && prevChildIndex >= curChildIndex) {
// If there can not find best child expr or push child's OptimizeGroupTask, The child has been
// pruned because of UpperBound cost prune, and parent task can break here and return
// prevChildIndex >= curChildIndex,说明child 已经optimize,
// 但childBestExpr=null,是因为curTotalCost > context.getUpperBoundCost(),下面有分析
// 代码执行到这里,表示此childGroup下 childRequiredProperty 链路都无效(cost太高)
break;
}
// =null 表示child group 未optimzed,现在开始optimize child
if (childBestExpr == null) {
// We haven't optimized child group
prevChildIndex = curChildIndex;
optimizeChildGroup(childRequiredProperty, childGroup);
return;
}
childrenBestExprList.add(childBestExpr);
// Get the output properties of children
PhysicalPropertySet childOutputProperty = childBestExpr.getOutputProperty(childRequiredProperty);
childrenOutputProperties.add(childOutputProperty);
// Change child required property to child output property
childrenRequiredProperties.set(curChildIndex, childOutputProperty);
// check if we can generate one stage agg
if (!canGenerateOneStageAgg(childBestExpr)) {
break;
}
if (!checkBroadcastRowCountLimit(childRequiredProperty, childBestExpr)) {
break;
}
// 合计 下游算子的cost => 当前算子的 cost
curTotalCost += childBestExpr.getCost(childRequiredProperty);
if (curTotalCost > context.getUpperBoundCost()) {
// 当前cost 超过规定的cost,表示肯定不是最优解(UpperBoundCost 以有算子链最小的cost)
break;
}
}
// Successfully optimize all child group
// child group 已全部Optimize
if (curChildIndex == groupExpression.getInputs().size()) {
// before we compute the property, here need to make sure that the plan is legal
ChildOutputPropertyGuarantor childOutputPropertyGuarantor = new ChildOutputPropertyGuarantor(context,
groupExpression,
context.getRequiredProperty(),
childrenBestExprList,
childrenRequiredProperties,
childrenOutputProperties,
curTotalCost);
curTotalCost = childOutputPropertyGuarantor.enforceLegalChildOutputProperty();
if (curTotalCost > context.getUpperBoundCost()) {
// cost 大于限定cost,此链路下groupExpression 对应的RequiredProperty 没办法用
break;
}
// update current group statistics and re-compute costs
if (!computeCurrentGroupStatistics()) {
// child group has been pruned
return;
}
// compute the output property
OutputPropertyDeriver outputPropertyDeriver = new OutputPropertyDeriver(groupExpression,
context.getRequiredProperty(), childrenOutputProperties);
PhysicalPropertySet outputProperty = outputPropertyDeriver.getOutputProperty();
// important
// 设置lowestCostExpressions、lowestCostTable,并更新 UpperBoundCost
recordCostsAndEnforce(outputProperty, childrenRequiredProperties);
}
// Reset child idx and total cost
// 开始计算下一组Properties
prevChildIndex = -1;
curChildIndex = 0;
curTotalCost = 0;
childrenBestExprList.clear();
childrenOutputProperties.clear();
}
}
private void optimizeChildGroup(PhysicalPropertySet inputProperty, Group childGroup) {
pushTask((EnforceAndCostTask) clone());
// context.getUpperBoundCost() 默认是MAX,随着优化任务改变
// newUpperBound 下游cost 的上限
double newUpperBound = context.getUpperBoundCost() - curTotalCost;
TaskContext taskContext = new TaskContext(context.getOptimizerContext(), inputProperty,
context.getRequiredColumns(), newUpperBound);
pushTask(new OptimizeGroupTask(taskContext, childGroup));
}
Cost = localCost + inputCost => CostModel.calculateCost Cost计算函数
每个physical expr 为起点深度优先,向下查找,首先会扣除它自身的Cost,并根据其上层的property requirement 以及expr 自身的property 特性,形成对其输入group 的physical property 要求,这样就从当前level 1 的(Cost , prop requirement1) 递归到了下层group (level 2),optimization goal变为了 (Cost - l1 Cost, prop requirement2)。
- initRequiredProperties:获取其输入group 的
physical property要求(Sort/Distribution) - 遍历physical property :
CostModel.calculateCost(groupExpression)计算当前Expression 的cost- 获取输入group 中满足
physical property且Cost 最小的GroupExpression(BestExpression),若不存在BestExpression- 若输入group 已Optimize 后,说明是输入group 满足
physical property的cost 太高( 不满足 < UpperBoundCost,看上面代码直接break),则这条链路到此结束(剪枝) - 若输入group 还未Optimize,optimizeChildGroup 开始优化
- 若输入group 已Optimize 后,说明是输入group 满足
optimizeChildGroup:- 注意UpperBound 变化
context.getUpperBoundCost() - curTotalCost pushTask((EnforceAndCostTask) clone()):等input group 计算结束后继续计算当前Cost,理解curChildIndex/prevChildIndex含义
- 注意UpperBound 变化
- 若成功获取所有input group的 BestExpression,就可以计算当前groupExpression 的Cost,并更新
lowestCostExpressions/lowestCostTable
// com.starrocks.sql.optimizer.task.EnforceAndCostTask#recordCostsAndEnforce
private void recordCostsAndEnforce(PhysicalPropertySet outputProperty,
List<PhysicalPropertySet> childrenOutputProperties) {
// re-calculate local cost and update total cost
curTotalCost -= localCost;
localCost = CostModel.calculateCostWithChildrenOutProperty(groupExpression, childrenOutputProperties);
curTotalCost += localCost;
// 设置lowestCostExpressions、lowestCostTable
setSatisfiedPropertyWithCost(outputProperty, childrenOutputProperties);
// 开始判断当前节点输出properties 与上游节点要求输出properties 是否匹配,是否要Enforce
PhysicalPropertySet requiredProperty = context.getRequiredProperty();
recordPlanEnumInfo(groupExpression, outputProperty, childrenOutputProperties);
// Enforce property if outputProperty doesn't satisfy context requiredProperty
if (!outputProperty.isSatisfy(requiredProperty)) {
// Enforce the property to meet the required property
// Properties 不匹配,要Enforce,那么Cost 也要重新计算(新加了Enforce 节点)
PhysicalPropertySet enforcedProperty = enforceProperty(outputProperty, requiredProperty);
// enforcedProperty is superset of requiredProperty
if (!enforcedProperty.equals(requiredProperty)) { // 如果enforced 和require完全相等,没必要再重写添加一次,enforceProperty已经操作过了
setPropertyWithCost(groupExpression.getGroup().getBestExpression(enforcedProperty), enforcedProperty,
requiredProperty, Lists.newArrayList(outputProperty));
}
} else {
// outputProperty is superset of requiredProperty
if (!outputProperty.equals(requiredProperty)) { // 如果ouput 和require完全相等,没必要再重写添加一次,上面已经操作过了
setPropertyWithCost(groupExpression, outputProperty, requiredProperty, childrenOutputProperties);
}
}
if (curTotalCost < context.getUpperBoundCost()) {
// update context upperbound cost
context.setUpperBoundCost(curTotalCost);
}
}
Enforce
对每个physical expr 来说,如果所属group的optimization goal 中的property requirement 可以被expr 本身输出的物理属性所满足,则可以直接应用该expr,否则需要加入enforcer 来强制目标属性
假设 A(any, any) ->B(sort, any) ,A作为B的input group 是property 不满足的,缺少sort。那么在A和B之间要加Enforce 来重新匹配
A(any, any) -> Enforce(sort, any) -> B(sort, any)
多了Enforce,Cost 自然增加。
// com.starrocks.sql.optimizer.task.EnforceAndCostTask#enforceProperty
// 为了output 满足require,增加 Enforce节点
// 如果DistributionProperty 满足,且OrderProperty 不为空,则需要enforceSortAndDistribute
// 为什么?看下面注释
private PhysicalPropertySet enforceProperty(PhysicalPropertySet outputProperty,
PhysicalPropertySet requiredProperty) {
boolean satisfyOrderProperty =
outputProperty.getSortProperty().isSatisfy(requiredProperty.getSortProperty());
boolean satisfyDistributionProperty =
outputProperty.getDistributionProperty().isSatisfy(requiredProperty.getDistributionProperty());
PhysicalPropertySet enforcedProperty = null;
if (!satisfyDistributionProperty && satisfyOrderProperty) {
if (requiredProperty.getSortProperty().isEmpty()) {
enforcedProperty = enforceDistribute(outputProperty);
} else {
/*
* The sorting attribute does not make sense when the sort property is not empty,
* because after the data is redistributed, the original order requirements cannot be guaranteed.
* So we need to enforce "SortNode" here
*
* Because we build a parent-child relationship based on property.
* So here we hack to eliminate the original property to prevent an endless loop
* eg: [order by v1, gather] -> [order by v1, shuffle] -> [order by v1, shuffle] may endless loop,
* because repartition require sort again
*/
PhysicalPropertySet newProperty =
new PhysicalPropertySet(DistributionProperty.EMPTY, SortProperty.EMPTY,
outputProperty.getCteProperty());
groupExpression.getGroup().replaceBestExpressionProperty(outputProperty, newProperty,
groupExpression.getCost(outputProperty));
enforcedProperty = enforceSortAndDistribute(newProperty, requiredProperty);
}
} else if (satisfyDistributionProperty && !satisfyOrderProperty) {
enforcedProperty = enforceSort(outputProperty);
} else if (!satisfyDistributionProperty) {
enforcedProperty = enforceSortAndDistribute(outputProperty, requiredProperty);
}
return enforcedProperty;
}
private PhysicalPropertySet enforceDistribute(PhysicalPropertySet oldOutputProperty) {
PhysicalPropertySet newOutputProperty = oldOutputProperty.copy();
newOutputProperty.setDistributionProperty(context.getRequiredProperty().getDistributionProperty());
// 增加enforce Expression => PhysicalDistributionOperator
GroupExpression enforcer =
context.getRequiredProperty().getDistributionProperty().appendEnforcers(groupExpression.getGroup());
// 更新cost
updateCostWithEnforcer(enforcer, oldOutputProperty, newOutputProperty);
recordPlanEnumInfo(enforcer, newOutputProperty, Lists.newArrayList(oldOutputProperty));
return newOutputProperty;
}
参考资料
The Volcano Optimizer Generator : Extensibility and Efficient Search
The Cascades Framework for Query Optimization
Orca: A Modular Query Optimizer Architecture for Big Data
更高效的Cascades优化器 - Columbia Query Optimizer
Cascades Optimizer工程实现之一columbia源码学习笔记