All of this relies on a good cost model. A good cost model needs good statistics.
源码目录:com.starrocks.sql.optimizer.OptimizerTaskTest#testTwoJoin
CostModel.calculateCost
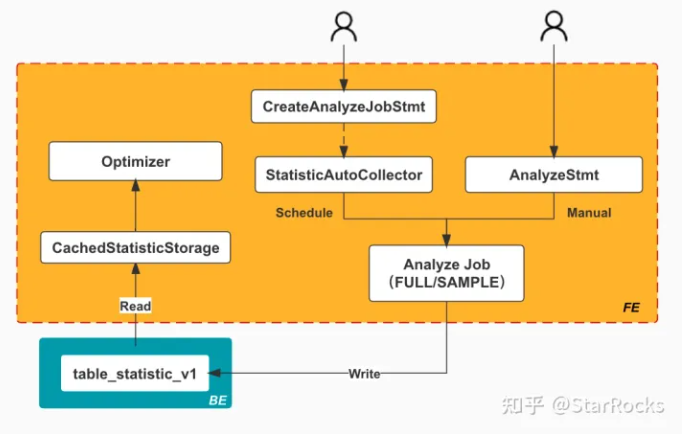
统计信息
Cost 计算依赖于Statistics,而Statistics依赖于信息收集
收集
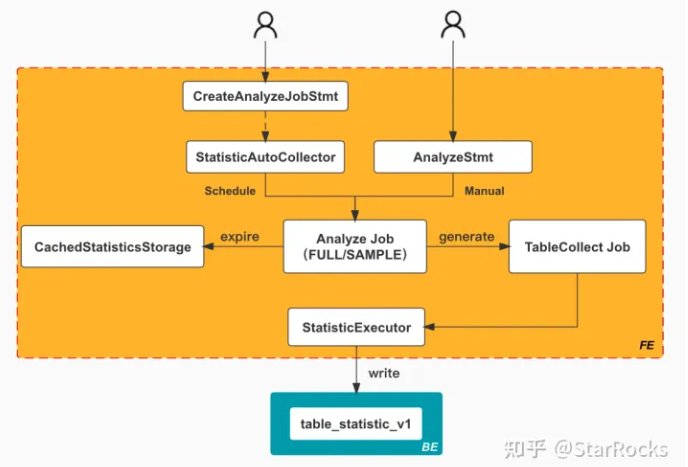
StatisticAutoCollector默认5分钟(statistic_collect_interval_sec) 收集一次- 存储:收集好的数据存在
_statistics_.table_statistic_v1表中
创建CollectJob
// com.starrocks.statistic.StatisticAutoCollector
protected void runAfterCatalogReady() {
...
if (Config.enable_collect_full_statistic) {
// 为每个table 创建一个CollectJob,顺序执行
// 元数据的库除外(_statistics_、starrocks_monitor、information_schema)
List<StatisticsCollectJob> allJobs = StatisticsCollectJobFactory.buildStatisticsCollectJob(
new AnalyzeJob(StatsConstants.DEFAULT_ALL_ID, StatsConstants.DEFAULT_ALL_ID, null,
AnalyzeType.FULL, ScheduleType.SCHEDULE,
Maps.newHashMap(),
ScheduleStatus.PENDING,
LocalDateTime.MIN));
for (StatisticsCollectJob statsJob : allJobs) {
AnalyzeStatus analyzeStatus = new AnalyzeStatus(GlobalStateMgr.getCurrentState().getNextId(),
statsJob.getDb().getId(), statsJob.getTable().getId(), statsJob.getColumns(),
statsJob.getType(), statsJob.getScheduleType(), statsJob.getProperties(), LocalDateTime.now());
// 每个job 都会记录状态
analyzeStatus.setStatus(StatsConstants.ScheduleStatus.FAILED);
GlobalStateMgr.getCurrentAnalyzeMgr().addAnalyzeStatus(analyzeStatus);
ConnectContext statsConnectCtx = StatisticUtils.buildConnectContext();
statsConnectCtx.setThreadLocalInfo();
// 开始执行;
STATISTIC_EXECUTOR.collectStatistics(statsConnectCtx, statsJob, analyzeStatus, true);
}
...
}
执行 CollectJob
// com.starrocks.statistic.StatisticExecutor
public AnalyzeStatus collectStatistics(ConnectContext statsConnectCtx,
StatisticsCollectJob statsJob,
AnalyzeStatus analyzeStatus,
boolean refreshAsync) {
Database db = statsJob.getDb();
Table table = statsJob.getTable();
...
try {
GlobalStateMgr.getCurrentAnalyzeMgr().registerConnection(analyzeStatus.getId(), statsConnectCtx);
// 执行收集sql,并将结果写入 table_statistic_v1 表
statsJob.collect(statsConnectCtx, analyzeStatus);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.warn("Collect statistics error ", e);
analyzeStatus.setStatus(StatsConstants.ScheduleStatus.FAILED);
analyzeStatus.setEndTime(LocalDateTime.now());
analyzeStatus.setReason(e.getMessage());
GlobalStateMgr.getCurrentAnalyzeMgr().addAnalyzeStatus(analyzeStatus);
return analyzeStatus;
} finally {
GlobalStateMgr.getCurrentAnalyzeMgr().unregisterConnection(analyzeStatus.getId(), false);
}
...
analyzeStatus.setStatus(StatsConstants.ScheduleStatus.FINISH);
analyzeStatus.setEndTime(LocalDateTime.now());
GlobalStateMgr.getCurrentAnalyzeMgr().addAnalyzeStatus(analyzeStatus);
BasicStatsMeta basicStatsMeta = new BasicStatsMeta(db.getId(), table.getId(),
statsJob.getColumns(), statsJob.getType(), analyzeStatus.getEndTime(), statsJob.getProperties());
GlobalStateMgr.getCurrentAnalyzeMgr().addBasicStatsMeta(basicStatsMeta);
// 1、更新CachedStatisticStorage,让其使当前table的信息失效
// 2、通过get 让CachedStatisticStorage 获取table_statistic_v1 最新数据,使其生效
GlobalStateMgr.getCurrentAnalyzeMgr().refreshBasicStatisticsCache(
basicStatsMeta.getDbId(), basicStatsMeta.getTableId(), basicStatsMeta.getColumns(), refreshAsync);
}
return analyzeStatus;
}
CachedStatisticStorage- 字面意思,Statistic Cache在内存,不用每次都去 table_statistic_v1 表获取
AsyncLoadingCache类型,在get(key)时,如果没有value,会异步加载 => 从 table_statistic_v1 表获取保持最新
收集的SQL 如下
- FullStatisticsCollectJob
INSERT INTO table_statistic_v1
SELECT $tableId, $partitionId, '$columnName', $dbId," +
" '$dbName.$tableName', '$partitionName'," +
" COUNT(1), $dataSize, $countDistinctFunction, $countNullFunction, $maxFunction, $minFunction, NOW() "
+ "FROM $dbName.$tableName partition $partitionName
- HistogramStatisticsCollectJob
INSERT INTO table_statistic_v1
SELECT $tableId, '$columnName', $dbId, '$dbName.$tableName'," +
" histogram($columnName, cast($bucketNum as int), cast($sampleRatio as double)), " +
" $mcv," +
" NOW()" +
" FROM (SELECT $columnName FROM $dbName.$tableName where rand() <= $sampleRatio" +
" and $columnName is not null $MCVExclude" +
" ORDER BY $columnName LIMIT $totalRows) t
- SampleStatisticsCollectJob
INSERT INTO table_statistic_v1
SELECT $tableId, '$columnName', $dbId, '$tableName', '$dbName', IFNULL(SUM(t1.count), 0) * $ratio, "
+ " $dataSize * $ratio, $countDistinctFunction, "
+ " IFNULL(SUM(IF(t1.`$columnName` IS NULL, t1.count, 0)), 0) * $ratio, "
+ " IFNULL(MAX(t1.`$columnName`), ''), IFNULL(MIN(t1.`$columnName`), ''), NOW() "
+ "FROM ( "
+ " SELECT t0.`$columnName`, COUNT(1) as count "
+ " FROM (SELECT `$columnName` FROM $tableName $hints) as t0 "
+ " GROUP BY t0.`$columnName` "
+ ") as t1"
StatisticsCalculator
上一小节,已经将数据收集并写入表中。本节分析如何将收集的数据变成Statistics
// com.starrocks.sql.optimizer.task.DeriveStatsTask
public void execute() {
...
ExpressionContext expressionContext = new ExpressionContext(groupExpression);
StatisticsCalculator statisticsCalculator = new StatisticsCalculator(expressionContext,
context.getOptimizerContext().getColumnRefFactory(), context.getOptimizerContext());
statisticsCalculator.estimatorStats();
...
}
Scan
// com.starrocks.sql.optimizer.statistics.StatisticsCalculator
public void estimatorStats() {
expressionContext.getOp().accept(this, expressionContext);
}
// logical、physical scan 逻辑相同
public Void visitLogicalOlapScan(LogicalOlapScanOperator node, ExpressionContext context) {
return computeOlapScanNode(node, context, node.getTable(), node.getSelectedPartitionId(),
node.getColRefToColumnMetaMap());
}
public Void visitPhysicalOlapScan(PhysicalOlapScanOperator node, ExpressionContext context) {
return computeOlapScanNode(node, context, node.getTable(), node.getSelectedPartitionId(),
node.getColRefToColumnMetaMap());
}
private Void computeOlapScanNode(Operator node, ExpressionContext context, Table table,
Collection<Long> selectedPartitionIds,
Map<ColumnRefOperator, Column> colRefToColumnMetaMap) {
Preconditions.checkState(context.arity() == 0);
// 1. get table row count
long tableRowCount = getTableRowCount(table, node);
// 2. get required columns statistics
// CachedStatisticStorage 中获取
Statistics.Builder builder = estimateScanColumns(table, colRefToColumnMetaMap);
if (tableRowCount <= 1) {
builder.setTableRowCountMayInaccurate(true);
}
// 3. deal with column statistics for partition prune
OlapTable olapTable = (OlapTable) table;
ColumnStatistic partitionStatistic = adjustPartitionStatistic(selectedPartitionIds, olapTable);
if (partitionStatistic != null) {
String partitionColumnName = olapTable.getPartitionColumnNames().get(0);
Optional<Map.Entry<ColumnRefOperator, Column>> partitionColumnEntry =
colRefToColumnMetaMap.entrySet().stream().
filter(column -> column.getValue().getName().equalsIgnoreCase(partitionColumnName))
.findAny();
// partition prune maybe because partition has none data
partitionColumnEntry.ifPresent(entry -> builder.addColumnStatistic(entry.getKey(), partitionStatistic));
}
builder.setOutputRowCount(tableRowCount);
// 4. estimate cardinality
context.setStatistics(builder.build());
// todo:visitOperator 还涉及谓词下推、映射操作
return visitOperator(node, context);
}
// com.starrocks.sql.optimizer.statistics.Statistics
public class Statistics {
private final double outputRowCount;
private final Map<ColumnRefOperator, ColumnStatistic> columnStatistics;
// This flag set true if get table row count from GlobalStateMgr LE 1
// Table row count in FE depends on BE reporting,but FE may not get report from BE which just started,
// this causes the table row count stored in FE to be inaccurate.
private final boolean tableRowCountMayInaccurate;
- visitOperator 还有谓词下推操作,后续再看;这个满重要的,影响基数估计(Output RowCount 准不准确由此决定,Cost大小由outputRowCount 决定)
- 这个类对Cost model 很重要,后续挑几个Operator 分析
逻辑还是比较清晰,获取table_statistic_v1表数据转换为ColumnStatistic (与table_statistic_v1表字段差不多)的逻辑都在 StatisticExecutor
// com.starrocks.sql.optimizer.statistics.ColumnStatistic
public class ColumnStatistic {
private final double minValue;
private final double maxValue;
private final double nullsFraction;
private final double averageRowSize;
private final double distinctValuesCount;
private final Histogram histogram;
private final StatisticType type;
Cost
计算公式
// com.starrocks.sql.optimizer.cost.CostModel
public static double calculateCost(GroupExpression expression) {
// 初始化ExpressionContext 信息
ExpressionContext expressionContext = new ExpressionContext(expression);
return calculateCost(expressionContext);
}
private static double calculateCost(ExpressionContext expressionContext) {
// CostEstimator: 统计信息 -> cost
CostEstimator costEstimator = new CostEstimator(ImmutableList.of());
CostEstimate costEstimate = expressionContext.getOp().accept(costEstimator, expressionContext);
double realCost = getRealCost(costEstimate);
LOG.debug("operator: {}, outputRowCount: {}, outPutSize: {}, costEstimate: {}, realCost: {}",
expressionContext.getOp(),
expressionContext.getStatistics().getOutputRowCount(),
expressionContext.getStatistics().getComputeSize(),
costEstimate, realCost);
return realCost;
}
public static double getRealCost(CostEstimate costEstimate) {
double cpuCostWeight = 0.5;
double memoryCostWeight = 2;
double networkCostWeight = 1.5;
return costEstimate.getCpuCost() * cpuCostWeight +
costEstimate.getMemoryCost() * memoryCostWeight +
costEstimate.getNetworkCost() * networkCostWeight;
}
权重系数
-
cpuCostWeight = 0.5 -
memoryCostWeight = 2 -
networkCostWeight = 1.5Cost = Cpu*0.5 + memory*2 + network*1.5
为啥没有Disk IO Cost?
OLTP 主要是 优化器需要决定不同的scan 方式,比如全表扫,走哪种索引,但是 SR 里面 scan的 索引都是自适应,或者是走索引的顺序是确定的,比如前缀索引,zonemap 索引,不同的表通过行数就可以简单评估 IO的cost。
Estimation
统计信息 -> Cost ?
// com.starrocks.sql.optimizer.cost.CostModel
public CostEstimate visitPhysicalNestLoopJoin(PhysicalNestLoopJoinOperator join, ExpressionContext context) {
Statistics leftStatistics = context.getChildStatistics(0);
Statistics rightStatistics = context.getChildStatistics(1);
double leftSize = leftStatistics.getOutputSize(context.getChildOutputColumns(0));
double rightSize = rightStatistics.getOutputSize(context.getChildOutputColumns(1));
double cpuCost = leftSize * rightSize + StatsConstants.CROSS_JOIN_COST_PENALTY;
double memCost = rightSize * StatsConstants.CROSS_JOIN_COST_PENALTY * 2;
// Right cross join could not be parallelized, so apply more punishment
if (join.getJoinType().isRightJoin()) {
cpuCost += StatsConstants.CROSS_JOIN_RIGHT_COST_PENALTY;
memCost += rightSize;
}
if (join.getJoinType().isOuterJoin() || join.getJoinType().isSemiJoin() || join.getJoinType().isAntiJoin()) {
cpuCost += leftSize;
}
return CostEstimate.of(cpuCost, memCost, 0);
}
逻辑很清晰,主要与需要处理的数据量相关:Statistics ComputeSize = Output RowCount * sum(column_size)
需要处理的数据量越大,节点的CPU开销、内存占用和数据 shuffle 的代价越大。
CMU721
课程中关于Cost 描述
- DISK-BASED DBMS COST MODEL
- CPU costs are negligible.
- Have to consider sequential vs. random I/O.
- POSTGRES COST MODEL:包含CPU and I/O costs,并有权重;以下默认设置适用内存不大数据都在磁盘(官方文档建议不要修改这些值)
- Processing a tuple in memory is 400xfaster than reading a tuple from disk.
- Sequential I/O is 4xfaster than random I/O.
- 经验
- Query opt is more important than a fast engine
- Cost-based join ordering is necessary
- 基数估计通常是错误的:真实世界的数据分布、字段的独立性(不相关->范式?) 很难用模型去拟合
- 尝试使用不依赖估计的运算符
- 优化方案:DBMS可以一起跟踪属性组(排列组合太大了)的统计信息,而不只是将它们都视为独立变量。
- Hash joins + seq scans are a robust exec model
- 可用的索引越多,计划就越脆弱(但平均速度也更快)
- 研究精确的模型是浪费时间
- 最好改进基数估计(决定性因素)
- Query opt is more important than a fast engine
I think that a combination of sampling + sketches are the way to achieve accurate estimations.